Minds On
Our changing planet
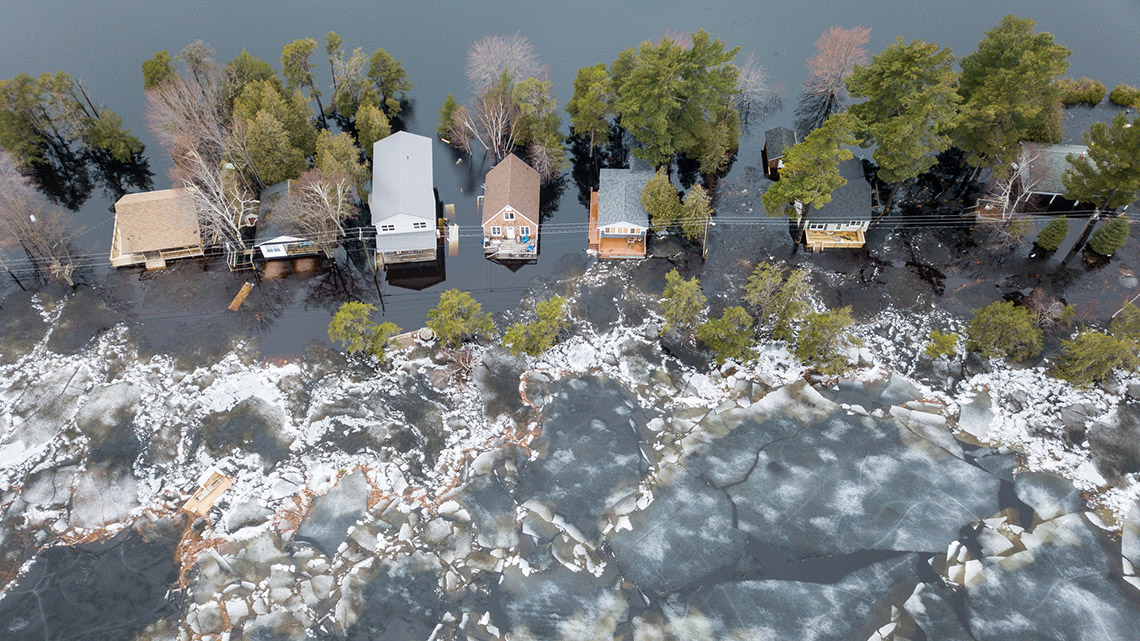
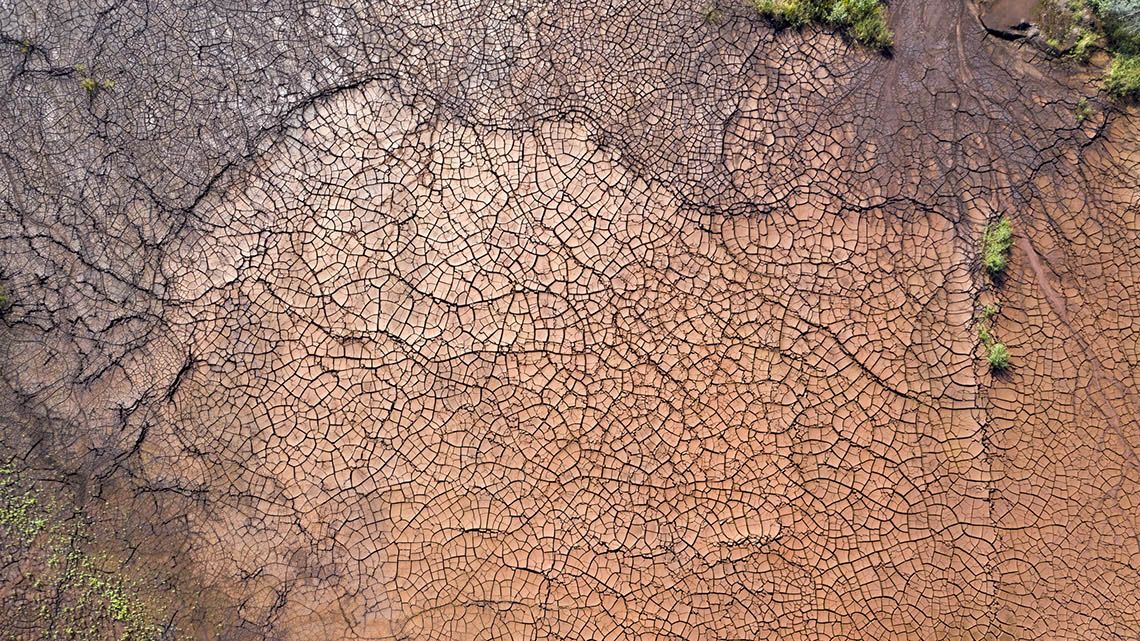
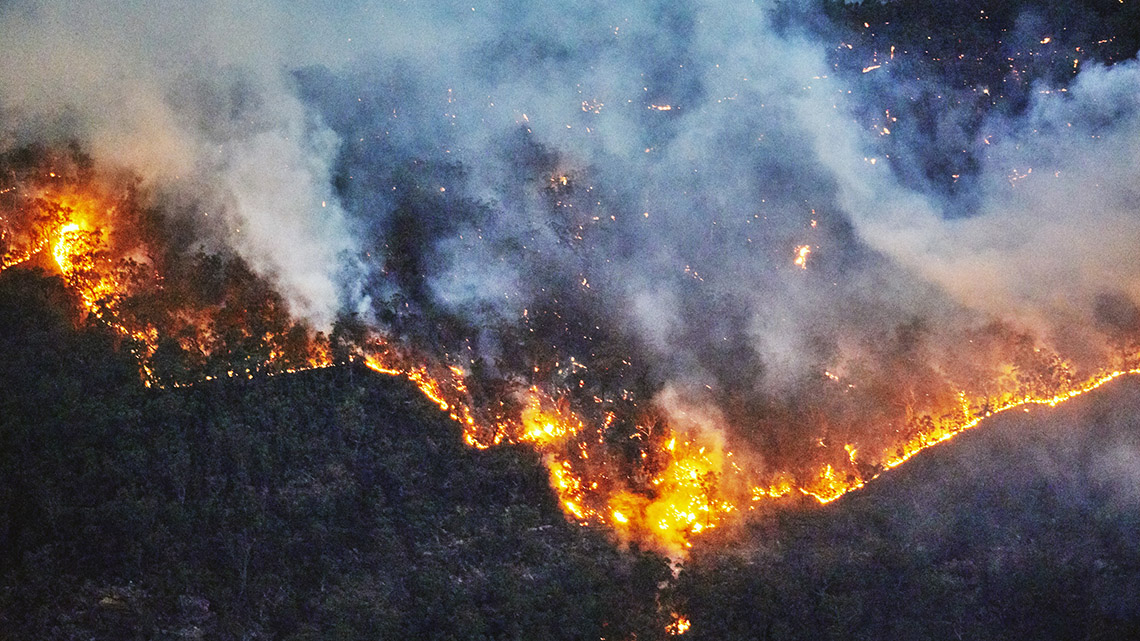
The following images were taken using drone technology. Explore the images and their descriptions and record what you observe and what you wonder about each image using a method of your choice such as in print, digitally or with an audio recording.
The images demonstrate some of the effects that a rapidly changing climate has already had on our planet, such as rising water levels leading to flooding, forest fires, and drought.
Brainstorm
Brainstorm
How do you think these effects of climate change would impact the diversity of life that exists in each of the locations impacted? What impact would this have on the ecosystem of our planet on the whole?
Record your thinking using a method of your choice. If possible, share your ideas with a partner.
Press ‘Learn More’ to access some additional information on the meaning of the diversity of life on our planet.
There are many different forms of life that exist on planet Earth. We call this biodiversity.
The term ‘bio’ refers to living things and ‘diversity’, in this instance, means variety or many differences. When we put the two terms together, biodiversity refers to the many different forms of life on our planet, the varied and unique habitats and ecosystems, and how it is all connected, either directly or indirectly.
Action
Global connection

