Minds On
How does technology help?
Explore the following carousel of images.
What do you notice about each example? What do you wonder?
What do all these examples have in common?
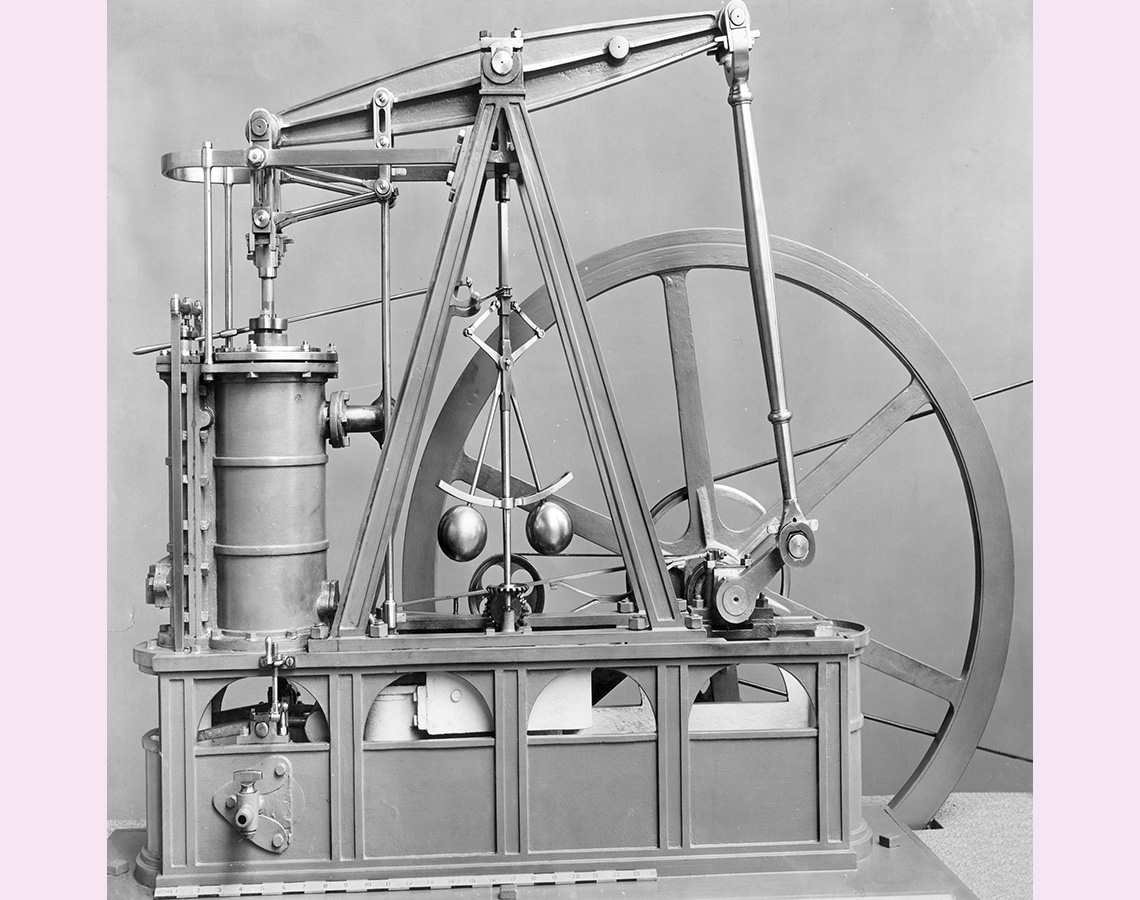
DescriptionImage 1: Historical photograph of a steam engine device. There is a large wheel beside a metal base. On the base is a tall T-shaped metal structure with two vertical arms on either end that go up and down. The one arm is attached to a cylindrical compartment with a lid that opens when the arm goes up. The arm on the other end is attached to a crank that turns the wheel when the arm goes down.
