Minds On
Rainbows
Have you ever experienced a rainbow?
What do you notice? What do you wonder?
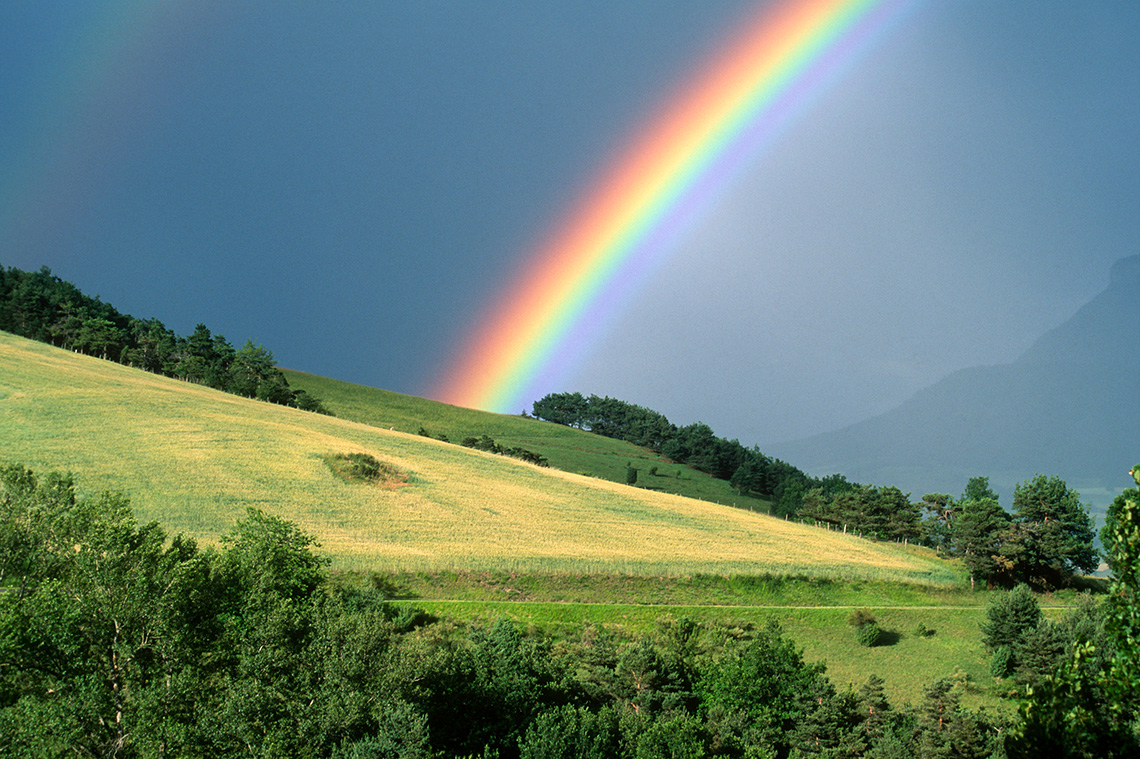

This image shows a colourful rainbow against a dark sky. It appears to be falling out of the sky towards the ground. The rainbow is made of different layers of light and colour, including red, orange, yellow, blue, green, purple. In the foreground, there are bright hills of green grass.
Complete the "Rainbows: Know and Wonder" activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document to record what you know and wonder about rainbows. You might choose to describe a time when you experienced a rainbow. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Share your ideas with a partner, if possible.
Action
What is a rainbow?
When waves of light move through the Earth’s atmosphere, they hit water droplets in the atmosphere and get bent or refracted. The light is refracted at different angles depending on their wavelengths, which is how different colours might appear in a rainbow.
Let’s explore the properties of light to help us understand rainbows.
Properties of light
There are many important facts about the properties and nature of light that we can examine to better understand this fascinating force of nature.
Explore the following interactive checklist for detailed information on the properties of light:
Light…
Check out this Science North video to learn more about the rainbow of colours found in visible light.
Don't worry about the materials or demonstration/experiment mentioned in the video. We'll explore that later!
Learning check
In this video, we explored the properties of light. Answer the following questions:
Hands-on Science
Hands-on science
Let’s make a rainbow! In order to discover more about how light can be refracted to make a rainbow, we will engage with specific parts of the Scientific Experimentation Process! In particular, we will be using skills associated with the following steps of the process: Ask, Analyze, and, if possible, Conduct.
Before beginning your experiment, explore this video that explains the Scientific Experimentation Process. This will help guide you as you work your way through this activity.
Check out this video to learn about the steps of the Scientific Experimentation Process.
We have already identified a question to ask: What is a rainbow? In addition, you have generated your own questions to investigate. We have also learned about the properties of light.
Next, we will observe a video clip and short experiment demonstration about light refraction in order to analyze the results. If possible, you may also conduct the experiment explored in the video if you can work with a trusted adult and access the necessary materials.
To begin, let’s observe the following experiment demonstration and video clip discussing how light refraction can be observed. Explore the following tabs to learn about the materials needed and experimental procedure for the “Make a Rainbow” experiment.
If you are conducting the experiment, please perform the following safety check:
Safety
Before you explore the following experiment, let’s perform a safety check.
If you do not have access to materials, access the “video demonstration” tab to explore the experiment in action. You can use the video to make your observations and draw your conclusions.
- a glass container
- water
- a small mirror
- flashlight or sunlight
- wall or white paper
- Fill a glass container halfway with water.
- Place a small mirror inside the container at an angle. Make sure that half of the mirror is out of the water and half of the mirror is in the water.
- Use a flashlight to shine light into the mirror, or place the container in bright sunlight.
- Using white paper or a surface, find out where the light is being reflected. Observe how the light appears.
- Move the container of water gently. Observe how the light is affected.
Check out the following video to explore a demonstration of the “Make a Rainbow” experiment.
Complete the following fillable and printable document Lab Sheet: Make a Rainbow or record your ideas using another method of your choice.
|
Materials needed |
|
|---|---|
|
Hypothesis – what do you think will happen? |
|
|
Procedure |
|
|
Observations *Remember observations can be recorded with pictures, numbers and/or words! |
|
|
Conclusions |
|
|
Questions |
|
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Lab Sheet: Make a Rainbow.
Future impacts
This learning activity connects new and existing approaches for young scientists to create positive changes in their communities.

