Minds On
Notice and wonder
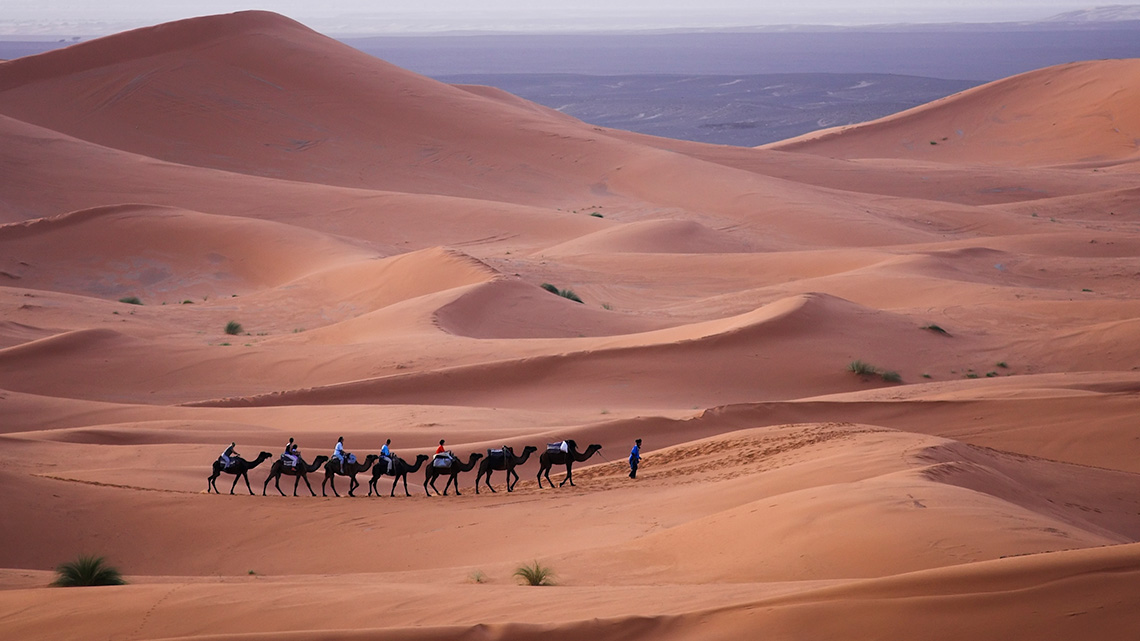
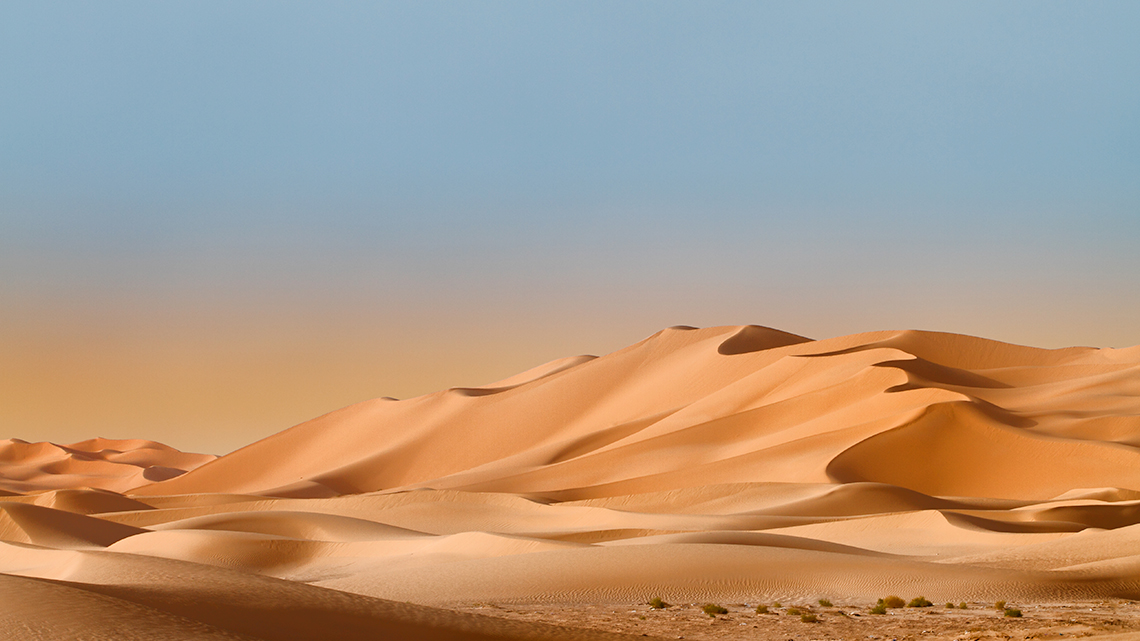
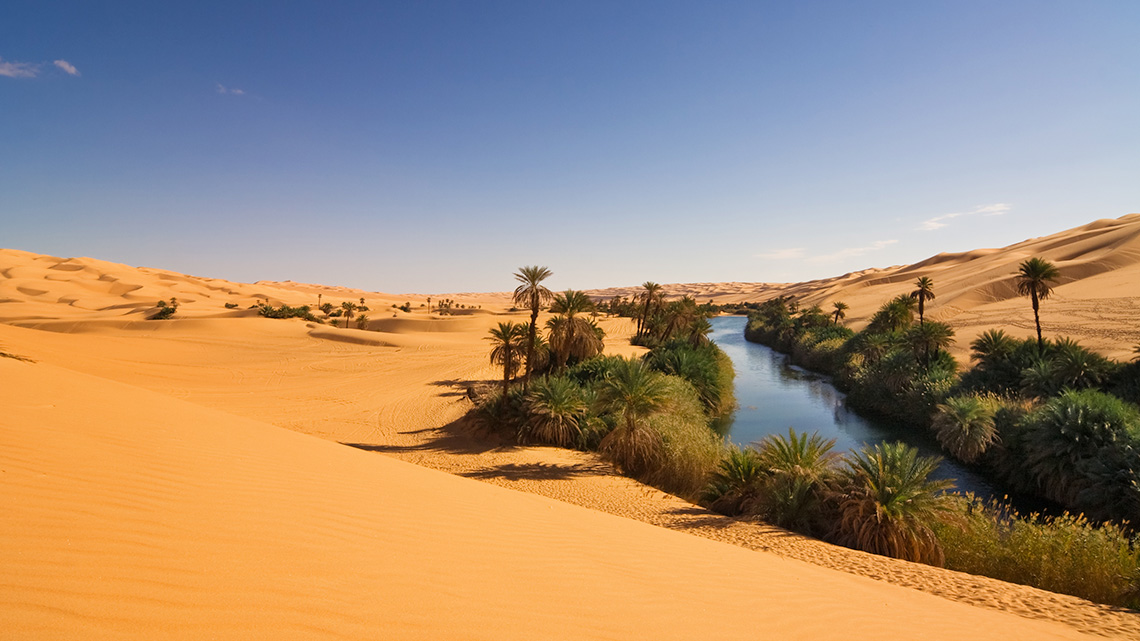