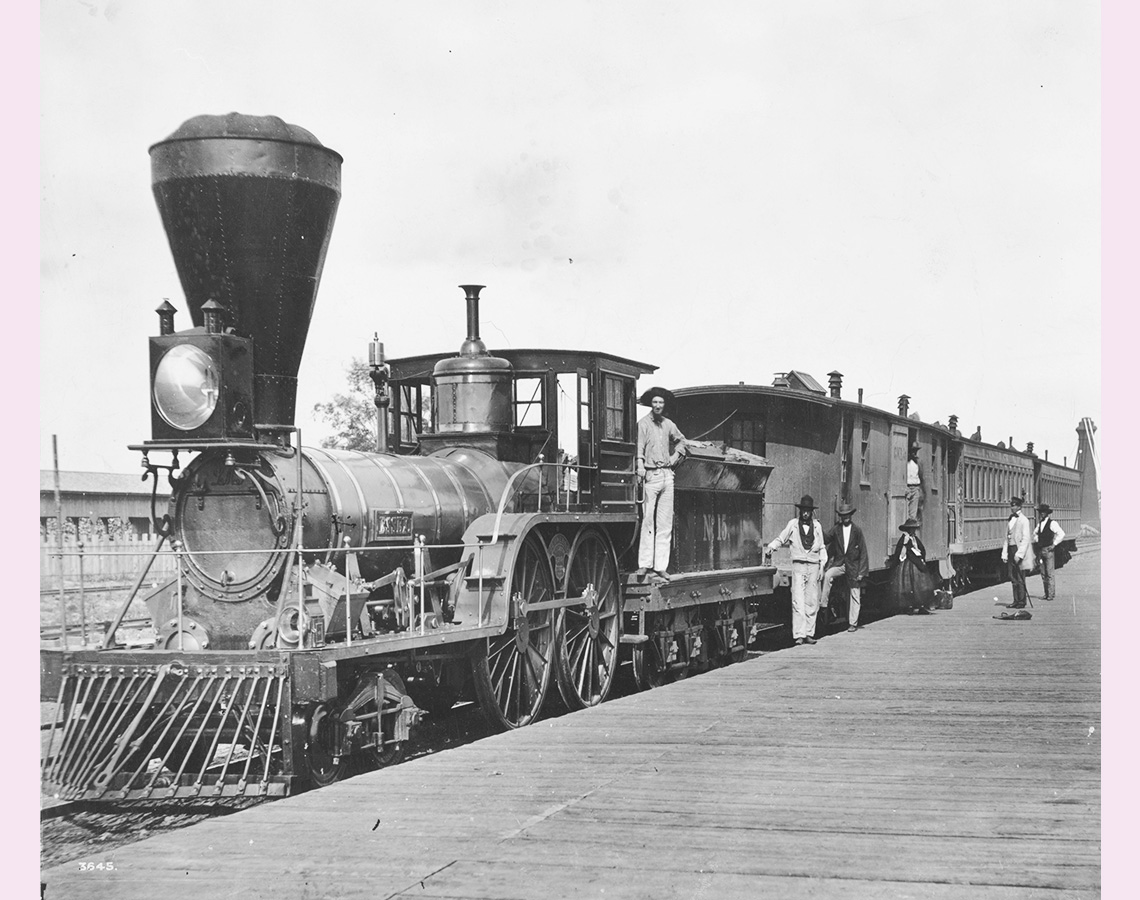
Image 2: A old locomotive train at a train station in 1859. The train has a large smoke stack on the front of the engine.
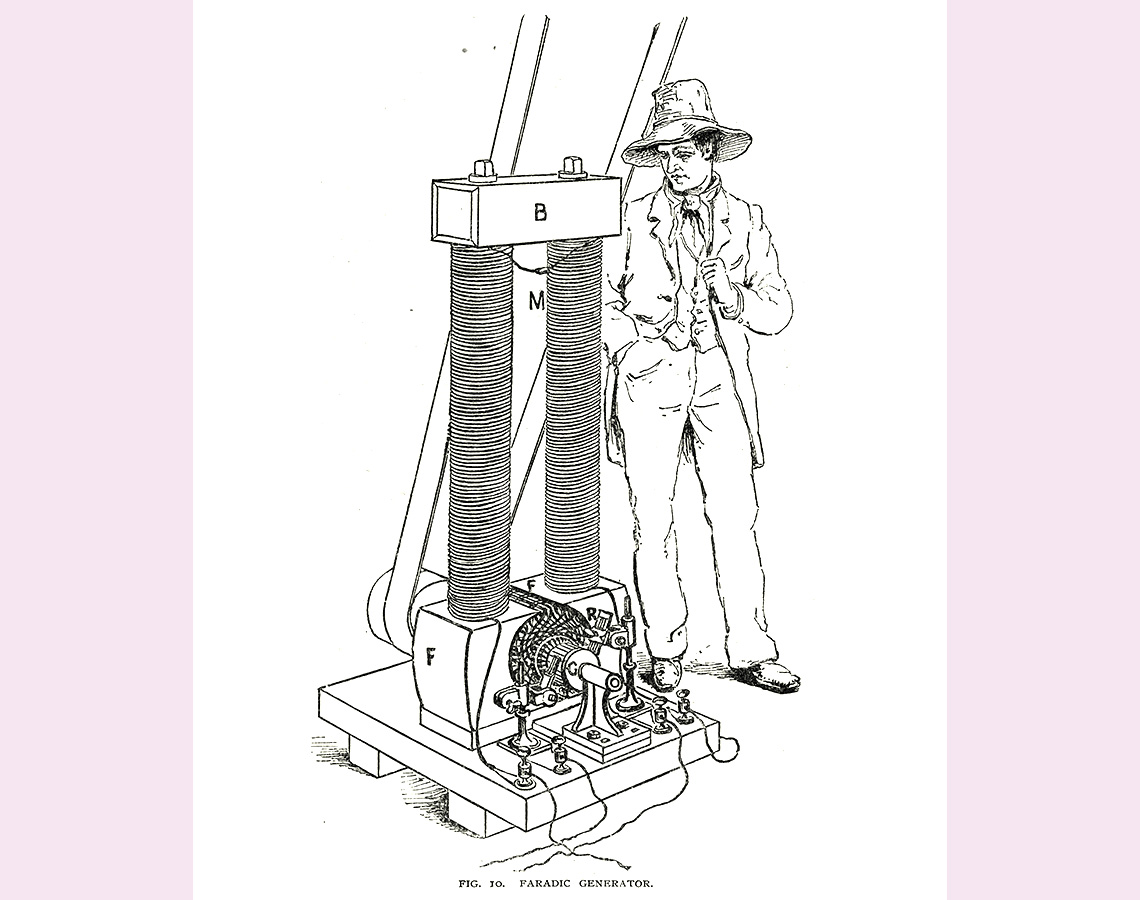
Image 3: An illustration of an electric generator. There is a rectangular prism base with a small metal mechanical box on top. On one side of this mechanical box is a cylindrical piece with a long belt wrapped around the bottom and then around an unknown