Minds On
Around the world
Plants can be found in many diverse climates around the world. Although they might appear a little different, there are parts that all plants have in common.
Let’s explore the following images of plants.
Then, try to determine what is similar about all the plants. Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
What similarities did you notice about all of the plants we previously explored?
Did you notice that all the plants seemed to have green leaves and stems?
Some of the plants had flowers.
All the plants had roots, but they were hidden in the soil or in soil under the water.
The plant
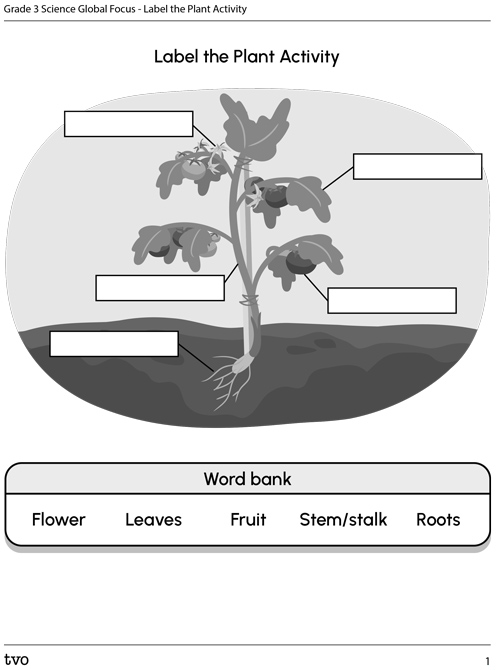
Now that you have explored different types of plants and parts of the plants, let’s try to label the parts of the following plant.

Complete the Label the Plant Activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
When you’re ready, press ‘Let’s Check!’ to access a labelled plant diagram.

A plant with five labelled parts: root, stem, leaves, fruit and flower. The plant has roots at the bottom in soil, and a stem or stalk growing above the ground. The stem has leaves growing on it. There is a fruit growing on the stem. There is a flower at the top of the plant.
Action
What do plants need?
Plants are living or biotic.
That means plants have certain needs to stay alive.
Plants need the following to stay alive:
- water
- air
- space to grow
- sunlight and warmth
- nutrients found in soil
Each part of the plant has a specific job to help the plant get the things it needs to live.

Check out this video entitled “Plant Problem” to learn more about the parts of a plant and what they need.
In this video clip, the Sparks Crew are investigating a giant plant that is growing so large that it is taking over the city!
After exploring the video, complete the following questions based on what you’ve learned.
Select the correct answer, then press “Check Answer” to see how you did.
Plant structures
Plants are structures that occur naturally in the environment. Like any other kind of structure, plants need to be strong and stable.

Roots
Roots play two important roles in helping the plant to stay alive. Let’s explore the roots!
As we learn more about roots, you will be making observations.
Observations are when you notice and record information that you have learned, which are important steps in the Scientific Research Process. The specific steps we will explore in the following task are: “Learn” and “Record.”
Time to learn! We can learn things from different places and people.

It’s time to record what you have learned. You could write it down, or make an audio or video recording.

Did you realize you have been achieving the “Learn” step after exploring the Hero Academy clip? The next activity will focus on the “Record” step, which can also be called the “Observe” step.
Check out the following checklist to guide how to record scientific observations.
I can make and understand observations by:
Try It
Your turn!
Let’s explore our observation skills with the following video clip.
After checking the video out, what were your observations?
You may explore the video once again to make your observations.
Complete the My Observations Activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
|
What did you notice? You may record points that you can observe with the senses as a description, an illustration, or another method of your choice. |
| What role do roots play in a plant’s survival? |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access My Observations Activity.
Press ‘Let’s Check!’ to access a completed My Observations Activity sheet.
|
What did you notice? I observed that a root began to grow under the soil in various directions and that one plant began to emerge from the soil to grow a stem and a few leaves. 
A bean sprout drawing with roots, a plant, and a leaf. The roots, plant and leaf are labelled. |
|
What role do roots play in a plant’s survival? Plants need roots to get the water needed to survive, and to help them be stable and not fall over. Both stability and water are key to a plant’s survival. |
Stem
Roots help to hold the plant firmly in the space where it is growing and to drink water, but the water needs to get to different parts of the plant.
That is made possible because of the stem or stalk of a plant.
Explore this video entitled “How Do Plants Drink Water” to learn more about xylem vessels.
Teacher Aldo explains how the xylem vessels inside the stem work with the roots to transport water to the rest of the plant.
Student Tips
Student tips
Let’s reflect on what we learnt from the video.
How does water get from the root to the rest of the plant?
Water travels from the root in the soil up the stem or stalk of the plant and delivers the water to all the other parts of the plant.