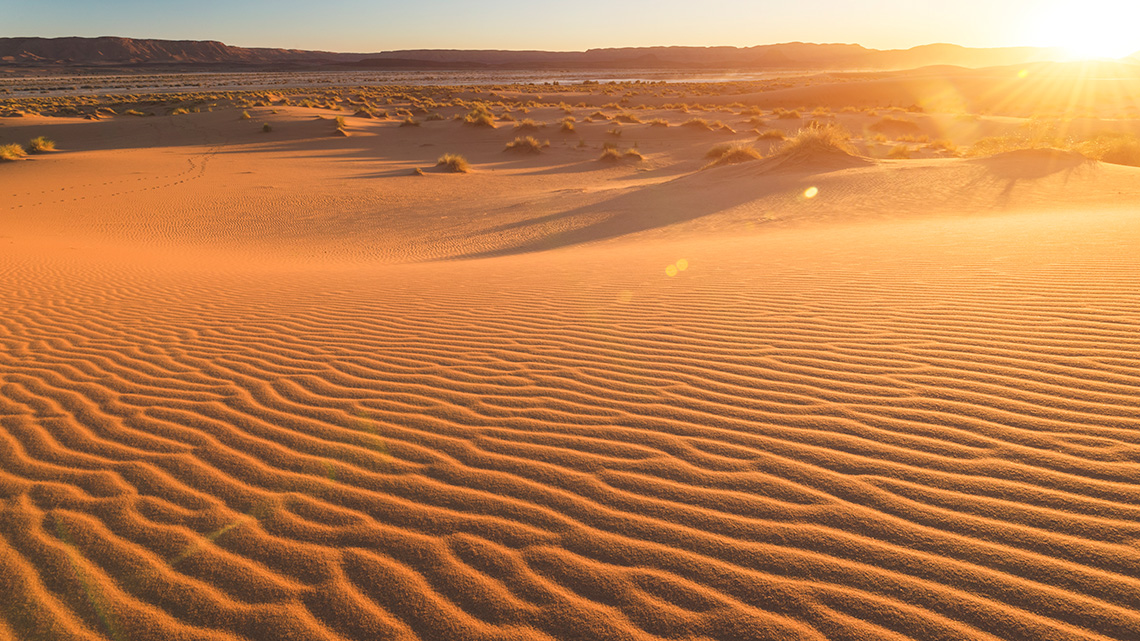
Explore the following images of the Sahara Desert located in Algeria.