object above the image. On the opposite side of this box is a crank and handle that extends into the machine. On top of this box are two long wires coiled into long cylinders attached to the base.
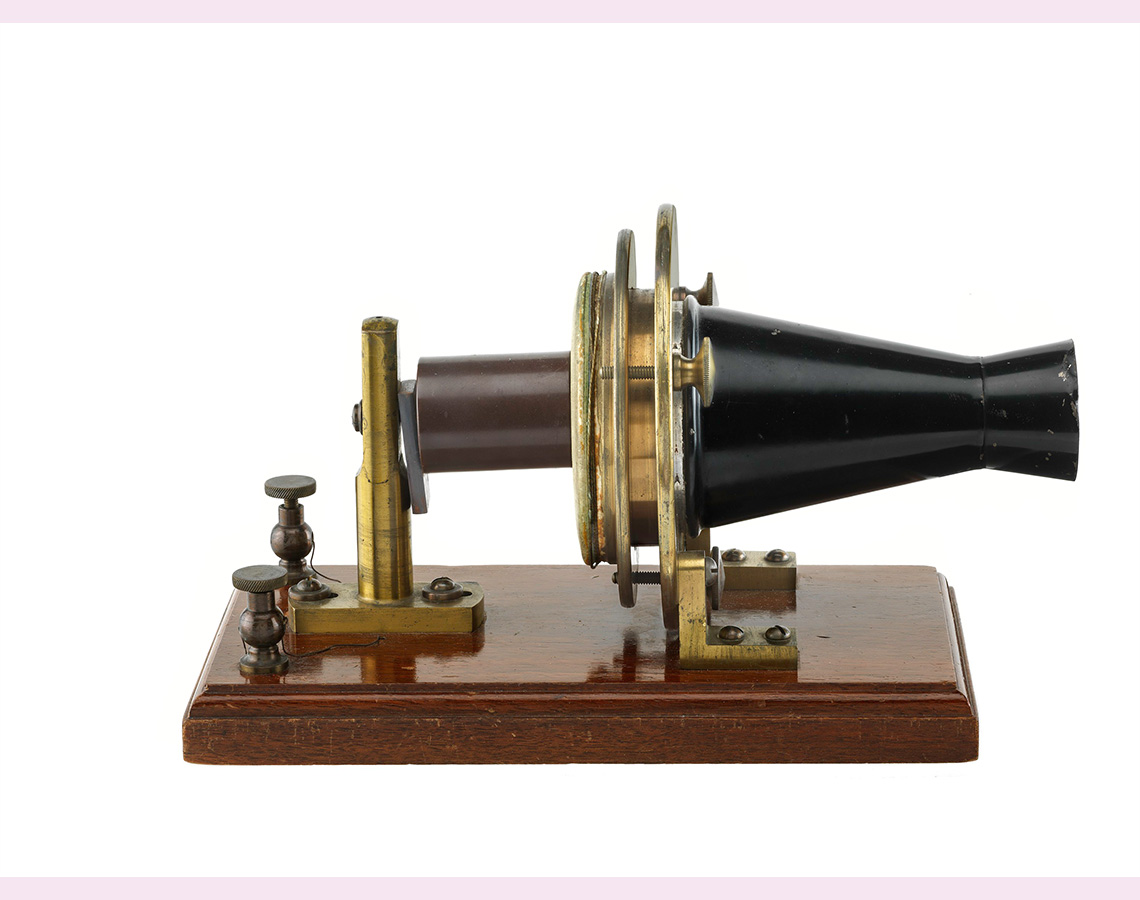
Image 4: Photograph of the first telephone. There is a rectangular base. Attached to the top of this base is a cylindrical mouthpiece with a wire attached. The wire is connected to two screws attached to the base.
