Minds On
The importance of soil
Explore the following carousel of images of soil. As you explore, record a list of reasons that you think soil is important using a method of your choice.
Press ‘Answers’ to compare your list to some possible answers.
Soil is important because it can…
- provide a habitat (home) for animals and other organisms (bugs, insects, etc.)
- provide a place to grow crops and food
- provide plants with water and nutrients
- stop flooding
- release and soak up gases
Changing the land
Now that you’ve brainstormed how important soil is to humans, animals, and environment, let’s think about how humans change soil over time.
The word “urbanization” means that many areas are becoming cities with lots of houses and buildings. This means that there is less farmland and small towns. When building a structure such as a home or planting a garden, people change or alter the soil.
- What do you think might happen to the environment or an animal’s habitat (home) if someone decides to build a community of 100 homes?
Record your ideas using a method of your choice. Think about the extra soil, the shape of the land, the animals and their homes, and even the air!
Urbanization
Explore and compare the two following photos. These photos are of the same place, taken many years apart before and after urbanization.
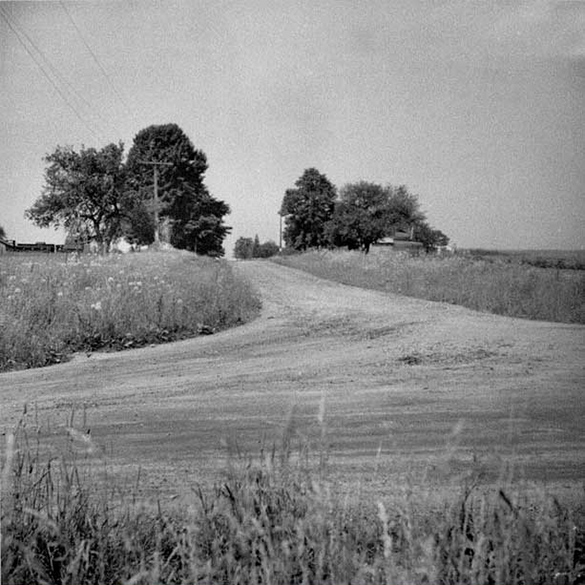

Before Urbanization

After Urbanization
Complete the Before and After Urbanization Table in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
|
Before and After Urbanization |
|
|---|---|
|
Record similarities and differences that you notice between the two previous images. |
|
|
Similarities |
Differences |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access the Before and After Urbanization Table.
Action
Erosion
Erosion is the process where different natural forces cause rocks and earth to wear away. Water, wind, and waves can all cause erosion. These forces also move bits of rock and earth to new places. Over time, this changes the shape of the land.
Press the following tabs to explore different ways that soil erosion can occur.
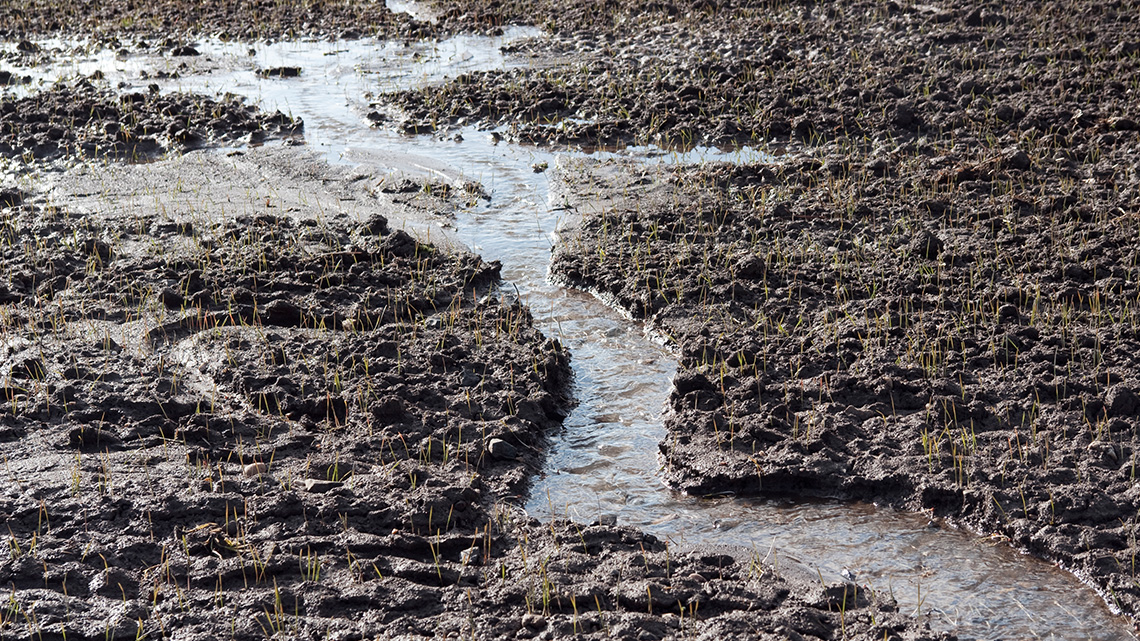
Rainfall can cause erosion. This happens when the rain hits the ground and when raindrops gather together then flow like a small stream.
