Minds On
How did it move?
Explore the following triangle plotted on a Cartesian plane.

A Cartesian plane with an x-axis and a y-axis. Both axes are numbered from 0 to 8. There are 2 triangles on the Cartesian plane. The first triangle has its lowest vertex, labelled A, plotted at the coordinate (2,0). The second triangle has its lowest vertex, labelled A prime, plotted at the coordinate (4,0).
One vertex of the triangle was initially at (2,0) on the Cartesian plane and is now at the new location of (4,0). The Cartesian plane has both a y- and x-axis which start at 0 and extend to 8 on both axes, counting by 1s.
Respond to the following questions. Record your ideas in a notebook or a method of your choice.
- How did the triangle change location?
- Which direction did the triangle move?
- What is the number of squares the triangle changed by?
Action
Exploring transformations on a grid
What is a grid?
A grid contains vertical and horizontal lines which are regularly spaced and cross each other at right angles to form squares.

Transformations are changes in a figure that result in a difference in its position, size, or orientation.
As a shape transforms, its vertices (points on a grid) move. This explains how transformations involve location and movement.
Translations
A shape can be translated or reflected on a grid.
A translation is a transformation that moves every point on a shape the same distance and in the same direction (this is also called a slide).
Things to consider about translations:
- a translation includes distance and direction
- when a shape is translated, every point on the original shape “slides” the same distance and direction to create a translated image (also called the translation vector)
- when describing the translation of an object you are describing how the location changes using directions (left, right, up, down) and by how many spaces
- typically, the horizontal distance (x) is given first, followed by the vertical distance (y)
For example, consider the following grid. On the grid, we could describe each point of the triangle moving “5 units to the right and 2 units up.” Where point A of our triangle was initially located at (1,1) the translated A′ (A Prime) is now at (6,3).

A Cartesian plane, with an x-axis and a y-axis, on a grid. There are 2 triangles plotted on the grid. The first triangle has 3 points labelled: A, B, and C. Point A is located at coordinate (1,1), point B is at (2,3), and point C is at (5,2). Arrows show that the triangle moves 5 units to the right, and 2 units up. The second triangle is the new translated triangle, and has 3 points labelled: A prime, B prime, and C prime. Point A prime is located at (6,3), point B prime is at (7,5), and point C prime is at (10,4).
Your turn
Explore the following shape and then answer the question about the translation that has occurred.

A Cartesian plane, with an x-axis and a y-axis, on a grid. There are 2 diamond shapes plotted on the grid. The original diamond shape has 4 points labelled E, F, G, and H. Point E is located at coordinate (5,3), point F is at (6,4), point G is at (7,3), and point H is at (6,1). The translated diamond shape has 4 points labelled: E prime, F prime, G prime, and H prime. Point E prime is located at (1,6), point F prime is at (2,7), point G prime is at (3,6), and point H prime is at (2,4).
Reflections
A reflection is a transformation that flips a shape over a line. The reflected image is the mirror image of the original shape.
Things to consider about reflections:
- a reflection involves a line of reflection that acts like a mirror
- when a shape is reflected, every point on the original shape is “flipped” across the line of reflection to create a reflected image
- the points on the original image are the same distance from the line of reflection as the points on the reflected image
- reflections are symmetrical
- when describing how an object is reflected, you are describing how something is reflected over a line of reflection
Consider one triangle labelled at ABC, a line of reflection, and the reflected triangle labelled as A′B′C′ (A prime, B prime, C prime) Point A is 5 units away from the line of symmetry and so is Point A′ (A prime).
The reflected triangle is displayed in the following image.

A triangle, a vertical line of reflection, and a reflected triangle appear from left to right on a grid. The triangle on the left has three vertices labelled: A, B, and C. The reflected triangle on the right also has three vertices, but its vertices are labelled: A prime, B prime, and C prime. Vertex A is located 5 units to the left of the line of reflection, and vertex A prime is located 5 units to the right of the line of reflection. The reflected triangle is like a flipped version of the original triangle.
Your turn
Explore the following grid. It displays a triangle labelled RST and a line of reflection.

