Minds On
The importance of soil

In this learning activity, you are going to explore:
- the good things about soil
- what is added to and absorbed by soils
- how Ontario makes soil healthier
Brainstorm
Soil
Consider the following questions:
- What is soil used for?
- Why is soil so important?
Complete the Soil Mind Map in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Action
What gets added to soil?
Soil is one of the most important things to plants!
Many people, like farmers, scientists, and gardeners, add things to soil to improve its health. These things are called additives. Two additives are fertilizers and pesticides.
Fertilizers

A fertilizer is a chemical that helps plants grow by adding nutrients to the soil.
While fertilizer helps plants to grow, there are also some bad things that happen when using fertilizer. For example, fertilizer sometimes contains metals that contaminate (adds unwanted stuff) the soil. This is not good for the plants or the land around the plants. One of the best types of fertilizers is compost, because it is natural and has no negative effects.
Explore the following Create video entitled “Plants–Natural Plant Fertilizer” to learn more about how natural fertilizer can be created.
Check your understanding!
Based on the previous video you just explored, complete the following activity.
For each sentence, select the missing word from the drop-down menu.
Pesticides

A pesticide is a chemical that is used to stop small organisms or animals from eating plants. These are sometimes called pests. Some good things about pesticides are that they help crops and plants to continue to grow without being eaten. They can also help prevent diseases because they make sure not a lot of bacteria can grow on plants.
However, pesticides are chemicals that change the soil health. They harm living organisms in the soil. They also limit how much water the soil can hold. Fruits and vegetables that grow in the soil where pesticides are used can have harmful chemicals on them. They need to be washed before humans can eat them.
Check your understanding!
Based on what you’ve learned about pesticides, complete the following activity.
For each statement, select true or false.
How does soil absorb water?
All plants need water to grow! Some plants need a lot of water to grow. Other plants only need a little bit.
Plants also need air from the soil. Many plants will die if there is too much water in the soil because the water fills the spaces where the air should be.
You are going to investigate how much water different types of soil absorb (hold) and drain (let through).
In the following video, water is poured over three types of soil: sand, loam, and clay. Before you begin examining the video, make a prediction.
Investigate
Predict
Predict which soil will absorb the most water (sand, loam or clay)? Which soil will absorb the least water? Why do you think this?
Record your prediction using the following checklist and chart, or in another method of your choice.
Prediction checklist
I can make a prediction by…
Complete the Predict, Observe, Conclude Chart in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Press the Activity button to access the Predict, Observe, Conclude Chart.
Activity (Open PDF in a new window)Now, explore the following video entitled “Types of Soil” to learn more about absorption in each type of soil. Using the following checklist and your Predict, Observe, Conclude Chart, or another method of your choice, record your observations after the first pour of water.
Observation Checklist
I can record my observations by…
Let’s explore the following Hungry SciANNtist video entitled “Types of Soil” now.
Based on your observations, respond to the following conclusion questions in your Predict, Observe, Conclude Chart, or in another method of your choice.
- Which soil absorbed the most water? Order them from the most amount of water absorbed to the least.
- Why do you think this happened?
Press ‘Hint’ to learn about the possible answers to the conclusion questions.
|
1. |
The loam soil absorbed the most water (85 ml), then the sand soil (65 ml), and the clay soil absorbed the least amount of water (5 ml). |
|---|---|
|
2. |
There could be many reasons why this happened, including:
|
Maintaining soil health
It is important to keep soil healthy because it is vital to plants, animals, and humans! A healthy soil has a balance of different things.
Explore the following image to learn about the components of the ideal soil.
 Description
Description
Air: Ideal soil would have 25% air. Soil needs air to support the plants and living organisms that live in it.
Water: Ideal soil would have 25% water. Soil needs water to provide nutrients to the plant through their roots.
Minerals: Ideal soil would have 45% minerals, including gravel, sand, silt, and clay. Minerals provide essential nutrients to the plants.
Organic matter: Ideal soil would have 5% organic matter. Soil needs organic matter to provide nutrients to crops and plants.
Ontario’s plan
Ontario has a plan in place to help improve and keep the soil healthy so that farmers can continue to grow food. The plan is also to keep the soil healthy for years to come.
Explore the following images to learn about the ways Ontario improves soil health.
Check your understanding!
Using the information you learned, match the following strategies for keeping soil healthy with their definition.
For each example, select the best definition.
Profile: The plant doctor
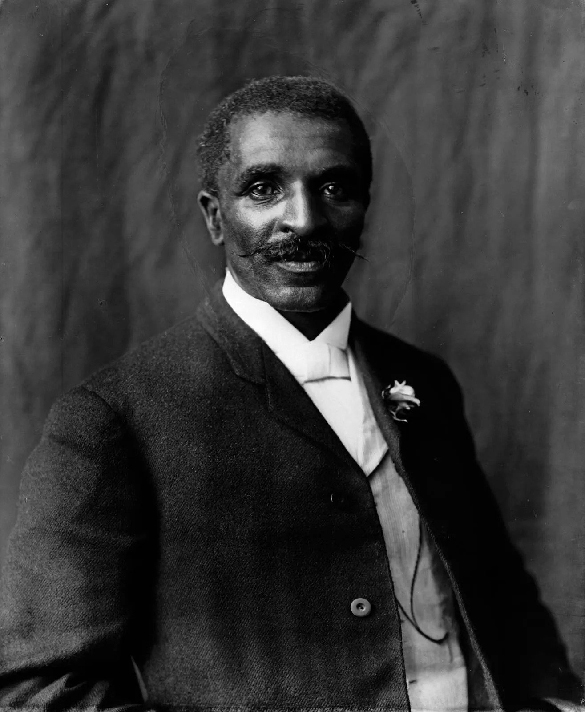

Another strategy that keeps soil healthy is regenerative agriculture. This was founded by Dr. George Washington Carver. He was known as “the plant doctor”. He was a Black farmer and scientist. He focused on improving soil health and ecosystems. He rotated crops each year and changed the crops he planted. This helped to make the soil healthy again for future crops. He also believed that composting and using natural fertilizers was better than using chemical fertilizers to keep the soil healthy for longer periods of time.
Explore the following Xavier Riddle and the Secret Museum video entitled “I Am George Washington Carver” to learn more about him.
Check your understanding!
Based on what you have learned, complete the following activity. For each sentence, select the missing word from the drop-down menu.
Consolidation
Share what you know about soil!

Portfolio
Portfolio
Choose one of the following options to demonstrate what you learned about soil and soil health in this learning activity.
- Draw a diagram with labels about a strategy for keeping soil healthy
- Create a poster in print or digitally about soil health.
Record your responses in a method of your choice.
Consider adding your work to your science portfolio.
Portfolio checklist
My final piece answers the following questions:
While planning my final piece, I considered the following:
Reflection
How do you feel about what you have learned in this activity? Which of the next four sentences best matches how you are feeling about your learning? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas about your feelings using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.