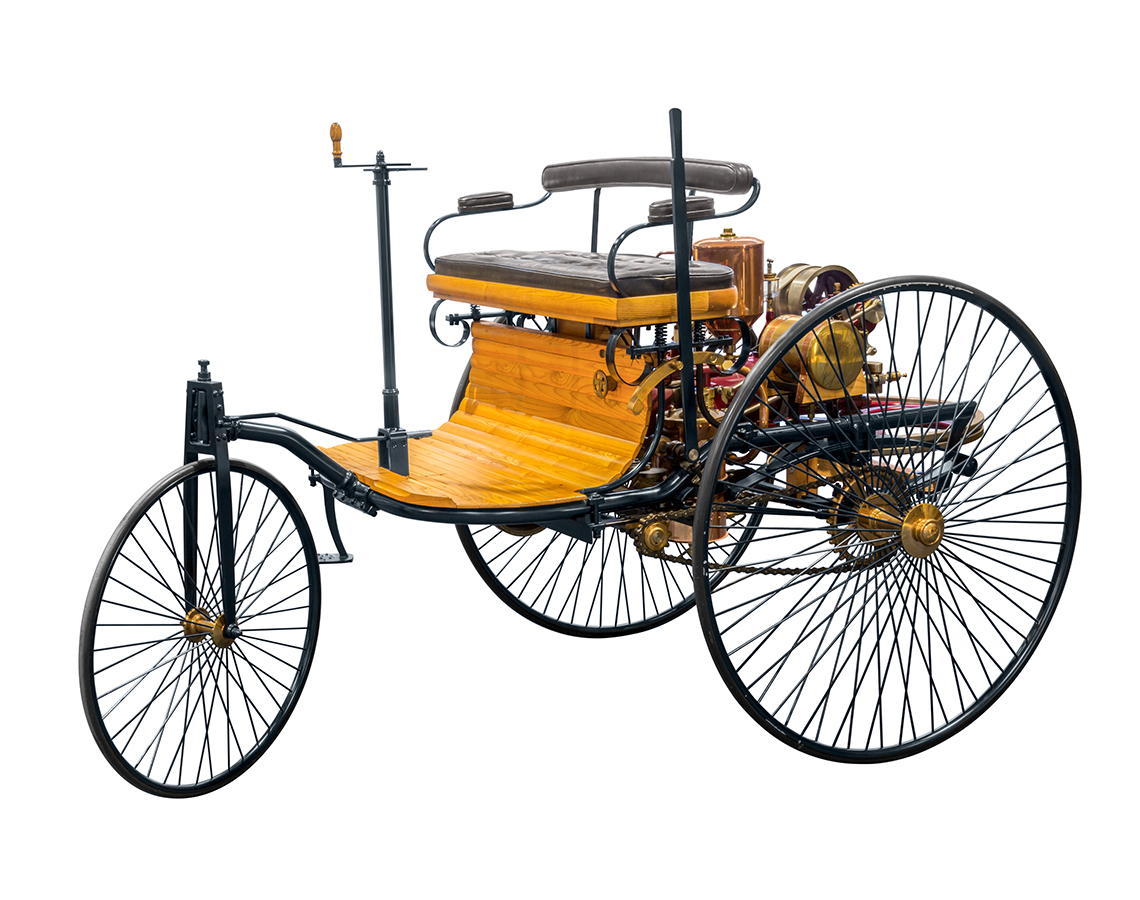
Image 5: Photograph of the first gas powered car. There are two large back wheels and one small front wheel. The wooden base between the front and back wheels has a lower piece for resting feet. There is a crank attached to this base with a long pole with the crank on top that is found in front of the single seat area. The motor is a series of metal cylinders that are found behind the seat.
Action
World-changing technology
In the Minds On, you explored examples of early technology.