Scientists, engineers and urban farmers are using the properties of light in innovative ways. Let’s find out how the rainbow of colours can be used to help plants grow.
Let’s grow!
What do plants need in order to grow? Why are plants important?
Which plant needs might be more challenging to meet when growing plants in the city?
How might the growing season be extended in order to grow plants all year long? Which plant needs would require extra support?
Record your ideas in a method of your choice.
Press ‘Hint’ to access some possible responses to the prompts.
Most plants need sunlight, space, soil, warmth, and water to grow.
Supporting the growth of plants is critically important for many reasons.
In addition to providing habitats, oxygen, and medicines, nurturing soil, and reducing air pollution, plants are essential food sources for many different species, including humans.

Grape harvesting in a field.
In Ontario, the outdoor growing season for plants lasts a few months. It typically begins in the spring and ends in the fall. Most of the local food we eat is grown outside of the city, in rural areas.
Urban farming
Some of the challenges of growing plants in the city include the lack of space and sunlight, and the cold temperatures during the winter.
In order to address these challenges, urban farmers have learned how to control temperatures and use the properties of light to grow plants indoors.
Vertical farming
Vertical farming is an innovative solution to address the lack of outdoor space in the city, and allows urban farmers to grow food all year long.
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops indoors, in vertically stacked layers.
Vertical farming often uses hydroponics, which supports plants in water to grow without soil. Many plants can be grown hydroponically, including lettuce, bok choy, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and strawberries.

Vertical farming is a growing sector of agriculture called agritech. Agritech refers to the technology used to grow food indoors.
Explore the following video to learn more about how technology is helping to control the growing environment in a vertical farm in Chelmsford, Ontario.
In the video, Stephan shows Jeyan how he can control everything on his vertical farm from his smart phone. This is because his farm has several sensors that detect things like temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, and soil moisture level.
These sensors produce data that Stephan can access live on his phone–that is, he always knows the current conditions on his farm, and can make decisions based on this live data.
LED lights
LED lights are used to grow plants indoors in many greenhouses, and in vertical farms. Let’s learn more about this innovative source of light.
“LED” stands for light emitting diode, the technology behind LED lights.
According to Energy Star, LED lights produce light up to 90% more efficiently than incandescent and fluorescent lightbulbs.
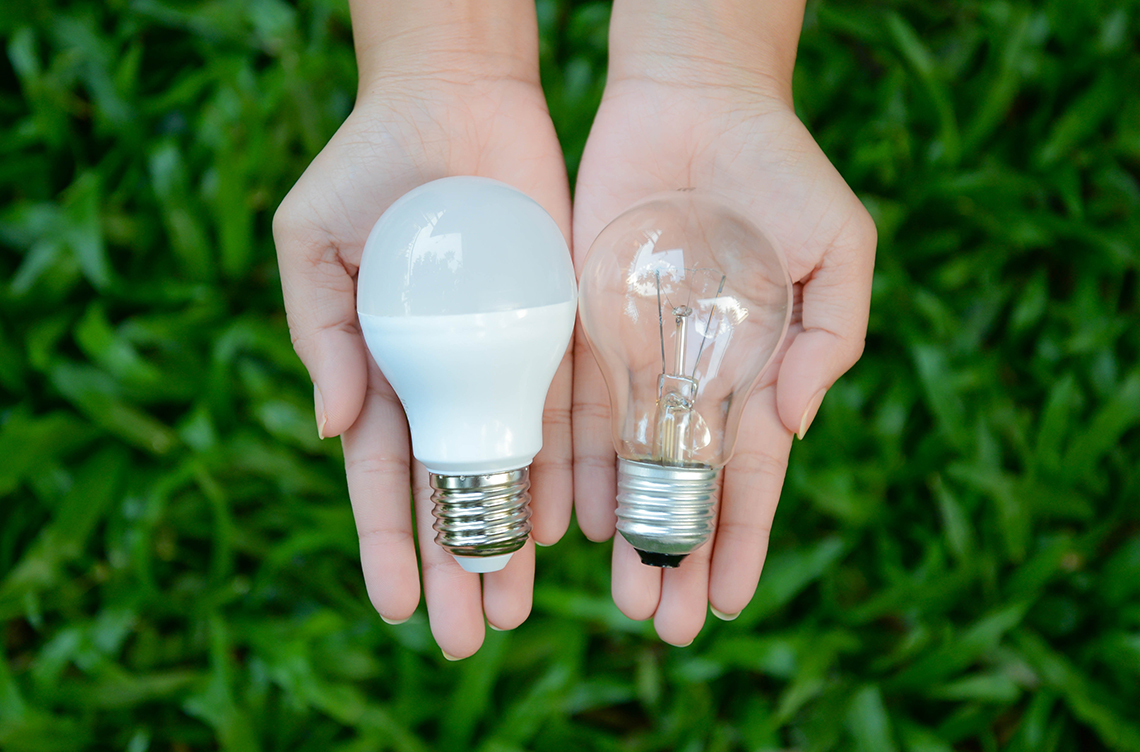