If soil erodes, then crops won’t grow very well. Also, soil that is carried away can pollute water ways.

Wind erosion usually takes place in dry areas. Wind picks up and carries away loose pieces of soil and dust.
Wind erosion will usually carry away the top layer of soil and its nutrients, making it difficult to grow crops.
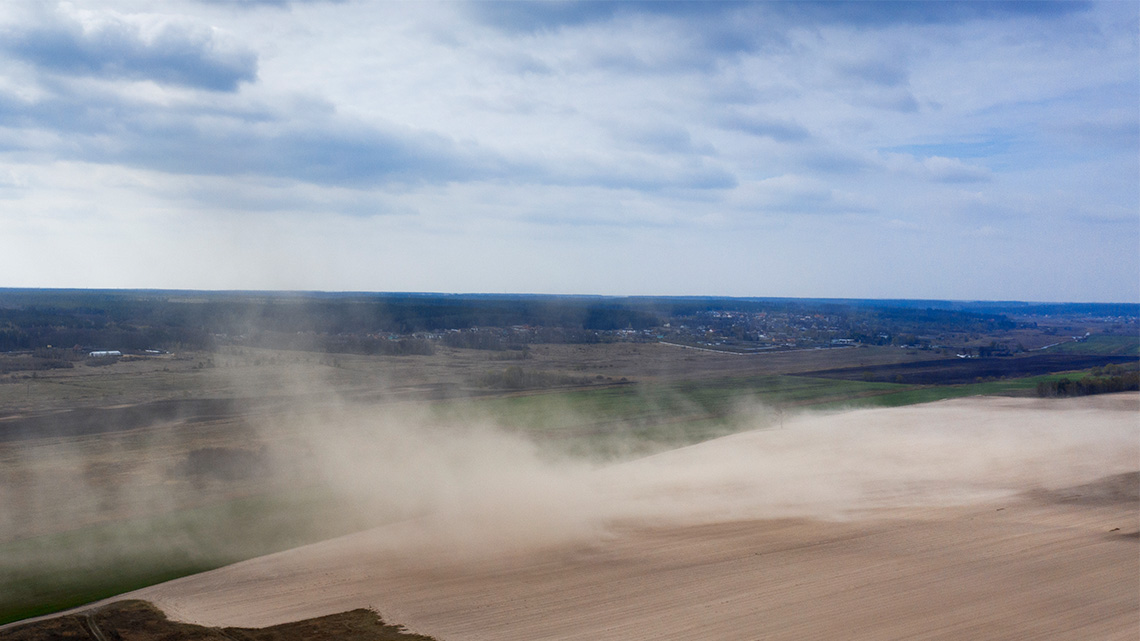

Similar to wind, waves also carry away small pieces of soil and carry it away. A wave can wash up onto a rock or soil and then carry away pieces as it flows back into the water.
Pause and Reflect
Erosion and soil
- What causes erosion?