After exploring the images, reflect on the following questions:
- What did you notice and wonder about the Sahara Desert in Algeria?
- What kinds of plants do you think grow in the Sahara Desert? Why do you think this?
Complete the Notice and Wonder Activity in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
| Notice and Wonder Activity | |
|---|---|
| I notice… | I wonder… |
| What kinds of plants do you think grow in the Sahara Desert? Why do you think this? | |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Notice and Wonder Activity.
Action
Environments
Growing food is an important activity that is key to human survival. Over time, people have had to adapt the way that they grow food.
All around the world, there are different types of environments:
- warm and sunny weather all year round
- a lot of rain or snow
- a combination of various weather conditions
As humans have adapted how they grow food, plants have also adapted to grow in the most unexpected environments.
Let’s learn more about plant adaptations!
Plant adaptations
What is an adaptation?
An adaptation is a characteristic of a living thing that helps it to survive in its environment. Plants adapt to their environment in diverse ways.
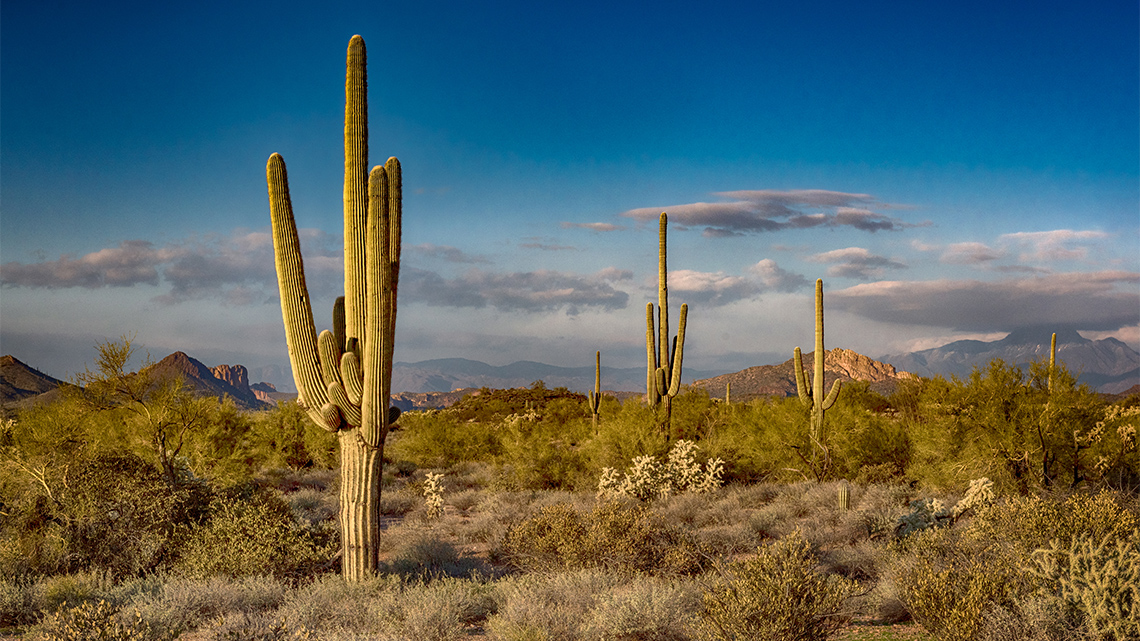