A Cartesian plane with an x- and y-axis. Both axes are numbered from 0 to 8. There is a horizontal line of reflection that stretches across the entire y coordinate 4, from point (0, 4), to point (8, 4). Below the line of reflection, there is a triangle with three points labelled: R, S, and T. Point R is located at coordinate (1,1), point S is at (3,3), and point T is at (4,1).
Describe the reflection that will occur for triangle RST. Where will the reflected image R′S′T′ (R prime, S prime, T prime) be located?
Explain your thinking. Record your ideas in a notebook or a method of your choice.
Student Tips
Reflection reminder
In a reflection, the points on the original image are the same distance from the line of reflection as the points on the reflected image.
Reflections are symmetrical.
When you are ready, press the ‘Answer’ button to reveal a possible response to the reflection question.
The reflected triangle will be the same number of units away from the line of reflection.
R′ (R prime) will be located 3 units up from the line of reflection. S′ (S prime) will be located one unit up from the line of reflection. T′ (T prime) will be located 3 units up from the line of reflection. The triangle will be facing down rather than up, as it is a mirror image.

A Cartesian plane with an x- and y-axis. Both axes are numbered from 0 to 8. There is a horizontal line of reflection that stretches across the entire y coordinate 4, from point (0, 4), to point (8, 4). Below the line of reflection, there is a triangle with three points labelled: R, S, and T. Point R is located at coordinate (1,1), point S is at (3,3), and point T is at (4,1). Above the line, there is a reflected triangle with three points labelled: R prime, S prime, and T prime. Point R prime is located at (1,7), point S prime is at (3,5) and point T prime is at (4,7).
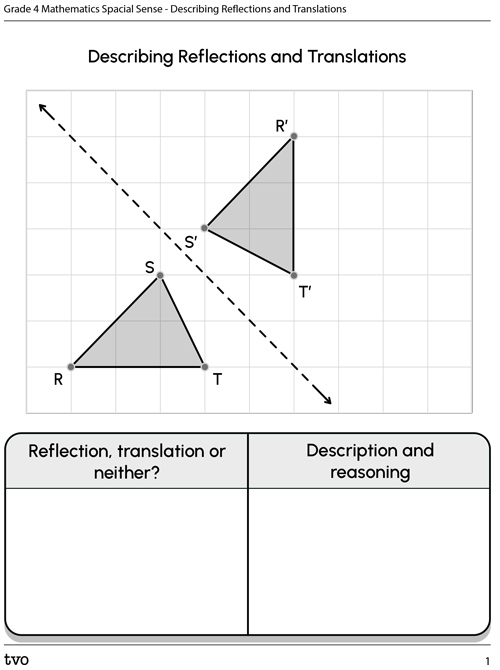
Task 1: Describing reflections and translations
Explore the following grids. For each grid, determine the type of transformation that has occurred.
If a transformation has occurred:
- Indicate that type of transformation (reflection or translation).
- Describe the transformation. How do you know a reflection or translation occurred?
- If a transformation has not occurred, explain how you know.
You can record your ideas in the following fillable and printable Describing Reflections and Translations document. You can also use another method of your choice.

There are two triangles on a grid, with a diagonal line running between them. The first triangle has three points labelled: R, S, and T. The second triangle has three points labelled: R prime, S prime, and T prime. Point R is 2.5 squares away from the line of reflection. Point S is half a square away, and point T is one square away from the line of reflection. On the opposite side of the line, point R prime is 2.5 squares away from the line of reflection. Point S prime is half a square away and point T prime is one square away from the line of reflection.

A Cartesian plane, with an x-axis and a y-axis, on a grid. There are two squares on the grid. The first square has four points labelled: A, B, C, and D. Point A is located at coordinate (1,4), point B is at (3,4), point C is at (3, 2), and point D is at (1, 2). The second square has four points labelled: A, prime, B prime, C prime, and D prime. Point A prime is located at coordinate (1,4), point B prime is at (3,4), point C prime is at (3, 2), and point D prime is at (1, 2).

There are two shapes on a grid with a vertical line between them. The shape on the left side has 6 points labelled: A, B, C, D, E, and F. Point D and point E are 1 unit away from the vertical line. The same shape appears on the right side of the line, but in reverse. This second shape has 6 points labelled: A prime, B prime, C prime, D prime, E prime, and F prime. Point D prime and point E prime are 3 units away from the vertical line.