In the late 18th and early 19th century many types of machines were invented to help with labour (work), transportation, and communication.
Let’s revisit the examples of early technology explored in the Minds On section.
Air pollution
While technology has many benefits, there are also downsides. When early technology was created, more and more natural resources were used.
Coal was burned to power the steam engine. This process created greenhouse gas emissions. Electric generators released chemicals and other pollutants into the air and waterways. Factories that manufactured early telephones created air pollution.
Based on the information in the following infographic, what are some of effects of air pollution on human beings?
How might air pollution affect a person’s daily life?
 Description
Description
An air pollution infographic. The reasons for air pollution are listed as: car exhaust, industrial facilities, agriculture, household and industrial waste, radioactive objects. The health effects of air pollution are listed as lung diseases, heart disease, nasal irritation, headache, nausea, and dizziness.
Global connection

The United Nations (UN) is a group of many countries from around the world that have come together to create a better future for people and the environment. They have created 17 goals called the Sustainable Development Goals.
This learning activity is connected to Goal #12: Responsible Consumption and Production. This means everyone should ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. Sustainable consumption and production will ensure efficiency, economic growth, and help the environment.
Modern technology
When someone has a new idea, and it improves what already exists, they have created an innovation. Consider the previous images and descriptions of early technology. What innovations have been made in each area:
- electricity
- transportation
- communication
What do you think are some of the benefits of modern technology? How does modern technology affect human health?
Choose one of the examples for each category of technology in the sections below. Using the information shared, identify the positive and negative effects of each example.
Complete the Positive and Negative Effects chart in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
|
Technological innovation: (Blank) (Blank) |
|
|---|---|
|
Positive Effects |
Negative Effects |
| What are some possible affects of this technology on human health? (use the diagram above to help you) |
|
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Positive and Negative Effects.
Electricity
The creation of electric generators led to multiple ways to generate electricity. This includes hydroelectric, wind, thermal, and solar power generation.
Press the following tabs to learn about the different ways to generate electricity.
