Minds On
Notice and wonder
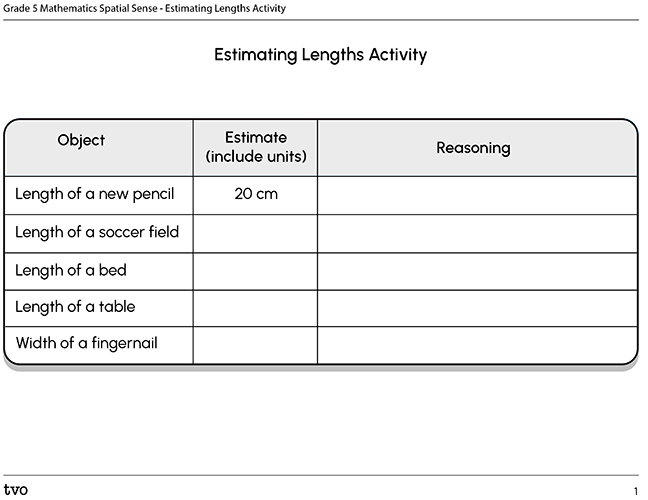
Which metric units would you use to estimate the length or area of the following examples? Why?
How can we create an appropriate estimate of length or area of an object?
Record your ideas in a notebook or a method of your choice.
Action
Benchmarks
When we estimate, we can use benchmarks for these metric units to make the most accurate estimations.
Benchmark for 1 mm and 1 cm
Consider some examples of objects that you know that measure about 1 millimetre (mm) and 1 centimetre (cm), and then compare them to the following benchmarks.

Some common things that are 1 mm in thickness are:
- a ruler
- a pencil lead
- a health or credit card
- a stack of 10 sheets of paper

Some common things that are 1 cm in length or width are:
- the length of a staple
- the width of a pinky finger
- the width of a marker
Press ‘Area’ to reveal a tip about measuring area in millimetres and centimetres.
Remember that when we are measuring area, we use square units. 1 square millimetre is equal to a square that is 1 millimetre on each side, while 1 square centimetre is equal to a square that is 1 centimetre on each side.

Benchmarks for 1 m and 1 km
Consider some examples that you know that measure about 1 metre (m) and 1 kilometre (km), and then compare them to the following benchmarks.

Some examples of things that are 1 m long are:
- the water depth of the shallow end of a swimming pool
- the base length of a large fridge
- the height of a countertop
Some examples of things that are 1 km long are:
- approximately 2 CN Towers (the height of the CN Tower is 553 m)
- the distance you can walk in 15 minutes
- the distance between about 25 telephone poles

Press ‘Area’ to access a tip about measuring area in metres and kilometres.
Remember that if you were measuring area, 1 square metre is equal to a square that is 1 metre on each side, while 1 square kilometre is equal to a square that is 1 kilometre on each side.


Which metric unit do I use?
Choosing an appropriate metric unit depends on what you are planning to measure. If you are measuring the length of a small item like a pencil, you could use millimetres or centimetres.
If you are measuring the length of a large object, space, or the distance between one point to another, you could use metres or kilometres. For example, you might use metres to measure the length of a car and kilometres to measure the length of a road.
Relationship between metric units
Another way to make accurate estimates, is to understand the relationship between the metric units mm, cm, m, and km.
1 km = 1,000 metres
1 m = 100 centimetres
1 cm = 10 millimetres
Select the most appropriate unit
When measuring length and area, we want to use metric units that make it easy for others to understand, and which are the most suitable based on the size of the object or space.
Explore the following objects and select the most appropriate metric unit. Which metric unit would you choose to describe the object? Why?
Estimating and measuring area

When estimating length, we want to identify the appropriate metric unit according to the size of the object. We can use benchmarks to help us.
We can use a ruler or metre stick to measure lengths in mm, cm, or m, and we can use applications and computer software to help us determine lengths in km.
When estimating area, we can use the same process by identifying the appropriate square metric unit according to the size of the object or space, and using benchmarks to guide us.
We know that we can measure the area of a rectangle using the formula A = b×h (area equals base length times height).
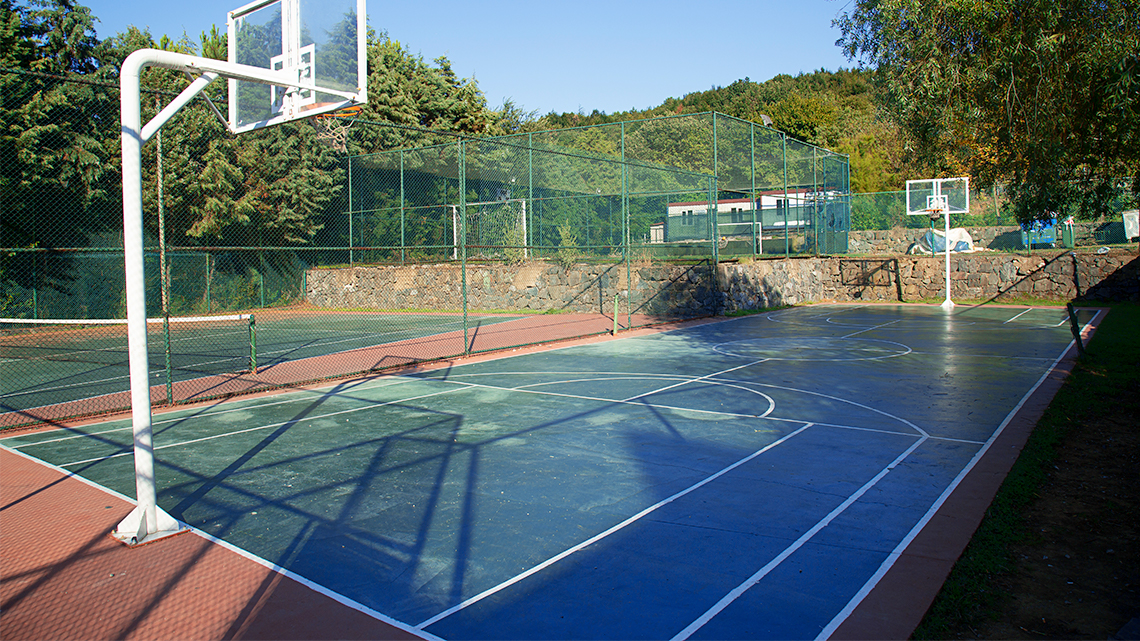
Task 1: Basketball court
Let’s estimate and calculate the area in the following word problems.
A new sports stadium is being built, which includes a full-sized basketball court. The stadium manager knows that the base length of the court will be 28 metres and the total area 420 square metres. But, they are missing the height and need it in order to submit the plans.
Estimate the height of the court, and then calculate the area to check your estimate. Was your estimate accurate?
Record your ideas in a notebook or a method of your choice.