- How does erosion impact soil?
Record your answers using a method of your choice.
Press ‘Answer’ to access possible answers.
Soil erosion can be caused by rain, wind, and waves.
Erosion makes it hard for crops to grow and for plants to get the nutrients they need from topsoil.
How humans impact the land
Humans can have both negative (bad) and positive (good) impacts on the land and animals around them. Creating new communities or taking apart old buildings impacts the environment.

Explore the following Mystery Files video entitled “The Mystery of the Shifting Shorelines” to learn more about different impacts that results from human actions.
Use information from the previous video to order the following events about the erosion of Toronto’s shoreline.
Explore another section of the Mystery Files video entitled “The Mystery of the Shifting Shorelines” and focus on how habitats are being impacted.
Pause and Reflect
Positive and negative impacts
- What is one positive (good) impact of building the Leslie Street spit?
- What is one negative (bad) impact of building the Leslie Street spit?
Press ‘Answer’ to access some possible answers.
Some of the positive impacts are:
- it gave a spot or created a habitat for wildlife species, like birds, turtles, and fish, to migrate to and live (wetlands)
- safe spot for families to enjoy the outdoors
Some of the negative impacts are:
- dumping unclean fill results in large chunks of concrete and metal from construction sites being dumped there, which can be dangerous for wildlife
- located close to an urban area, so roads and cars may be dangerous to animals trying to migrate there
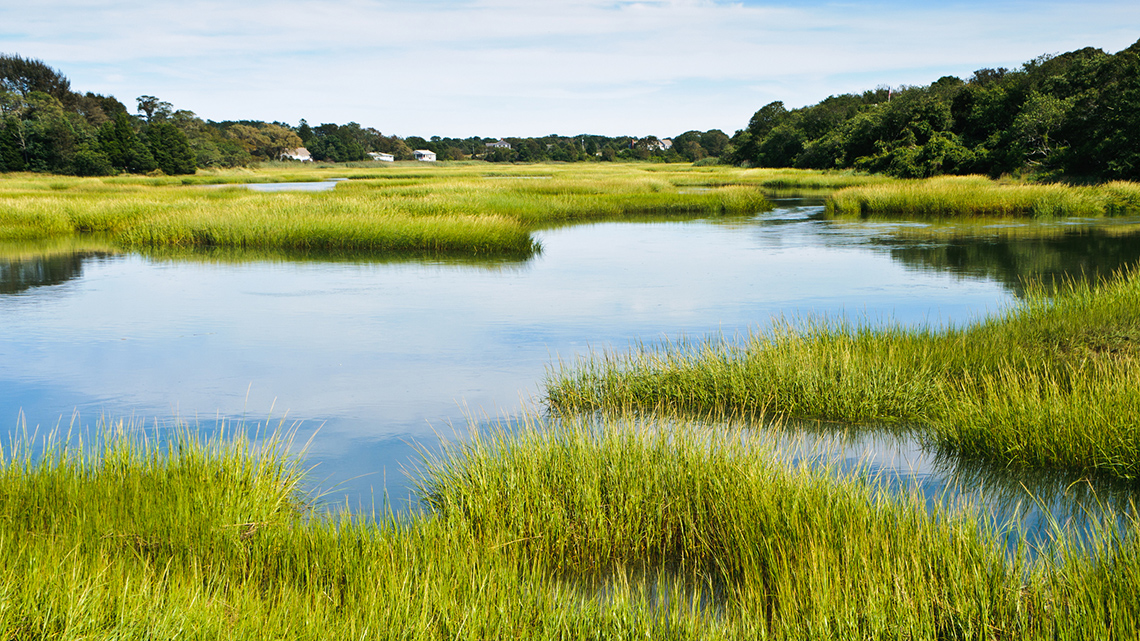
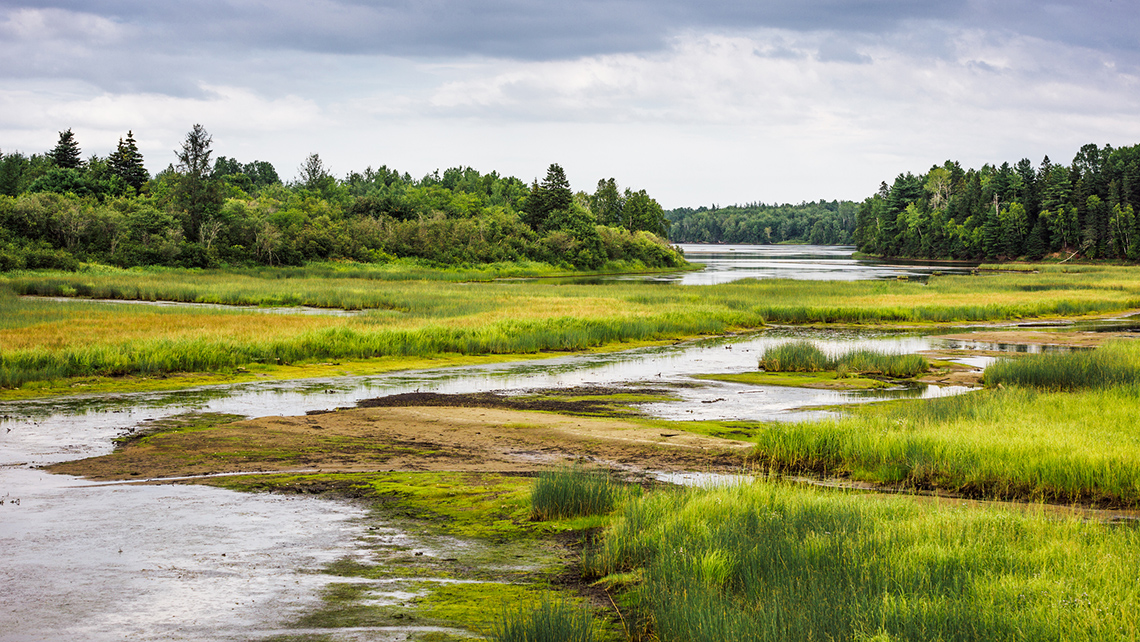
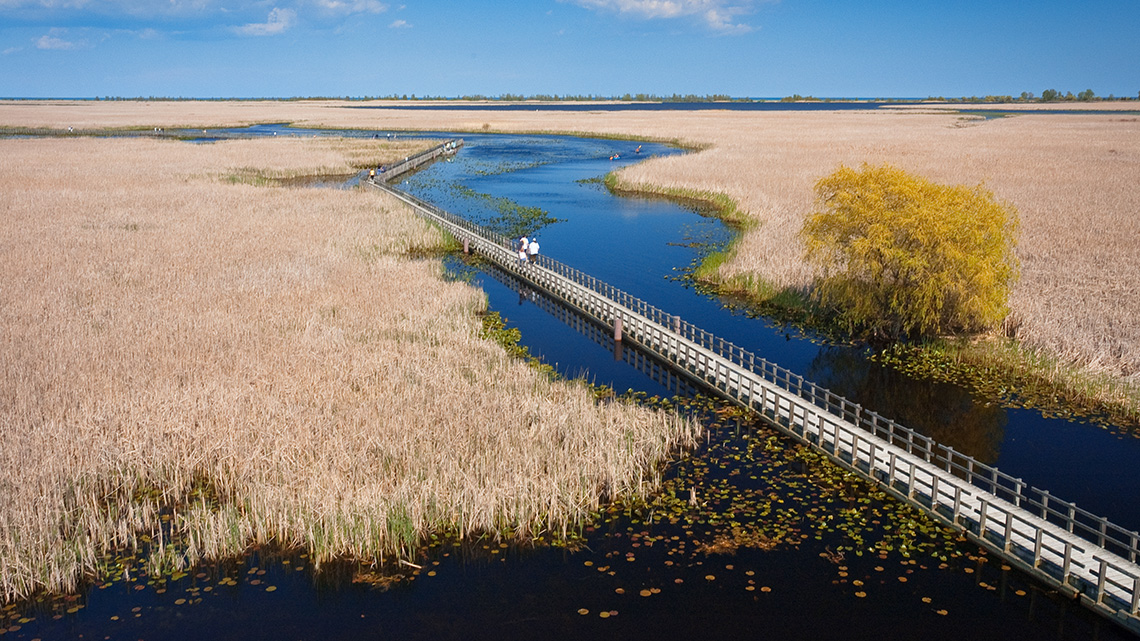
Wetlands
At the end of the last video, they were talking about wetlands that were being developed as a safe habitat for many plants and animals to live.