The United Nations (UN) is a group of many countries from around the world that have come together to create a better future for people and the environment. They have created 17 goals called the Sustainable Development Goals.
This learning activity is connected to Goal #13: Climate Action. This means everyone should help reduce climate change and its impact. Storms, disasters, and lack of food and water are made worse by climate change.
Exploring the effects of climate change

An illustration of the Earth with a big, bright sun shining down on it causing different effects of climate change to be visible on the planet: drought, forest fires, loss of habitat, more severe storms, rising ocean levels/melting ice caps, and animals being displaced from their habitat. Included is thermometer with the temperature rising to signify the rising temperature on the planet.
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in both temperature and weather patterns around the world. While these shifts are considered a natural process, human activities have speed up this process at an unprecedented rate and temperatures are rising faster than our environment can safely adjust and adapt to.
In this learning activity, we are going to focus our investigation on the following five effects of climate change as identified by the United Nations (n.d.):
- not enough food
- increased drought
- loss of species
- a warm, rising ocean
As you learn about these effects, your task is to record the causes and effects of these issues, focusing specifically on how they are impacting biodiversity on our planet.
Complete the Climate Change: Cause and Effect Chart in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Press the Activity button to access the Climate Change: Cause and Effect Chart.
Activity (Open PDF in a new tab)Press the following tabs to access more information on some of the effects of climate change, their causes and the impact on biodiversity on our planet.