Most hydroelectric stations use the natural drop of a river, like waterfalls, rapids, or a dam built across a river to provide the change in height needed to produce kinetic energy (energy of movement).
- Water is collected in the reservoir, then channeled into a pipe called a penstock that carries the water down to the turbine.
- As the water flows down the penstock, the water pressure increases.
- This pressure causes the turbine to spin, which in turn spins a generator.

Hydroelectric plants produce almost no greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide) but construction may have required flooding of land and disruption of animal and human homes.
Wind turbines work much like hydroelectric stations. Instead of moving water, they use wind energy (energy of moving air) to create kinetic energy. Wind causes the turbine to spin, which is connected via gears to a generator. Wind turbines need to run a long time to produce electricity. In order produce large amounts of electricity, many wind turbines are required.
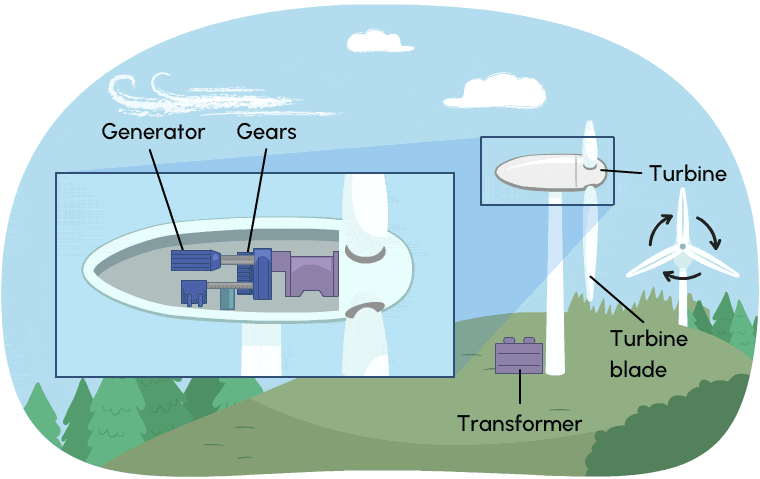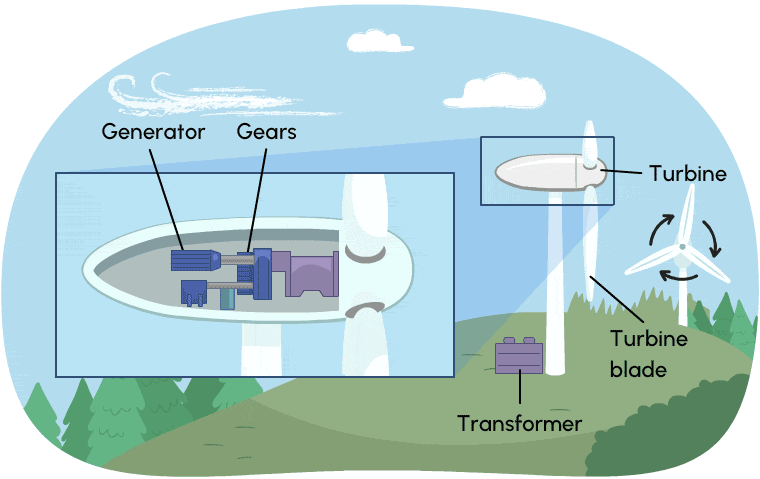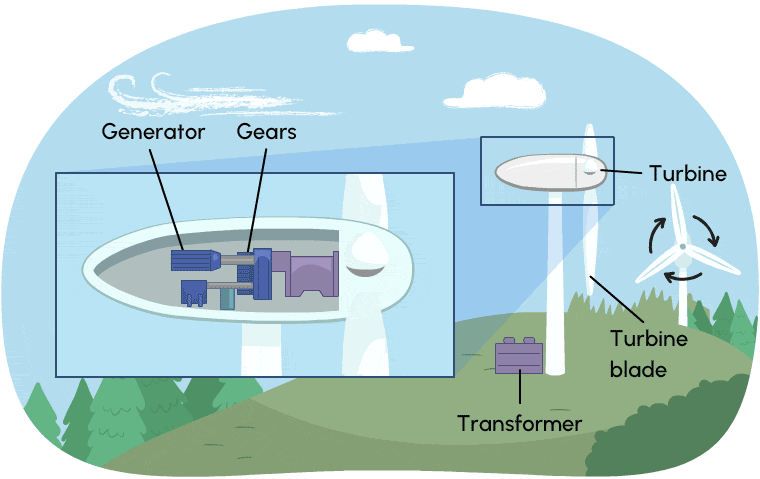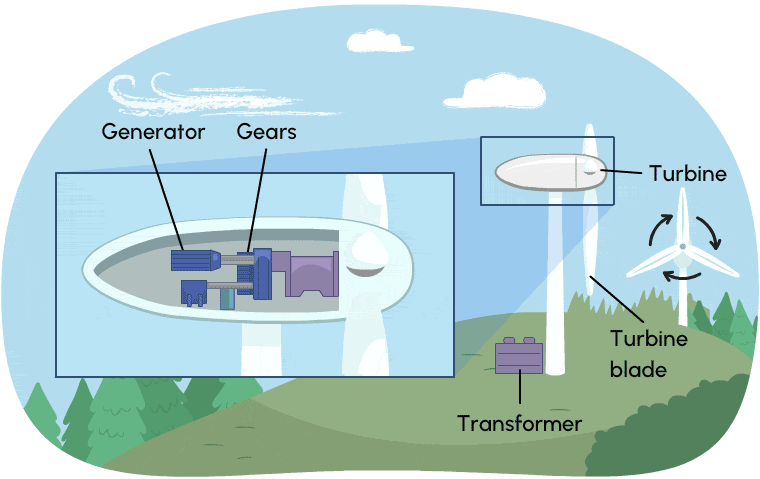
Wind turbines produce almost no greenhouse gases, but they require large amounts of land which can affect natural habitats.
Thermal generating stations use steam to spin their turbines. To create the steam, water is heated in boiler tubes that surround a large industrial furnace that burns coal, oil, or natural gas, depending on the type of generating station.
The steam is then transferred under pressure to the turbine, causing the turbine to spin and in turn, spin the generator.
The steam from the turbine condenses back to a liquid using cooling water from a lake, and is pumped back to the boiler, where it is reheated to continue the process.
 Description
Description
Thermal generating stations use steam to spin their turbines. To create the steam, water is heated in boiler tubes that surround a large industrial furnace that burns coal, oil, or natural gas, depending on the type of generating station.
The steam is then transferred under pressure to the turbine, causing the turbine to spin and in turn, spin the generator.
The steam from the turbine condenses back to a liquid using cooling water from a lake, and is pumped back to the boiler, where it is reheated to continue the process.
Unlike other fuels, uranium is not burned. Uranium atoms release large amounts of heat through a process called fission (splitting of atoms).
Instead of burning coal, oil, or natural gas, Canada’s CANDU nuclear reactors use the fission of natural uranium (a radioactive metallic element) to convert nuclear energy (energy that holds the nucleus together in an atom) into kinetic energy.