Let’s check if your estimate and calculations are accurate. Press ‘Answer’ to reveal a solution to the area calculations.
I know that 20 × 20 equals 400. If the base length is 28, then I would estimate that the height is 16.
If I know the base length and area of the court, I can use the formula A = b × h to calculate the height of the court.
420 m² = 28 m × h
420 m² ÷ 28m = h
h = 15 m
The height of the new court will be 15 metres.
Task 2: Carpet areas
Sometimes we use a non-standard unit of measurement, such as a pencil length. You might not always have a ruler or tape measure available. However, if you know how long something is, such as a pencil, you can still use it to measure.

A library recently purchased new rectangular carpets and needs to calculate how much space each carpet will take up. The library owner only has an unsharpened pencil to use to measure. When the carpet is unrolled on the ground, it measures approximately 12 pencils long and 4 pencils wide.
Think about which unit of measure you might use to measure the base length and height of the carpet? An unsharpened pencil is about 20 cm long or about 0.2 m.
Using the most appropriate unit of measurement, calculate the area of the carpet.
Record your ideas in a notebook or a method of your choice.
Press ‘Answer’ to reveal a possible step-by-step solution.
Possible solution:
12 pencils would be about 12 × 0.2 = 2.4m. This would be the height of the carpet.
4 pencils are about 4 × 0.2 = 0.8m. This would be the base length of the carpet.
A = b × h
A = 0.8 m × 2.4 m
A = 1.92m²
The carpet area is 1.92 square metres.
The library owner wants to have two of these carpets side-by-side with a space of 0.5 meters between them. If the library wants to calculate the area for two carpets, with a space in between, how would we find the area?
Describe how the base length and height would change, and then calculate the total area.

Press ‘Answer’ to reveal a possible step-by-step solution.
Possible solution:
The height of the carpets remains 2.4 metres.
The new base length of the carpets, plus distance, is 2.1 metres.
(New base length: 0.8 + 0.5 + 0.8 = 2.1)
A = b × h
A = 2.1 × 2.4
A = 5.04m²
The total area of the two carpets and space in-between, is 5.04 square metres.
Consolidation
Task 1: How long?
Using the objects listed below, or examples of your own, estimate the length, and choose the most appropriate unit of measurement. Explain your reasoning using a method of your choice.
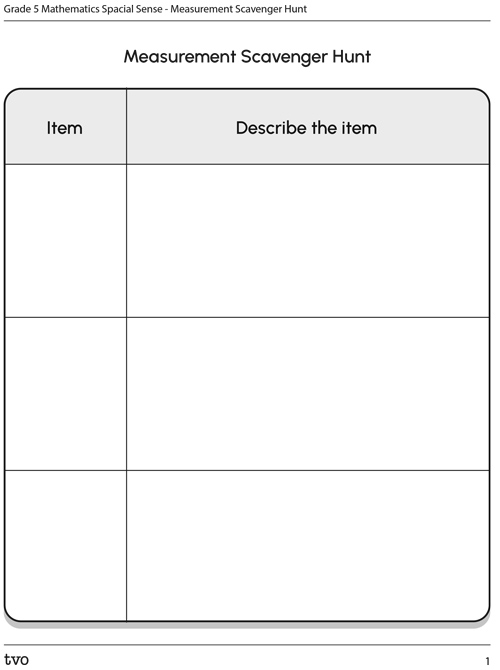
Task 2: Measurement scavenger hunt
Explore and select 2-3 household rectangular item, like a book, paper, table, etc.

Describe the following:
- Which unit of measure would you choose to measure the item?
- Which measuring tool could you use to measure the item?
- How would you calculate the area?
Record your work in the following chart or another method of your choice.
If possible, measure the item, and calculate the area of each.
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel...
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.
Connect with a TVO Mathify tutor
Think of TVO Mathify as your own personalized math coach, here to support your learning at home. Press ‘TVO Mathify’ to connect with an Ontario Certified Teacher math tutor of your choice. You will need a TVO Mathify login to access this resource.
TVO Mathify (Opens in a new tab)