A wetland is a piece of land that humans have added water to. It is a low-lying ecosystem that is flooded by water to provide a habitat for plants and animals. You may also hear a wetland referred to as a marsh, swamp, or bog.
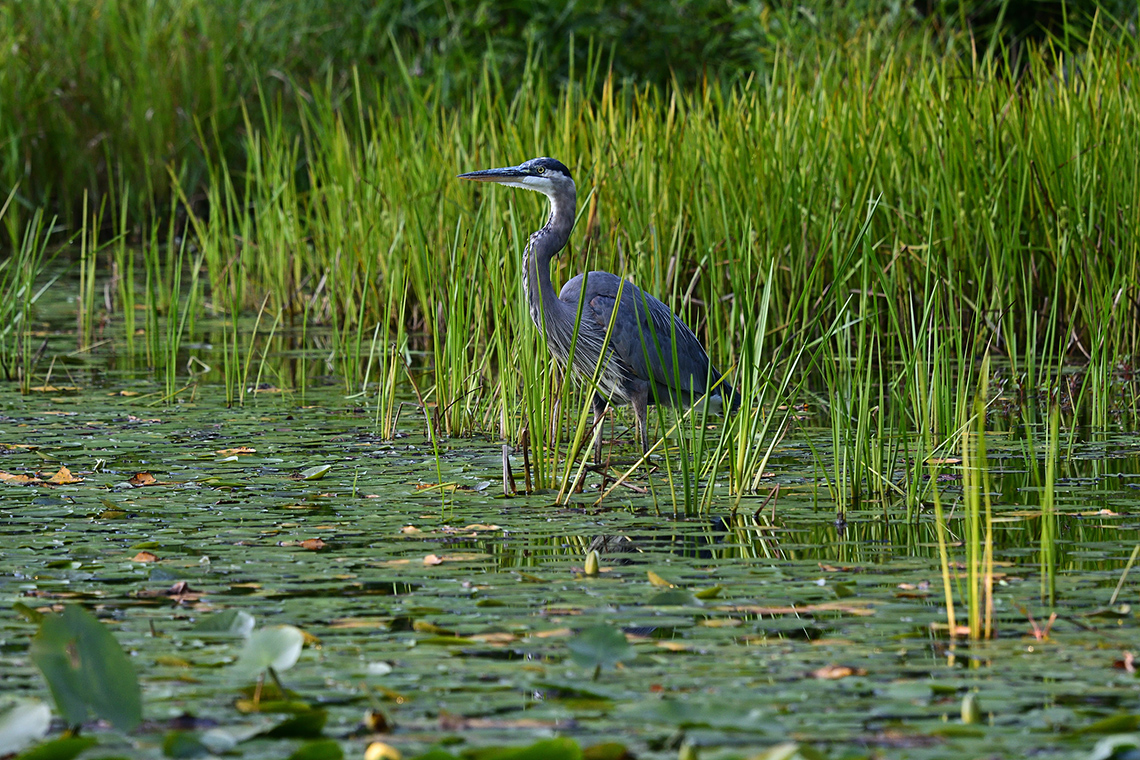
Explore the following carousel of wetlands.
Brainstorm
Wetland ecosystem
What types of plants and animals do you think live in a wetland ecosystem?
Record your answers using a method of your choice.
Press ’Who Lives in a Wetland?’ to access examples of animals and plants that might be found in a wetland.