In a CANDU reactor, the fission process heats up heavy water (water with hydrogen replaced by one of its isotopes called deuterium), which in turn heats up ordinary water in a boiler. The steam is piped over to the turbine hall, where it drives the huge turbine and generator that produces the electricity we use.

In a CANDU reactor, the fission process heats up heavy water (water with hydrogen replaced by one of its isotopes called deuterium, which in turn heats up ordinary water in a boiler. The steam is piped over to the turbine hall, where it drives the huge turbine and generator that produces the electricity we use.
Nuclear plants produce almost no greenhouse gases, but it is still not clear how nuclear fuel disposal affects the environment.
A solar farm is a large collection of photovoltaic (PV) solar panels that absorb energy from the sun, convert it into electricity and send that electricity to a power grid for distribution.
The panels at solar farms are usually mounted to the ground instead of rooftops and come in all shapes and sizes. Large scale solar farms consist of hundreds of thousands of solar panels that absorb energy from the sun, generate an electric current, and distribute that power on high-voltage power lines.
The electricity travels along those power lines to an electricity grid, eventually making its way to homes.
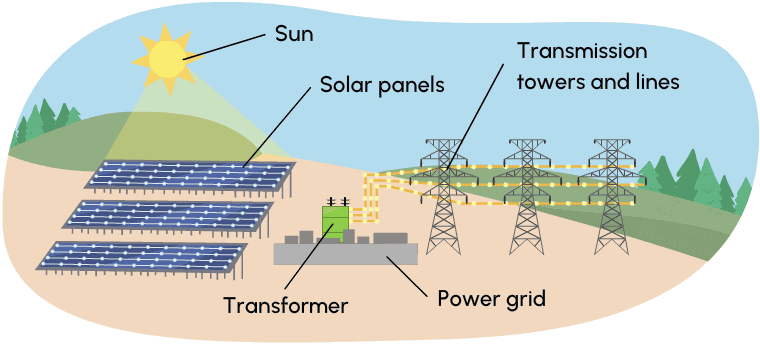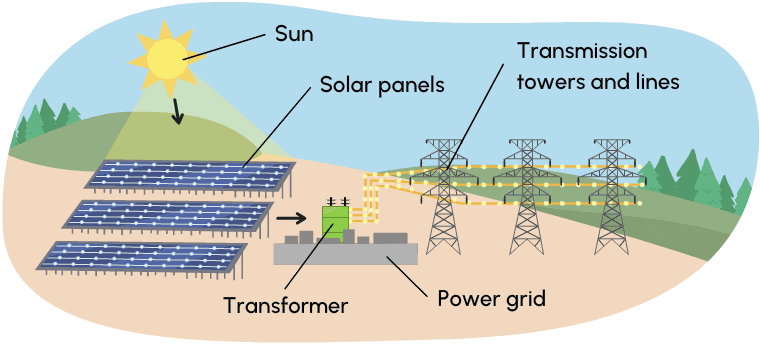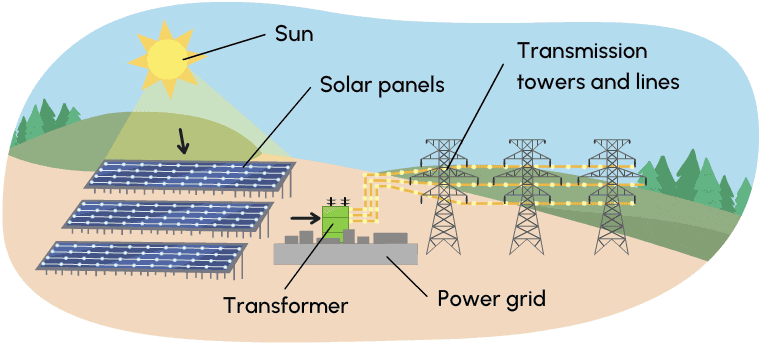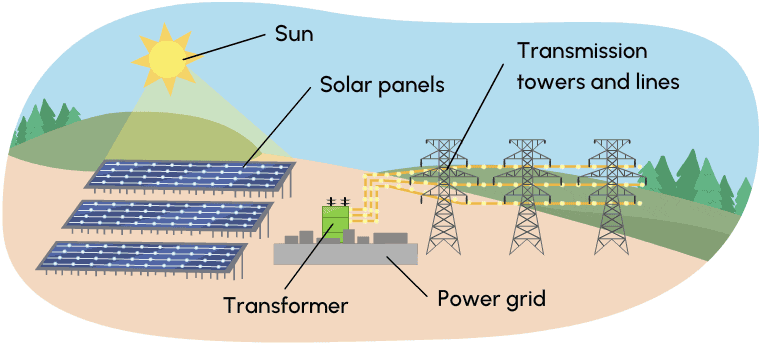
Solar farms are expensive to set up, and difficult to change, or move, once created. Since they are dependent on sunlight, they can be unreliable in the amount of power generated over long periods of time. Recycling of solar panels is also limited.