Leaves

Leaves are the food factories of the plant.
The green leaves of plants are able to make their own food from sunlight and water.
This is very different from animals who have to find and eat their food!
This process is known as photosynthesis. The word photosynthesis can be separated into two smaller words:
- photo is “light” in Ancient Greek
- synthesis means “putting together” in Ancient Greek
So, plants can put their own food together by using light.
Let’s explore the following video to learn more about photosynthesis.
Based on what we learned in the previous video, organize the following steps of photosynthesis.
For each ‘step’, select the corresponding photosynthesis description.
Investigate
Investigate
Let’s investigate the following image of a leaf that has been underwater in the sun for a few hours.
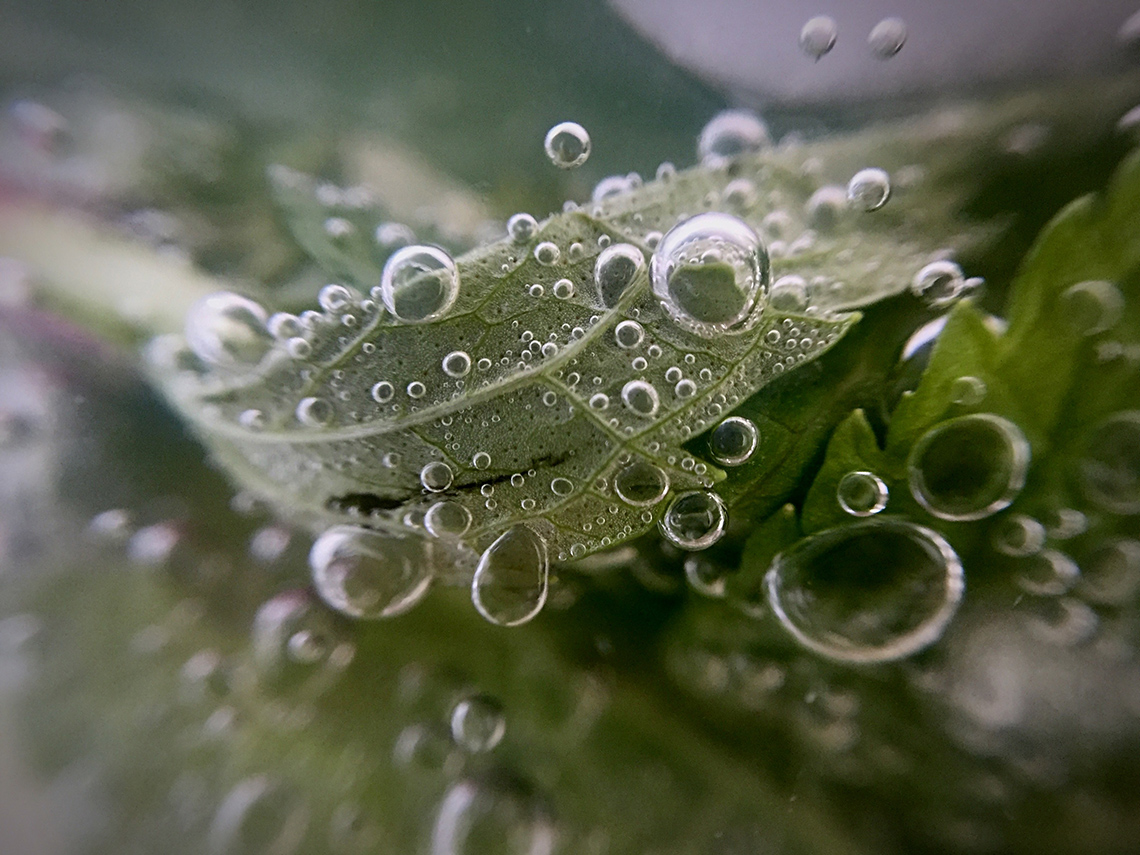