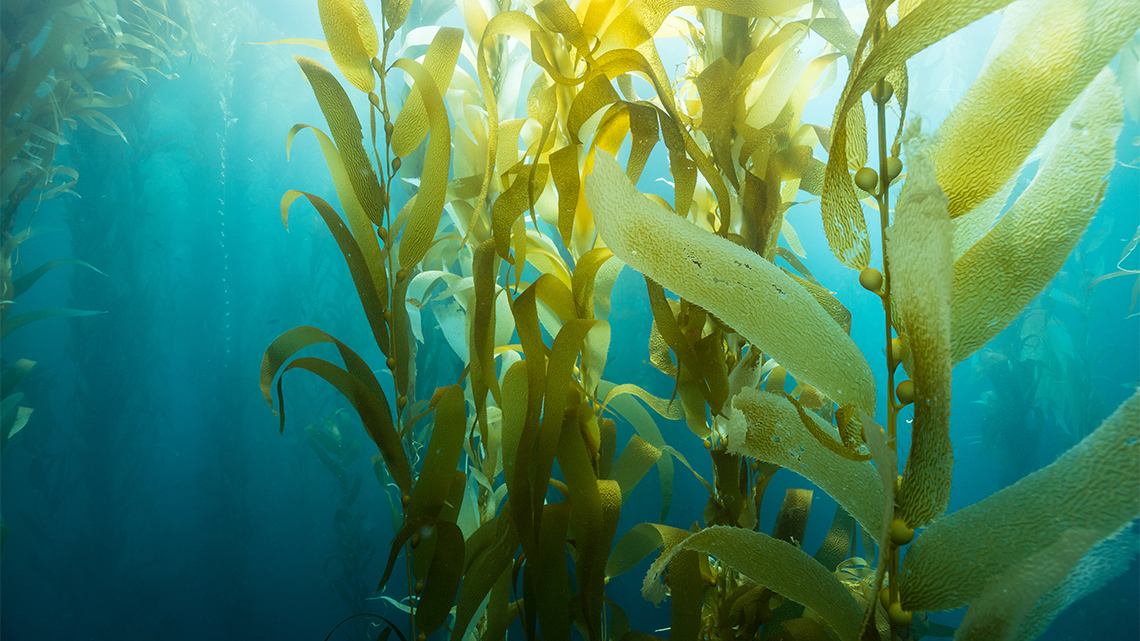
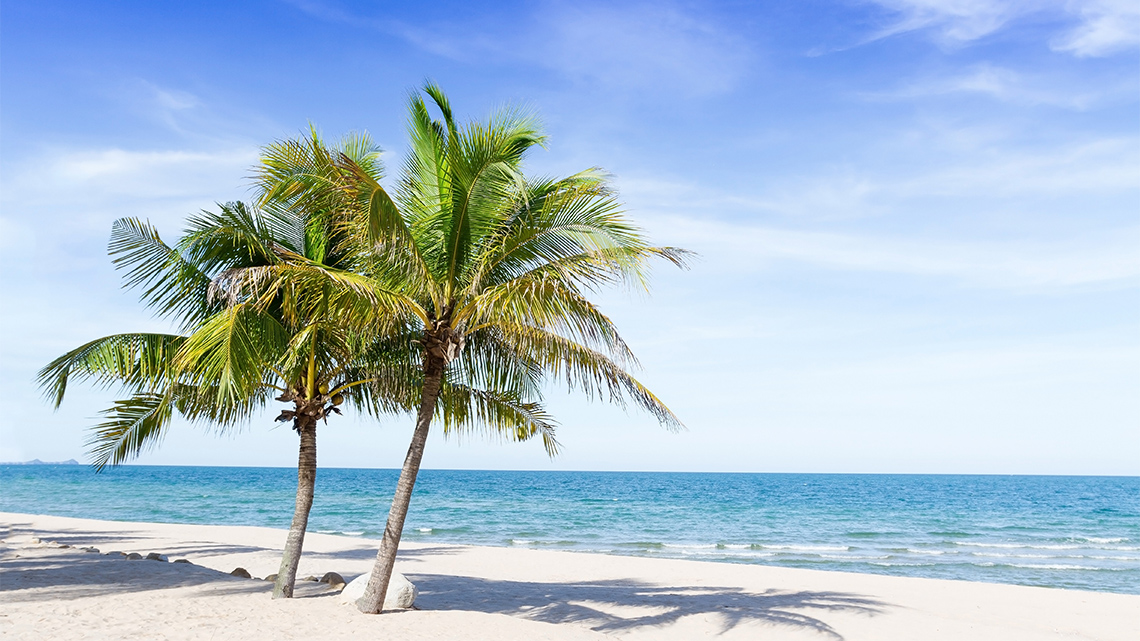
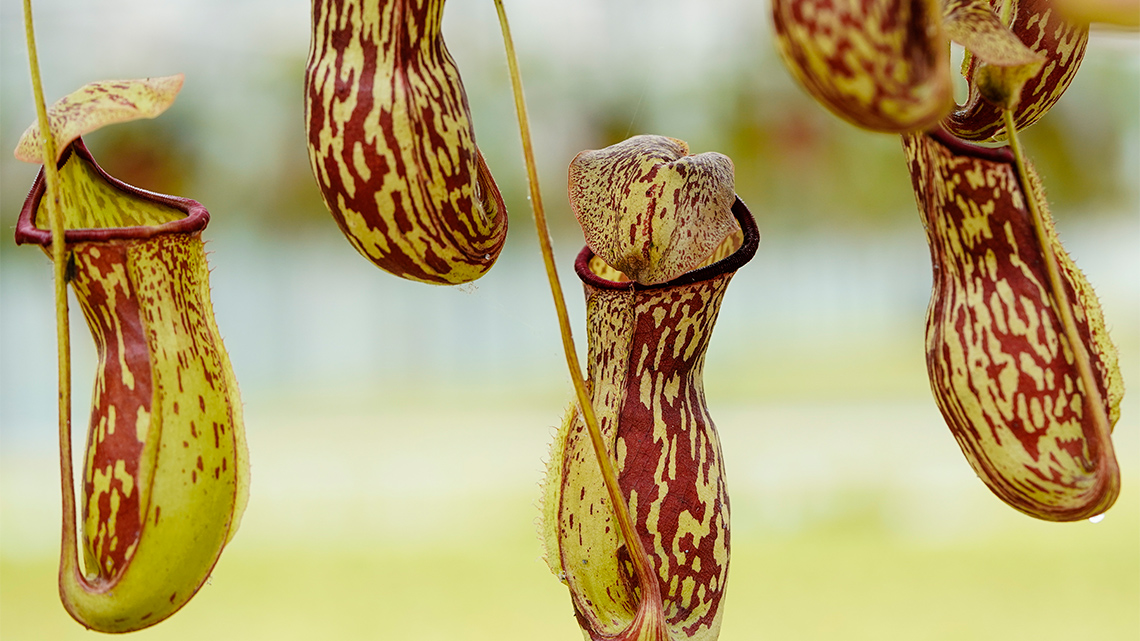
Check out the following images to learn more about plant adaptations:
Plants truly come in all different shapes and sizes.
Can you think of any other adaptations a leaf or plant might have that helps it survive?
Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
Adapting to seasons
Unlike animals, plants cannot get up and move around each time the season changes.
Many plants respond to the seasons in order to survive.
Explore the following image of the changing seasons, and think about how do plants change with each season?
Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
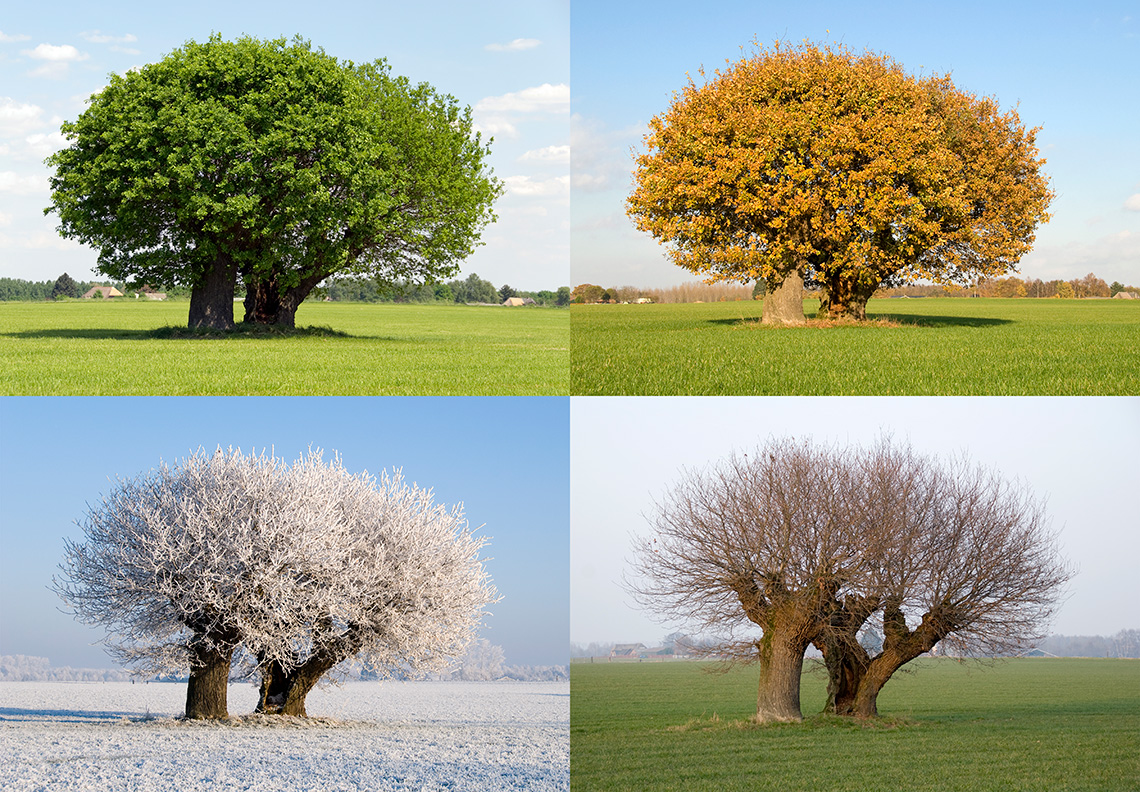

A tree changing during the four seasons. The spring tree is growing green leaves. The summer tree is very full of green leaves. The autumn tree has orange and brown leaves that are falling off. The winter tree has no leaves, and its branches are covered in snow.
Did You Know?
Did you know?
How do you think plants survive different seasons? What about winter?
Let’s explore the following three ways a plant can survive winter:
- Dormancy is when plants temporarily stop growing or grow very little during the winter months. The plants stop growing because there is a lack of sunlight needed to grow. Dormancy helps plants save the little water that they have during the winter months. For example, grass turns brown and “dead” during winter, but then turns green again once spring arrives.
- Losing leaves is another way plants adapt to survive the winter months. When they lose their leaves, it helps the plant save energy. Having less leaves means the plant doesn’t need to provide nutrients to those leaves anymore. They can now focus their energy on other areas they need to survive.
- Storing food is a third way plants survive the winter. Storing food helps a plant survive on stored nutrients when there is little sunlight during the winter months.
Adapting to environments
A habitat is a place where living things, including plants, live. Not all plants can survive in the same habitats.
Press the following tabs to access diverse habitats and plant adaptations.

Cactus
Desert plants receive very little water and plenty of sunlight, so they usually have special features of storing and conserving water.
An example of an adaptation are the spines and thorns that a cactus has instead of leaves. These plants are dormant for years until rain falls. The small roots absorb the water when it rains. The spikes protect a cactus from animals.

Grasslands
Grassland, also known as the prairies, have very hot summer and cold winters, and can be windy. Rainfall is sometimes high and sometimes low. The roots of grass go deep into the soil to absorb as much water as possible. They have narrow and soft stems to help them bend in the winter.

Tundra
The tundra is very cold, mostly covered in snow and ice, and does not get a lot of rain. An example of a tundra plant is moss. Moss does not need soil to grow. It has a hairy stem and small leaves that are very close together to help it survive.

Water lily
Living in water is not always easy, so plants need special adaptations to survive.
Sunlight cannot reach deep into the water. One example is the water lily, which has floating flowers and leaves on the water’s surface and roots that are underwater. This helps the plant get the sun and oxygen it needs to survive, along with the water at the root.
