Minds On
From single cells to entire organisms
Observe the following carousel of illustrations and captions:
Consider what you observed as you navigated through the images. In a method of your choice, respond to the following question:
- Why might it be important for scientists to study a topic at its most basic level?
Press ‘Hint’ to access a prompt to help guide your thinking.
Action
Cells: the basic units of life

This diagram demonstrates the progression from single cell all the way to an entire organism.
In Science, cellular biology is “the study of cell structure and function, and it revolves around the concept that the cell is the fundamental unit of life” (Bisceglia & Miko, 2010). There are many advancements in technology that have supported a closer understanding of cells and cell processes.
Research conducted by cellular biologists greatly contributes to the innovations in healthcare due to their specific area of focus
Healthcare is a field that relies upon research in cellular biology because it enhances our understanding of human life. A better understanding of an organism like the human body and its systems can help to keep people healthy, and since the cell is the most basic unit of life, life-saving research and innovation must begin at the cellular level.
Working in cellular biology
There are many positions in the field of cellular biology that use technological innovations to support a better understanding of human life. The professional options across the field of cell biology are broad, and often require expertise in a variety of subject areas such as mathematics, technology, engineering, and scientific research.
Press the following tabs to access details about the following professional roles in the field of cellular biology.

Cytologists play a central role in advancing our understanding of cells and cell processes. Cytology is the study of single cell types, typically from a fluid sample, and is primarily used to screen for cancer or other abnormalities. Cytologists, or cytotechnologists, are professionals who study cells through microscopic examinations and other laboratory tests.
Diagnostic cytologists are responsible for examining cell specimens using microscope technology, and both identifying and diagnosing cancerous and pre-cancerous cells.

Forensic lab analysts diagnose issues at the cellular level in specimens that are collected and submitted by police departments. Samples that are taken as physical evidence are submitted to forensic laboratories, where they will be examined by the analysts and technologists who work specifically with biological materials (i.e. saliva, hair, skin, blood).
Forensic lab analysts will examine specimens in order to develop DNA profiles and identify other important biological data as it relates to the criminal proceedings. They require technology that allows for a detailed reading of data with small, cellular-level sample sizes.

Librarians are trained to be specialized information experts, and there are libraries to house directories of research data pertaining to human biology and the medical field. Certain medical librarians – sometimes called medical information specialists – must be familiar with how to examine cells and cell processes in order to support other healthcare personnel in finding data such as samples or specimens.
Medical librarians work in hospitals, healthcare centres, universities and medical schools. As university medical centres continue to grow their data collections, hospitals and healthcare outlets seek the assistance of medical librarians in locating new and relevant information when accessing their collections.
Review your understanding
Consider the following question:
- How does the field of cellular biology impact healthcare?
Record your thinking in a method of your choice.
Press ‘Suggestion’ to access a hint to help guide your thinking.
Innovations in healthcare technology
The work of different careers in cellular biology, especially as it connects to healthcare, would not be possible without advanced technology.
While the development of different technological devices is constant, there are certain core innovations that continue to shape how researchers study cells and cell structure today.
Explore the following set of flashcards to explore examples of ground-breaking technology that has shaped our understanding of cell processes.
Spotlight: the scanning electron microscope (SEM)
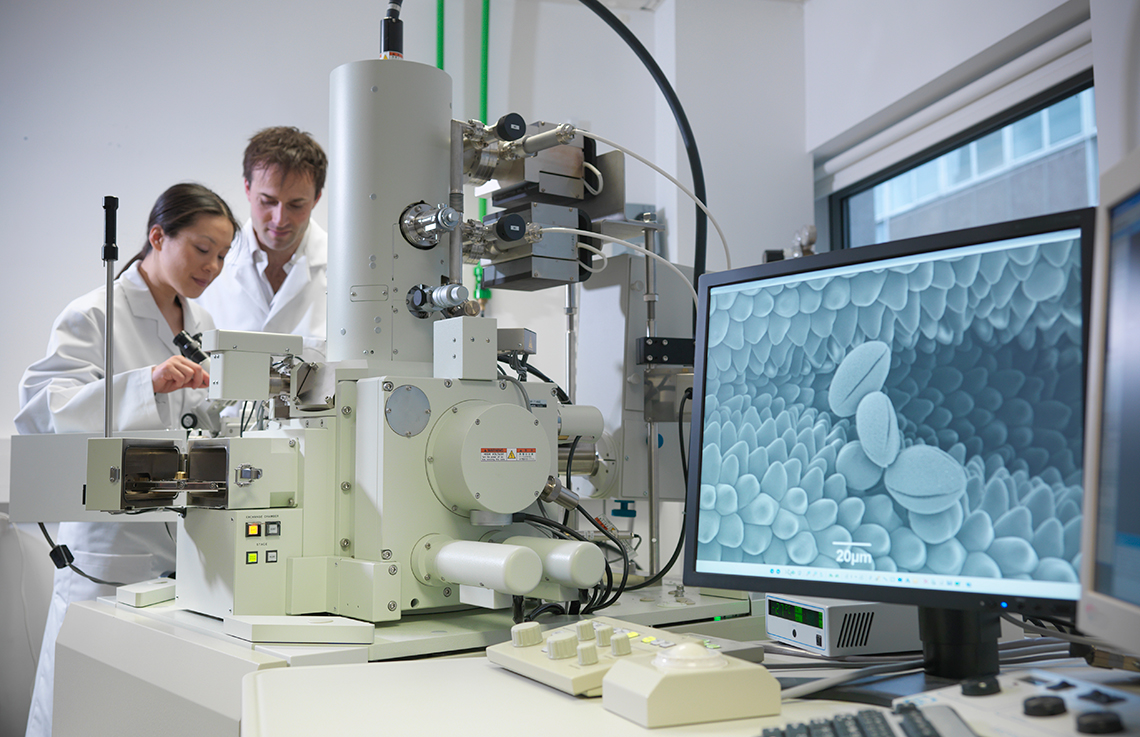