Using your observation skills, what do you notice? What do you think this means?
Record your ideas in a method of your choice.
When you’re ready, press ‘Let’s Check!’ to access an observation about the leaf.
The leaf has bubbles on the surface. The leaf is releasing oxygen.
If possible, the next time you are outdoors with an adult, try to bring a leaf indoors and put it in a bowl of water to make your own observations.
You can use a rock or a few coins to keep the leaf underwater.
Plant survival
We have learned about some of the basic needs of a plant, like water, sunlight, and nutrients. We have also explored how the different parts of a plant, like the stem, roots and leave, all work together to help it survive.
Sometimes, plants have trouble accessing their most basic needs.
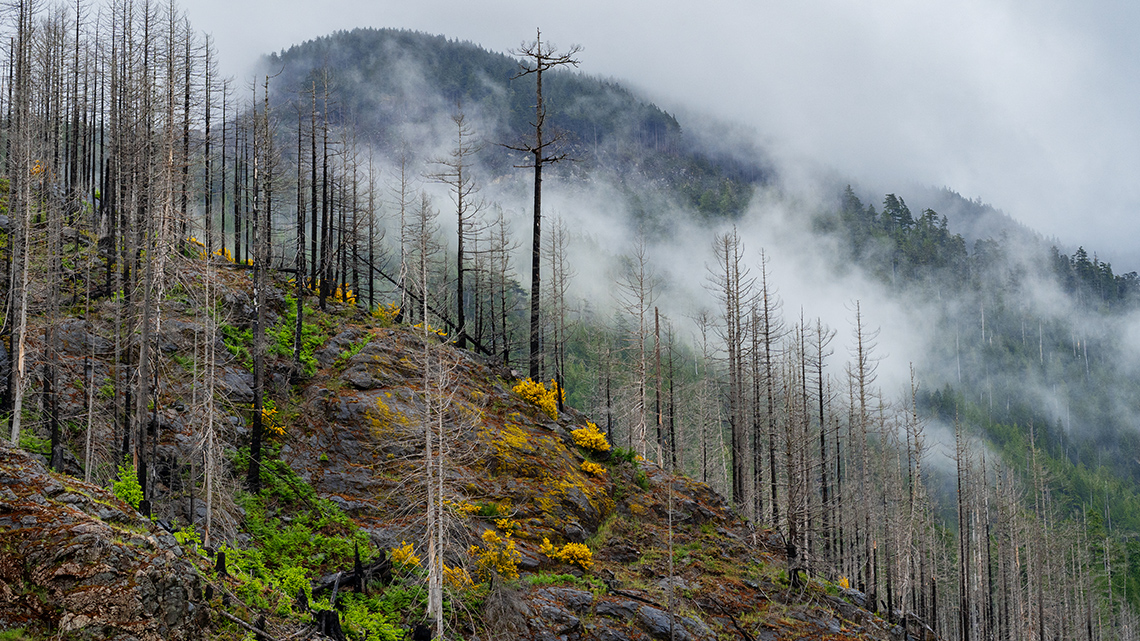
Extreme weather conditions can not only block off access to plant needs, but they can damage the important parts of a plant, too!
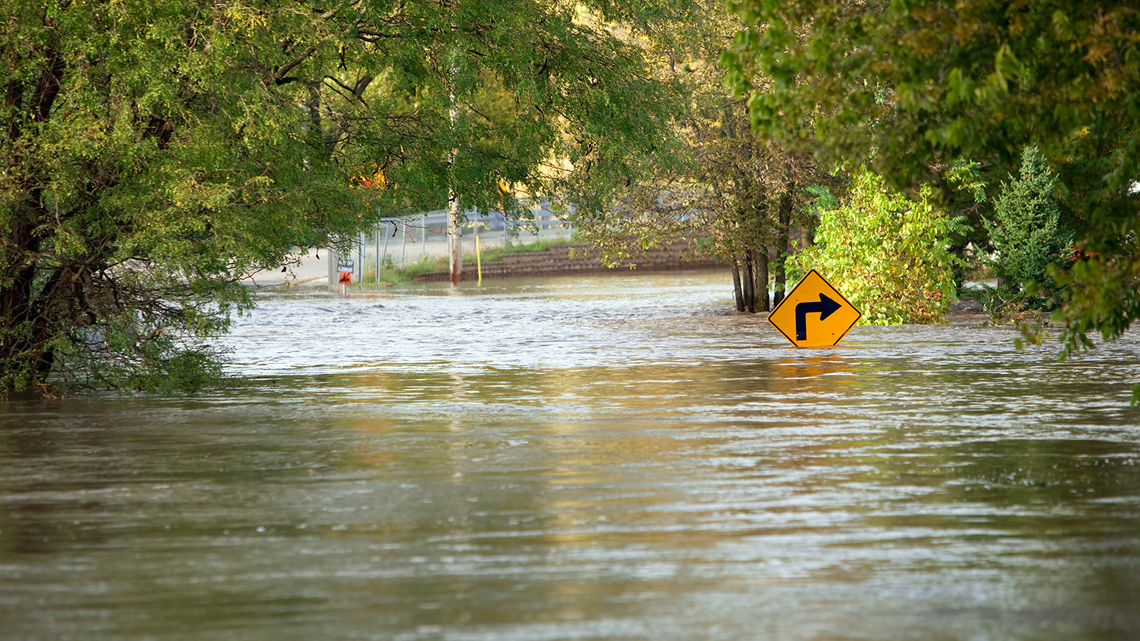
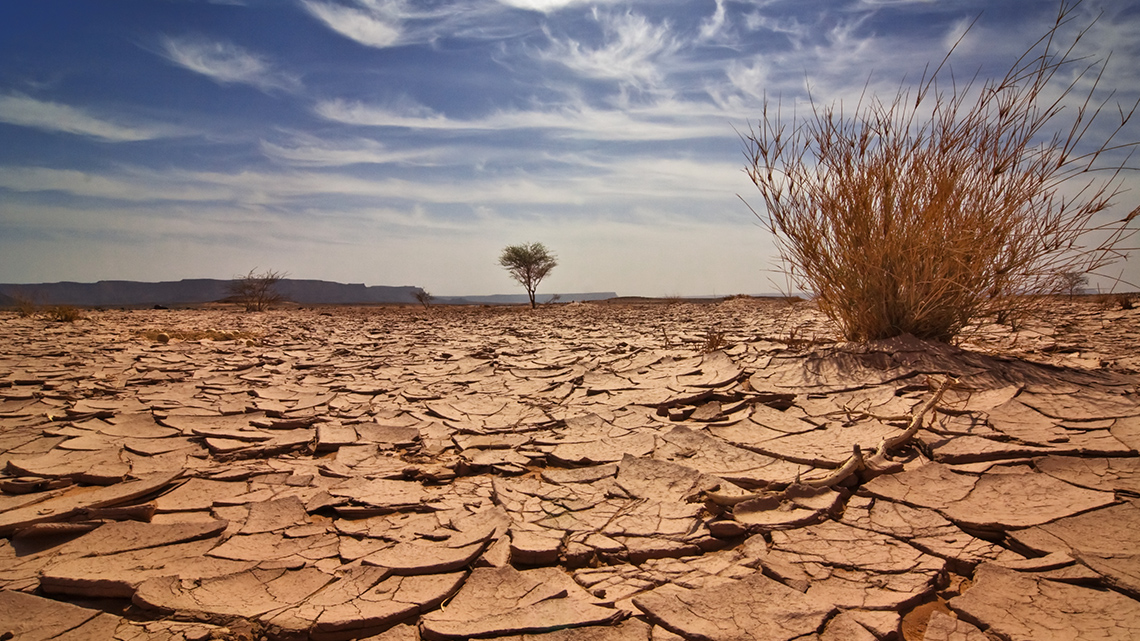
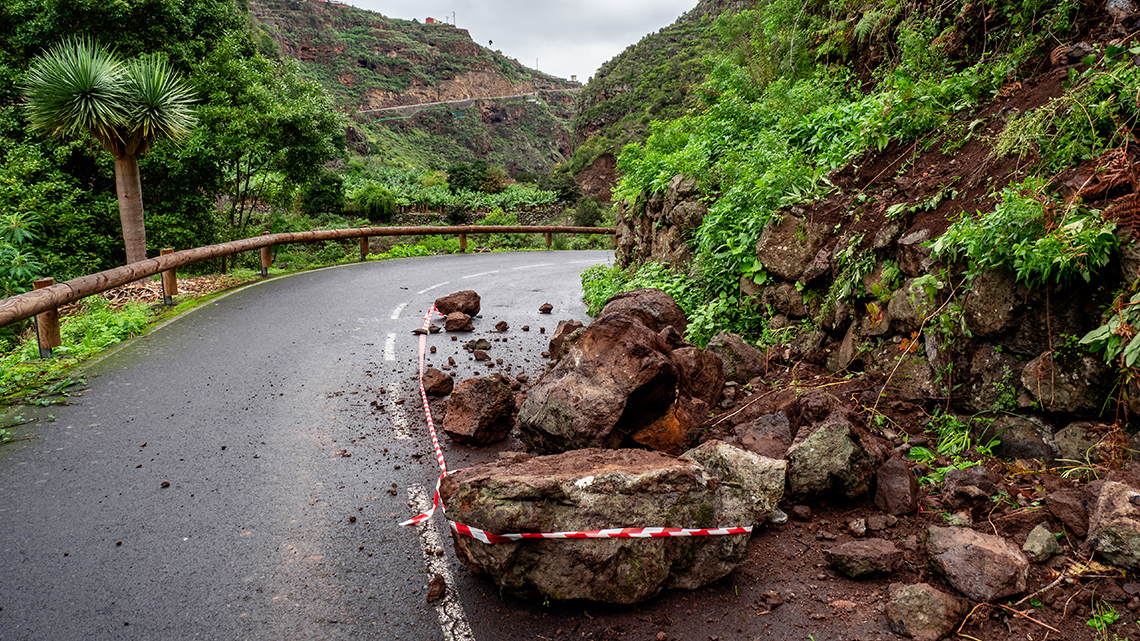
Explore the following images and descriptions of extreme weather conditions that could threaten plant survival.
After exploring the images and captions, reflect on how a weather condition might affect a plant’s survival.
Choose one of the following weather conditions:
- flood
- drought
- earthquake
- wildfire
Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
When you’re ready, press ‘Let’s Check!’ to access possible responses.
- With floods, plants can “drown” if given too much water and not enough air bubbles or oxygen.
- During a drought, a plant cannot get enough access to the water it needs to survive, so its soil will lose the important nutrients.
- During an earthquake, the plant’s roots could be shaken or even ripped out so that it is no longer stable, or other parts of the plant could be crushed.
- With wildfires, the plant is exposed to pollution in smoke, instead of the clean oxygen it needs. The fire can burn or destroy entire plants.
Drought and hunger
Access this video clip entitled "Drought" to learn more about how droughts affect plants.
What did you notice about the result of drought on plants? What else can droughts threaten?
Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
Did You Know?
Did you know?
When environments lose access to the water they need, the plants that grow there – especially fruit and vegetable crops – will not be able to survive.
When food sources decline, this makes the worldwide problem of hunger even harder to address. This is why the United Nations identified this as one of their Sustainable Development Goals.
United Nations and zero hunger
Just as much as humans and animals depend on plants for food, shelter, medicine, and more – plants equally rely on humans to take action to protect and preserve their habitats.
The United Nations is guiding the global sustainability effort to help improve life on earth by the year 2030, which is linked to the protection of the plants that provide us with food.
Connecting to the world