An electrician is a skilled trades professional who specializes in electrical wiring of buildings, stationary machines, and different types of equipment. Electricians work to install new electrical parts and to fix and maintain existing electrical parts and systems. Some electricians might also have a background in wiring ships, airplanes, and cable lines.
What other jobs could there be which relate to power generation?
Transportation
The development of electric power and the gas-powered engine has led to all kinds of innovations in transportation.
Press the following tabs to explore different kinds of innovations in transportation.
After Carl Benz completed the first gas-powered car, many innovations have been made to car design.
Self-starter:In 1911, the electric self-starter was invented and patented in 1915 by Charles Kettering. Before the electric engine starter motor was created, the engine had to be started by hand with a big crank which was quite physical and dangerous.
Materials: The materials for the body of the car were made of natural fibres. Modern cars are created using aluminum and plastics.
Safety: Seat belts, airbags and automatic locks have improved safety in all cars.
Electric power: Hybrid vehicles are a blend of internal combustion engines used in a gas-powered car, as well as electric power.
Electric vehicles work using electric power which is stored in batteries. Electric cars do not release any pollutants, but they do need to charge regularly at a charging station in order to work.


Over time, diesel engines replaced steam to power trains. Railroads have developed technologies that allow them to transport passengers over long distances at much higher speeds than the original steam engine.
In addition, there are high-speed trains in some parts of Europe and East Asia where passengers can reach far destinations in a few hours.
 Description
Description
Using a car on average emits one-hundred-and-seventy grams of carbon dioxide per kilometre per person. Using a bus on average emits one-hundred-and-eighteen grams of carbon dioxide per kilometre per person. Using a train on average emits forty-five grams of carbon dioxide per kilometre per person. Walking or biking emits zero grams of carbon dioxide per kilometre per person.
Fossil fuels and coal are burned to generate electricity and to power many modern trains. This process releases chemicals and toxins into the atmosphere. These harmful chemicals are breathed in by humans and animals and are harmful to their health over long periods of time.

An automotive technician is a skilled trades professional who fixes, examines, and works to maintain vehicles. They perform inspections, identifying any area that requires repairs, running tests and replacing any damaged or old parts. They must have a strong understanding of vehicle and road safety rules and record each step they take to complete repairs.
What other jobs can you think of in the area of transportation?
Communication
There have been many innovations made in communication since Alexander Graham Bell invented and patented the first working telephone in 1876.
Press the following tabs to learn about different innovations in communication.

To create a mobile phone:
- Raw materials are extracted from the earth to create each part of a mobile phone. These materials such as crude oil and copper are processed to create plastic parts, fiberglass sheets and copper wiring. The processes of extracting raw materials from the earth and making those materials into usable parts for the cell phone can release pollutants into the air which affect humans, animals and the environment.
- Next, plastics and fiberglass are used to create the circuit board base while the circuit and wires are made using copper and added with glues and a protective coating.
- Phone screens are manufactured by creating layers of liquid crystal between layers of glass or plastic. Batteries are made from different types of metals.

Telecommunication systems include the telephone wires, cables, satellites, mobile technology etc. which allow us to send messages using electricity. While early technology telecommunication systems included telegraphs, telephones and radio, modern telecommunication systems include telephone, radio, television, computers, internet etc.

Line workers are skilled trades professionals who install or repair electrical power systems and telecommunication cables. This can involve:
- inspecting and testing power lines
- stringing power lines between poles towers and buildings
- operating power equipment when installing and fixing poles, towers and lines
- laying underground cable
- installing aerial (overhead) cables over lakes and across rivers
- setting up service for customers
What other jobs might there be in the area of telecommunications?
Consolidation
Let’s reflect!

All of the technologies we use have benefits and drawbacks associated with them. Responsible use of technology can help us to address the negative impacts and protect our planet.
Consider what you have learned and respond to the following questions. You may record your ideas using a method of your choice. Share your thoughts with a partner, if possible.
- How have different types of technology changed or evolved over time?
- Why is it important to know the positive and negative impacts of technology, including the affects on human health?
- What is an example of how technology can have a harmful impact on human life?
- What might be some of the skills needed for a skilled trades professional highlighted in each area of technology? Why do you think this professional is necessary for this area of technology?
- Describe the biggest surprise about the impacts of technology on human health. Why was this a surprise?
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.