There are two rectangles on a grid. The first rectangle has 4 points labelled: A, B, C, and D. Point A is located at (2,5), point B at (6, 5), point C at (6, 2) and point D is at (2. 2). The second has 4 points labelled: A prime, B prime, C prime, and D prime. Point A prime is located at (11, 9), point B prime at (15, 9), point C prime at (15, 6) and point D prime is at (11, 6).
Press the Activity button to access Describing Reflections and Translations.
Activity (Open PDF in a new tab)When you are ready, press the ‘Answer’ button to reveal possible solutions to this activity.
| Grid | Reflection, translation or neither? | Description and reasoning |
|---|---|---|

Description
There are two triangles on a grid, with a diagonal line running between them. The first triangle has three points labelled: R, S, and T. The second triangle has three points labelled: R prime, S prime, and T prime. Point R is 2.5 squares away from the line of reflection. Point S is half a square away, and point T is one square away from the line of reflection. On the opposite side of the line, point R prime is 2.5 squares away from the line of reflection. Point S prime is half a square away and point T prime is one square away from the line of reflection. |
Reflection | The image is reflected diagonally and the points on the original image are the same distance from the line of reflection as the points on the reflected image. |

Description
A Cartesian plane, with an x-axis and a y-axis, on a grid. There are two squares on the grid. The first square has four points labelled: A, B, C, and D. Point A is located at coordinate (1,4), point B is at (3,4), point C is at (3, 2), and point D is at (1, 2). The second square has four points labelled: A, prime, B prime, C prime, and D prime. Point A prime is located at coordinate (1,4), point B prime is at (3,4), point C prime is at (3, 2), and point D prime is at (1, 2). |
Translation | Each point moves 7 units right and 3 units up. |

Description
There are two shapes on a grid with a vertical line between them. The shape on the left side has 6 points labelled: A, B, C, D, E, and F. Point D and point E are 1 unit away from the vertical line. The same shape appears on the right side of the line, but in reverse. This second shape has 6 points labelled: A prime, B prime, C prime, D prime, E prime, and F prime. Point D prime and point E prime are 3 units away from the vertical line. |
Neither | The image is not a reflection because the points on the reflected image are not the same distance from the line of reflection as the points on the original image. |

Description
There are two rectangles on a grid. The first rectangle has 4 points labelled: A, B, C, and D. Point A is located at (2,5), point B at (6, 5), point C at (6, 2) and point D is at (2. 2). The second has 4 points labelled: A prime, B prime, C prime, and D prime. Point A prime is located at (11, 9), point B prime at (15, 9), point C prime at (15, 6) and point D prime is at (11, 6). |
Translation | Each point moves 9 units right and 4 units up. |
Consolidation
Predicting and plotting reflections and translations
Using the provided descriptions and images, predict the results of the following transformations, then determine where the translated shape will be.
Plot the shape's transformation or reflection on the provided grids. You can also use another method of your choice.
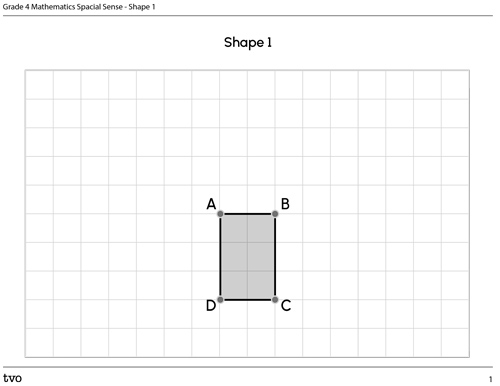
1) Translation
Predict then translate the following rectangle left 6 units and up 5 units. Plot the translated image using the following printable Shape 1 document or use another method of your choice.

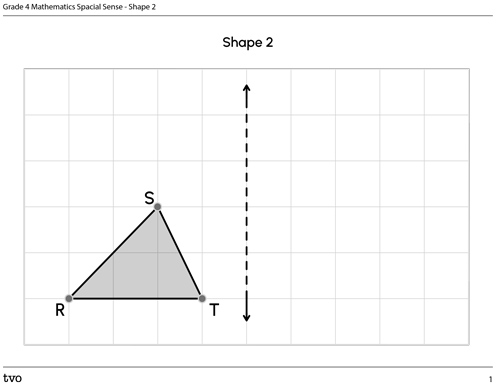
2) Reflection
Predict then reflect the following triangle along the line of reflection. Plot the reflected image using the following printable Shape 2 document or use another method of your choice.

On the left side of a grid, there is a triangle with 3 points labelled: R, S, and T. Point R is located at (1,1), point S at (3,3), and point T at (4,1). The line of reflection is to the right of the triangle, 1 unit away from point T.
Think about your learning
Record your responses for the following questions in a notebook or a method of your choice.
- How might a Cartesian plane be helpful when describing a transformation?
- Why must a reflected image be the same distance from the line of reflection as the original image?
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel...
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.
Connect with a TVO Mathify tutor
Think of TVO Mathify as your own personalized math coach, here to support your learning at home. Press ‘TVO Mathify’ to connect with an Ontario Certified Teacher math tutor of your choice. You will need a TVO Mathify login to access this resource.
TVO Mathify (Opens in a new tab)