The scanning electron microscope (SEM) is an advanced type of electron microscope that produces the highest resolution of cell imaging at 100,000 times magnification.
Unlike the single beam of electrons used by other, simpler versions of the electron microscope, the SEM projects a beam of electrons that moves back and forth across the surface of a cell (Molnar et al., 2021).
Advantages
- This kind of scan provides an even more detailed picture of the cell structures in the specimen, as it renders information about the characteristics of the cell’s surface through reflection.
- This method of studying cells has improved accuracy and magnification in comparison to light (i.e. non-electron) microscopy.
Disadvantages
- SEMs are large and must be stored and used in a space without the possibility of electric or magnetic interference.
- The price and maintenance of these devices can be a compromising factor, as SEMs are considerably more expensive than less sophisticated electron microscopes.
Your turn to research!
Now that you have reviewed some key information about innovations used in the field of healthcare that have shaped our understanding of cells and cell processes, it is time to research one specific device or form of technology in greater detail. You may choose one of the examples from the flashcards or select a different innovation of your choice.
Before beginning your research, explore this video that explains the scientific research process to help guide you while you are completing the task.
Check out this video to learn about the steps of the Scientific Research Process.
After reviewing the video, explore the following interactive checklists to support your research process.
I can choose resources by
I can analyze and interpret findings by
Complete the Innovative Healthcare Technology activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
| Innovation: | |
| Background information: | |
| Advantages: |
|
| Disadvantages: |
|
| Sources: |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access the Innovative Healthcare Technology Chart.
Consolidation
Putting it all together
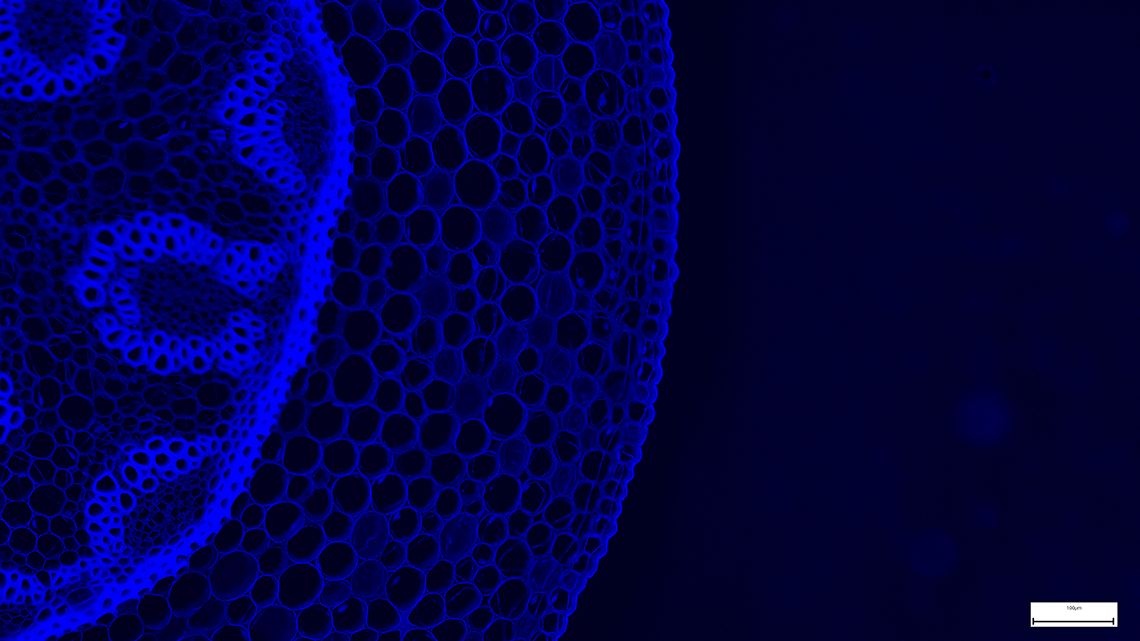
Microscopic photograph of the surface of a tongue cell
In your independent research task, you sought information about some of the disadvantages of the healthcare innovation you investigated. Some of the disadvantages of the scanning electron microscope, for example, concerned the demanding cost and size of this sophisticated device.
Consider some of the limitations or restrictions you noted in your research, and propose at least two developments that could help improve the effectiveness of this technology.
Record your response in a method of your choice.
Reflection
As you read the following descriptions, select the one that best describes your current understanding of the learning in this activity. Press the corresponding button once you have made your choice.
I feel…
Now, expand on your ideas by recording your thoughts using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.
When you review your notes on this learning activity later, reflect on whether you would select a different description based on your further review of the material in this learning activity.
Press ‘Discover More’ to extend your skills.
Discover MoreBe the next big thing!
In this learning activity, you have been exploring engineers and how they solve real-world issues.
Create an “Engineering Club” for your school or community and communicate about your club in a method of your choice, for example, a poster, Tweet, or audio recording. In your message, be sure to exclude when engineers are important to our future!