Let’s experiment!
The creative ways that plants will adapt to their surroundings may seem mysterious, but scientists can learn more about how adaptations work through conducting experiments.
Now, it is your turn! In the upcoming task, we will use the Scientific Experimentation Process to explore how a plant adapts to an environment with access to sunlight versus an environment without sunlight.
This activity will focus on the “Predict” and “Experiment” steps of this important scientific process.
Predicting is when you make a guess about what you think will happen in your experiment.

When you do an experiment, you are trying to find out the answers to the questions you asked.

Now, let’s explore the following experiment!
Safety
Before you explore the following experiment, let’s perform a safety check.
Hands-on Science
Plant adaptations
Let’s predict and observe how a plant adapts to an environment with no sunlight versus a plant in an environment with sunlight. If possible, try to perform the experiment over the course of several days.
Press ‘Hint’ to access how to make predictions.
Check out the following checklist to guide your predictions:
I can make a prediction by…
Press ‘Hint’ to access guidelines for making observations.
Check out the following checklist to guide your observations:
I can make and understand my observations by…
Now, let’s explore the science experiment! Be sure to record your predictions and observations in the following organizer or another method of your choice.
As you check out the following experiment, complete the Plant Investigation in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Check out the following images to access the experiment’s steps, and to learn more about how plants can adapt!
Press ‘Materials’ to explore the materials needed to perform the experiment yourself, if possible.
Materials:
- two glass jars
- soil
- plant seeds
- water
- a space in the sun for the first jar
- a space in the shade for the second jar
After the experiment, be sure to record your observations and conclusions in the “Plant Investigation” organizer, or another method of your choice.
United Nations and zero hunger
Connecting to the world

The United Nations (UN) is a group of many countries from around the world that have come together to create a better future for people and the environment. They have created 17 goals called the Sustainable Development Goals.
This learning activity is connected to Goal #2 which is called Zero Hunger. This means that everyone should have access to safe and nutritious food. Nutritious food helps someone grow and gives them energy.
Using plants for food is one way that people all over the world can help each other access safe and nutritious food.
The desert
During the Minds On section of this learning activity, we explored images of the Sahara Desert in Algeria. As you may have brainstormed, many crops are hard to grow in the Sahara Desert due to the extreme heat, wind, and sandstorms.
Plant adaptations in this kind of environment are extremely important!
In connection with the United Nations goal, Zero Hunger, Taleb Brahim and the World Food Programme have been working with people living in Algeria to grow barley in the desert in a unique way.

Barley plants
This is the process of growing plants in sand, gravel, or liquid, with added nutrients, but without soil. With hydroponics, barley is able to get the nutrients from sources other than soil and they require much less water.
Hydroponics helps with UN Goal #2 Zero Hunger, because the barley can be fed to the farm animals, which improves their meat and milk production. This results in providing higher quality food to people. The hydroponic units are also powered by solar energy, making them environmentally friendly. This is one example of how plants have adapted to be successful in new growing conditions!
Consolidation
Review your learning

Let’s describe three different plant adaptations that you learned about today.
These can be natural plant adaptations that happen in the environment, or adaptations that humans use to help grow food.
Use the following questions to guide your thinking:
- What is different about the plant or its environment that helps it adapt?
- Why does the plant have to adapt?
- How does the plant adapt?
Record your ideas in a notebook or another method of your choice.
Create a plant
Let’s create a plant!
- Choose one of the habitats that we explored throughout the learning activity.
- Create a plant that features at least one adaptation for that habitat, so that it would be able to provide food.
As a challenge, add more than one adaptation to your plant!
- Be sure to include a detailed description of the adaptation and explain how your chosen adaptation helps your plant to survive and provide food to help with the UN Goal “Zero Hunger.”
Complete the Create Your Own Plant Activity graphic organizer in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
| Create Your Own Plant Activity |
|---|
|
Create a plant for one of the following habitats:
|
|
What is your plant’s adaptation? Create a detailed description/illustration. Explain how your chosen adaptation helps your plant to survive. |
| Does your plant have a second adaptation? |
| How will your plant be adapted to provide food? |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Create Your Own Plant Activity.
Reflection
How do you feel about what you have learned in this activity? Which of the next four sentences best matches how you are feeling about your learning? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas about your feelings using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.