Some animals that live in wetlands are:
- snakes
- salamanders
- turtles
- insects
- crayfish

Wetland Animals
Some plants that live in wetlands are:
- cattails
- water lilies
- tamarisk
- common reed

Wetland Plants
Wetlands have so many purposes! Most importantly, wetlands are built to provide a home for varies types of wildlife and plants.
Benefits of wetlands
Wetlands are also used to prevent flooding by soaking up big amounts of water so that it cannot reach a city. Think about it like a sponge soaking up water. When there is less rain, the wetland slowly releases the water in the surrounding area.
Also, a wetland is able to filter water and make it cleaner. Water travels to the bottom of a wetland and then is pushed back upwards. When it is pushed up, it travels through gravel and plant roots which filters the water and removes anything harmful.
Lastly, wetlands can prevent erosion. Let’s learn more about this!
Ontario connection
This learning activity highlights people, places, or innovations that relate directly to the province of Ontario. Enjoy the exploration!

Check out the following maps to explore where in Ontario the Leslie Street Spit Wetland is located.
Map of Leslie Street Spit Wetland. The map focuses on the area around Lake Ontario. Leslie Street Spit Wetland is the wetland habitat that extends into Lake Ontario with Downtown Toronto in the north-west, and the Toronto Islands on the west of the Leslie Street Spit Wetland.
The City of Toronto created a wetland habitat on the shore of Lake Ontario called the “Leslie Street Spit”. This wetland was created when fill was added to the lake to extend the land into the water.

Erosion experiment
Let’s conduct an experiment to explore how a wetland can prevent flooding and erosion.
Erosion is the process where different natural forces, such as water, wind, and waves, cause rocks and earth to wear away.
These forces also move bits of rock and earth to new places. Over time, this changes the shape of the land. Soil erosion often occurs from water, wind, or waves.
Investigate
Investigate
Investigate the following video and use the graphic organizer, or another method of your choice to make a prediction and record your observations.
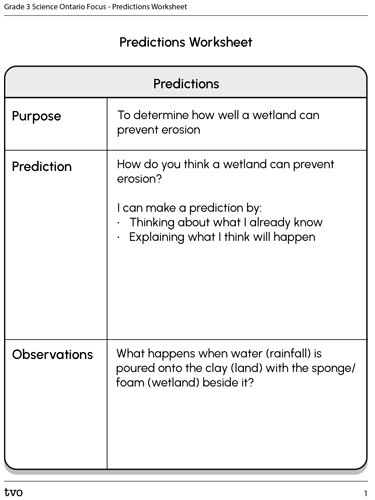
Prediction
Complete the Predictions Worksheet in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
After you’ve made your predictions, explore the following video then record your observations on your Predictions Worksheet or recording.
Consolidation
Communicate your results!
Based on the previous experiment, what happened to the rainwater with and without the wetland?
Record your ideas using a method of your choice.
Press ‘Experiment Results’ to access some results of the erosion experiment.
You should have noticed that when the wetland was removed, the water quickly overflowed into the bottom of the paint tray liner. However, when there was a wetland there, it absorbed most of the water and prevented the bottom of the tray from overflowing (like a flood).
Most wetlands are shallow basins that collect water and slow its rate of flow and also retain water for a time. This slowing process helps reduce flooding and also helps prevent soil erosion.
- If a wetland is destroyed, and houses are built in its place, what might happen to the houses during a severe rainstorm? Why?
Record your answer using a method of your choice.
Press ’Answer’ to access one possible answer.
They might be flooded because the wetland will not be there to absorb and slow the rush of water from higher ground.

Share your knowledge
A community member has asked you what you think about removing a wetland to build a new housing area.
- What would you tell them?
- Should they leave the wetland there, or remove it? Why?
Create a comparison poster, brochure, audio recording, or another method of your choice, to show the benefits of wetlands and how it prevents erosion. Include labels and descriptions on your final piece.
Use the following checklist to guide you while communicating your results.
Sharing knowledge checklist
I can communicate my results by…
Reflection
How do you feel about what you have learned in this activity? Which of the next four sentences best matches how you are feeling about your learning? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas about your feelings using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.