An incandescent and LED lightbulb.
Press the following tabs to access more important details about LED lights.
Common LED lights include amber, red, blue, and green. To produce white light, LEDs are combined with a material that converts light to “white”.
Why is LED lighting ideal for indoor farming?
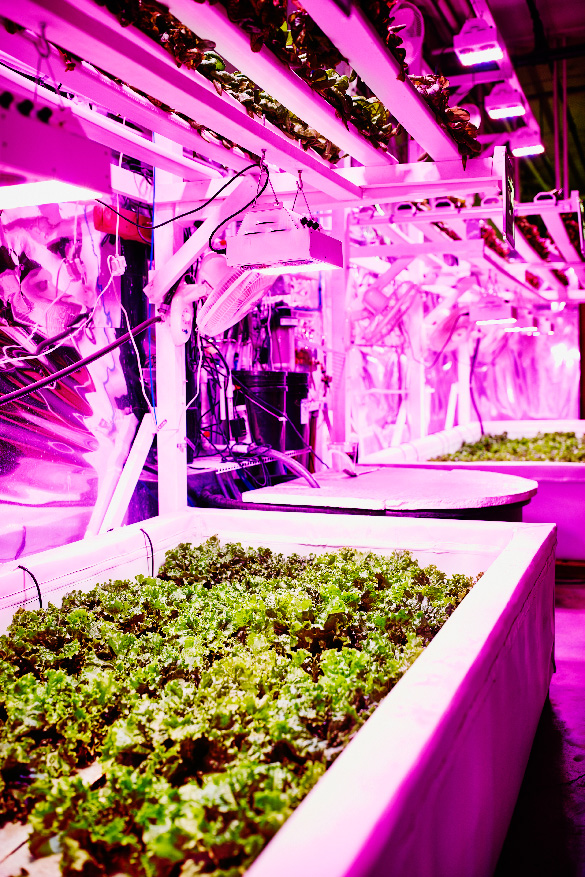

Pink LEDs shine over an indoor farming plot of organic lettuce.
Scientists have learned that plants only need specific colours and wavelengths to grow. Different colours of LED lights can be absorbed and reflected by plants to support growth.
Greg Volente explains how the colour of light affects plant growth at different stages of its life cycle.
Seeds and new sprouts grow best with blue light. Blue light is very important because it increases the amount of chlorophyll, which helps plants to produce their own food through photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plant leaves and stems. It allows plants to absorb light energy and turn it into food.
Red light and blue light are important when plants begin to flower. They help plants to grow new leaves.
Purple or violet light can be used throughout the growing cycle to enhance the colour, smell, and taste of plants, such as the organic lettuce in the previous image. This secondary colour can be made by mixing the primary colours of red and blue.
Consolidation
Farming and the properties of light
In this learning activity, we have explored the properties of light and considered how they are being used in innovative ways by urban farmers.

Pause and Reflect
Pause and reflect
- What are the properties of light that can be used to help plants grow indoors?
- Why are LED lights used for indoor farming?
- What are some of the advantages of vertical farming?
- What are some of the challenges of vertical farming?
- What are the potential impacts of growing local produce all year long for local communities?
Record your ideas in a method of your choice. Share your ideas with a partner, if possible.
Press ‘Answer’ to access an example of how to respond to the previous question prompts.
The advantages of vertical farming include: growing a large crop of plants in a small area; the growing season is extended all year long; the temperature, light and water are controlled; pesticides and chemicals are not used; provides local produce to northern communities; less fuel is required to import food; less water is used compared to traditional farming; crops are resistant to extreme weather conditions.
The challenges of vertical farming include: large energy demands; increased hydro costs and electricity bills; the start-up costs are very expensive; use of non-renewable energy may cause more pollution; requires access to technology; loss of traditional knowledge about farming and growing plants.
LED lights are energy efficient and last a long time. They do not emit heat, so they can be placed close to the plants, which are stacked on vertical shelves. LED lights can shine directly on the plants. Red-blue lights can be used to maximize plant growth.
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.