There is a significant relationship between climate change, food production, and food security. As temperatures rise, there is an increase in extreme weather events, droughts, and floods, which affects fisheries, crop production, and livestock. As the ocean becomes warmer, it also becomes more acidic, which puts marine species that are a source of food at risk. There are also costal farmlands that are often flooded by saltwater, ruining the crops, because of the rising water levels.
An increase in temperature diminishes water supplies and grasslands that livestock rely on for grazing. Extreme storms are becoming more common, which can directly damage or drown crops. Rising temperatures also result in more droughts and water shortages, which causes less water for irrigation, making crops harder to grow. Heat waves are expected to become more frequent with climate change, making livestock and crops more vulnerable to disease.
The changes to the global food system are a primary driver of biodiversity loss, with agriculture alone being identified as a threat to species at risk of extinction. As the world works to produce more food at a lower cost to feed the growing population, land is being cleared to be used as farmland which creates a loss in biodiversity. Less biodiversity means food webs are put at risk, and ecosystems become unbalanced and could begin to collapse.

Warmer temperatures on our planet enhance evaporation, which reduces surface water and dries of out soil and vegetation, leading to drought. Climate change reduces water availability, making it harder to come by in some areas of the world, which directly affects many species. When drought occurs, some ecosystems dry up entirely, affecting the biodiversity in that area. Some species can adapt, but not all.
Extreme heat and dry conditions are also favourable for increased wildfires, which destroys habitats and causes a rapid loss of biodiversity.

The changes that climate change brings, such as rising temperatures, forest fires, extreme weather, invasive species, and disease are all among the threats that are impacting biodiversity and the loss of species both on land and in the ocean. The world is losing species at a rate that is 1000 times greater than any other time recorded in human history, and many species are at the risk of becoming extinct due to climate change. Species are forced to adapt to new climate patterns (changing rainfall, longer and warmer summers, etc.). Many species are forced to relocate away from less favourable climate conditions to new areas that will meet their needs.
Climate change also threatens ecosystems across the food chain. Species that are lowest on the food chain are often affected first, and this impacts the rest of the food chain and biodiversity in a specific area. Invasive species are among one of the main causes of biodiversity loss and species extinction, which are increased by climate change, as species migrate or move to new areas.

The ocean soaks up most of the heat from global warming due to its size and dark colour. As it absorbs the heat, the temperature of the ocean rises and so does the water level because of thermal expansion.
The ocean is also a natural absorber of carbon dioxide. Because of the burning of fossil fuels, there is excess carbon dioxide in our atmosphere than there is naturally. This, in turn, means the ocean becomes more acidic which endangers marine life such as feeding, development and breeding, as well as affecting the natural interactions between species.
Rising temperatures cause coral bleaching and the loss of breeding groups for marine fishes and mammals. Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients.
Now that you’ve finished your investigation, compare your ideas with some possible answers by accessing the following document titled Cause and Effect Answers.
|
Effect of climate change |
How is climate change causing this effect? |
Impacts on biodiversity |
|---|---|---|
|
Not enough food |
|
|
|
Increased drought |
|
|
|
Loss of species |
|
|
|
A warm, rising Ocean |
|
|
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Cause and Effect Answers.
Pause and Reflect
Pause and reflect
Consider the following questions. Record your thinking in your notebook or using another method of your choice.
How is climate change impacting the biodiversity of species both on land and in the ocean?
How are all the effects of climate change interconnected? (Hint: Think about the effects that you just investigated and how they impact each other and work in a cycle).
Exploring solutions with drones
There are many different effects of climate change that are impacting the environment and biodiversity. Innovative solutions are consistently being designed and engineered to help slow or reduce these effects and provide sustainable and reliable solutions. One of these innovative solutions are the use of drone technology.
Drones are flying robots that can be remotely controlled or flown using software-controlled flight plans and a GPS. Drones and satellites are able to measure biodiversity with their unique bird’s eye view of land. Drones are great tools for scientists studying the biodiversity in different ecosystems.