The United Nations (UN) is a group of many countries from around the world that have come together to create a better future for people and the environment. They have created 17 goals called the Sustainable Development Goals.
This learning activity is connected to Goal #2 which is called Zero Hunger. This means that everyone should have access to safe and nutritious food. Nutritious food helps someone grow and gives them energy.
Using plants for food is one way that people all over the world can help each other access safe and nutritious food.
This learning activity ties to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal #2 of Zero Hunger.
Consider the following:
- Why might we connect drought and global hunger?
- How could we describe the harmful effects of drought on the parts of a plant?
Record your thoughts in a notebook or another method of your choice.
Consolidation
Review your learning

We have explored how each individual part of a plant has a specific job, and how plants feed themselves using the process of photosynthesis!
We have also explored some of the extreme weather conditions that can threaten a plants’ survival.
So, how can plants keep themselves alive? And how can different weather conditions put plants at risk?
Complete the Plant Conditions Activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
|
1. Describe or illustrate each different part of a plant (roots, stem, leaves, flower, etc.). How can each part help the plant survive? |
|
2. Choose an extreme weather condition:
You may also choose another extreme weather of your choice. Then, reflect on how it can affect the plant’s ability to survive. For example, what might happen to seeds planted in soil after an earthquake? |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Plant Conditions Activity.
Reflection
How do you feel about what you have learned in this activity? Which of the next four sentences best matches how you are feeling about your learning? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas about your feelings using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.