Drones are also used by farmers in several different ways to help crop production. Drones can view an entire field and help determine where the best place to plant crops are at any specific time. They can also plant seeds with precision and efficiency. Drones are equipped with technology that allows them to take clear images and help farmers spot any ruined crops, allowing them to act quickly to address the problem. Drones also help farmers determine where fields are drying out or pooling water to help prevent erosion and increase proper irrigation. Farmers can use drones to evenly water crops or spray them with fertilizer.
Explore this Climate Watch Shorts episode entitled “Farming in a Changing Climate” to learn more about how farmers in Ontario are evolving their methods to adapt to our changing climate.
Pause and Reflect
Pause and reflect
Consider the following questions. Record your thinking in your notebook or using another method of your choice.
According to the video, what are some of the opportunities and challenges that farmers are facing as a result of climate change?
How are farmers trying to develop more durable plants? (Hint: What is biocontrol?)
Press ‘Hint’ to access some possible answers to the questions asked.
The average temperature is increasing, which crops usually like, will mean a longer growing season. However, there is also a risk of drought and dry conditions which makes it difficult to grow some crops.
Biocontrol is a way to prevent pests from damaging crops, which makes a plant more resistant, and then less pesticides are needed. This helps protect against new pests that are introduced because of climate change.
Drones and biodiversity
Drones are also used to study, research, and help save biodiversity. They can be used to detect, manage, and combat wildfires. Wildfires highly impact the biodiversity of a forest. A drone can help firefighters tackle the wildfire and then also use ‘seed dropping’ as a method to restore the area afterwards. Afterwards, the drones can monitor the progress of the forest and its biodiversity. Drones are also used to study ocean biodiversity. Drones can fly above whales and capture their blow (sneezes) and use the data to gather information about species in the ocean. Even on land, drones can accurately monitor and detect small shifts in wildlife population and therefore conserve threatened and endangered species.
Did You Know?
Monitoring biodiversity with drones
The eelgrass meadows in Pacific Rim National Park, British Columbia, provide a habitat for various birds, mammals, fish, and invertebrates. This biodiversity of species works to lessen the effects of climate change by removing a large amount of carbon from the atmosphere, turning it into oxygen.
Explore this episode of Leo’s Fishheads entitled “Fish Talk With Leo” to learn more about the eelgrass meadows and how they are being monitored for biodiversity using drone technology.
Many other scientists and conservationists are using drone and other technologies to help get a bigger picture of larger areas to monitor the effects of climate change on biodiversity of various organisms.
Do you know of any other examples such as in Pacific Rim National Park?
Drones are also being used for other environmental tasks such as mechanical pollination. As a result of climate change, bee populations have been rapidly declining, and bees play a very important role in pollinating many of the worlds’ plants and crops. Drones are being used as an alternative crop pollinator. The pollen is taken from trees and flowers and goes through a purification process to prevent the spread of disease before being redistributed by a drone. This positively impacts food security and biodiversity of plants.
Another innovative use of drone technology is in the planting of trees by dropping seeds in areas impacted by natural devastation or deforestation.
Check out this video entitled “Tree-Planting Drones” to learn more about how drones are being used to restore biodiversity in areas of Australia previously devastated by wildfires.
Check your understanding
Check your understanding of effects of climate change and how drones are being used to help counteract the problems these effects are causing on our planet.
For each questions, select the correct answer, then press ‘Check Answer’ to see how you did.
Consolidation
Your turn

Task A
In this learning activity, you explored four major effects of climate change. Choose two of those effects and explain what is contributing to them and how they are impacting the environment, specifically the impacts on biodiversity. Explain your thinking using a method of your choice (i.e., paragraph, audio recording, poster board, slideshow, etc.).
Press ’Effects of Climate Change’ to access a list of the four major effects explored in this learning activity.
- not enough food
- increased drought
- loss of species
- a warm, rising ocean
Task B
You have been asked to create a presentation to younger students about how drones are being used to study biodiversity and as a solution to some of the effects of climate change. Your presentation should include the following information:
- a description of what drones are
- an explanation of how drones are being used to measure biodiversity and why this is important
- information on how drones are being used to lessen the effects of climate change (Hint: consider farming, forest fires, mechanical pollination, biodiversity)
To present your information to your young audience, you could create a brochure, a speech, a storybook, an infographic, or another method of your choice.
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.



