Minds On
Structures
Explore the following carousel of structures in Ontario.
Brainstorm
What is a structure?
- What are some examples of structures?
- What materials are used to make structures?
- Who makes structures?
- What is the purpose of structures?
Brainstorm answers to the previous questions by completing the Structures Mind Map in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Press ‘Answer’ to access the definition of a structure.
A structure is defined as a framework that holds a load and has a definite size, shape, and function. Let’s learn more about structures!
Source: Ontario Science Curriculum
Action
Form and function of structures
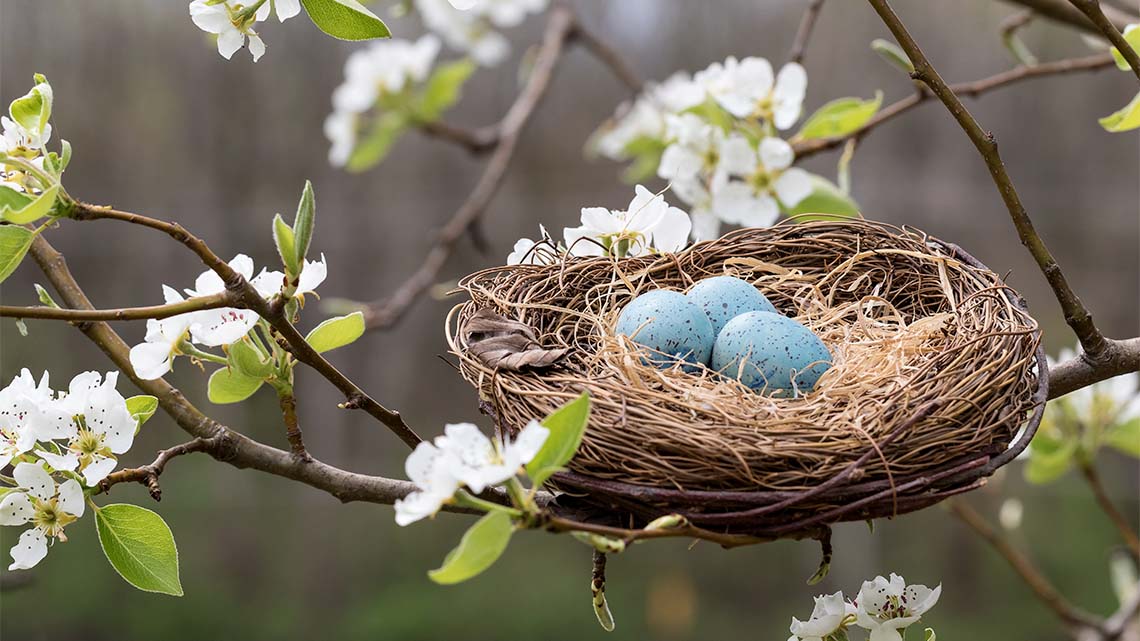
Explore the following images of the structures below.
Consider the images from the previous carousel and answer the following questions:
- Why are these structures important?
- Who or what might use these structures?
Record your answers using a method of your choice.
Press ‘Answers’ to access some possible answers.
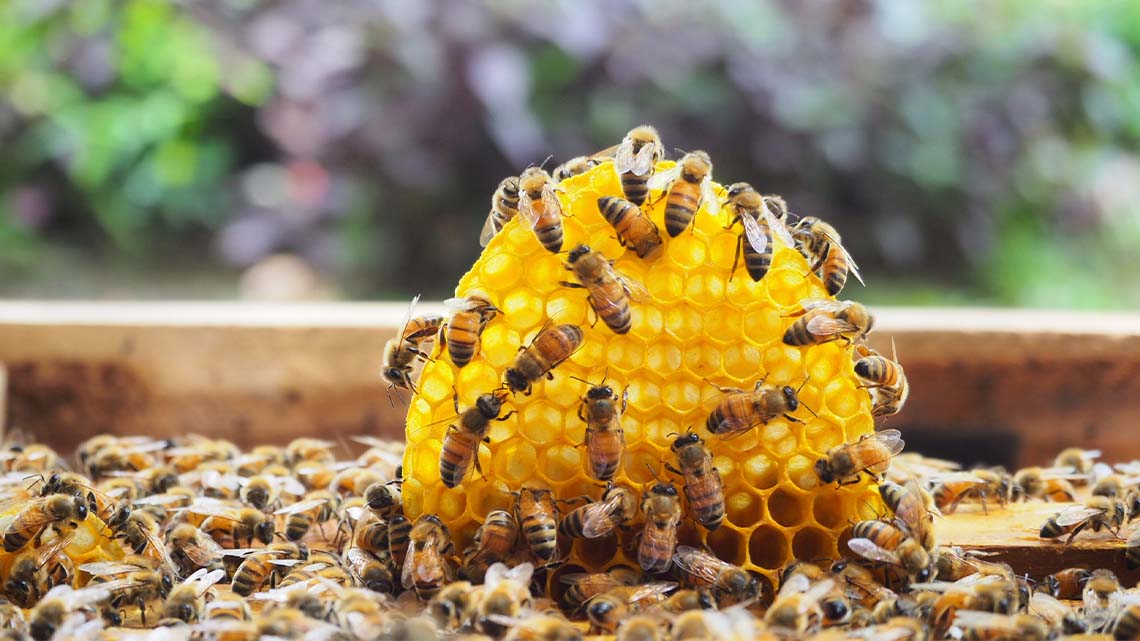
- The bird’s nest is a structure that is used by birds as a shelter and to hold eggs.
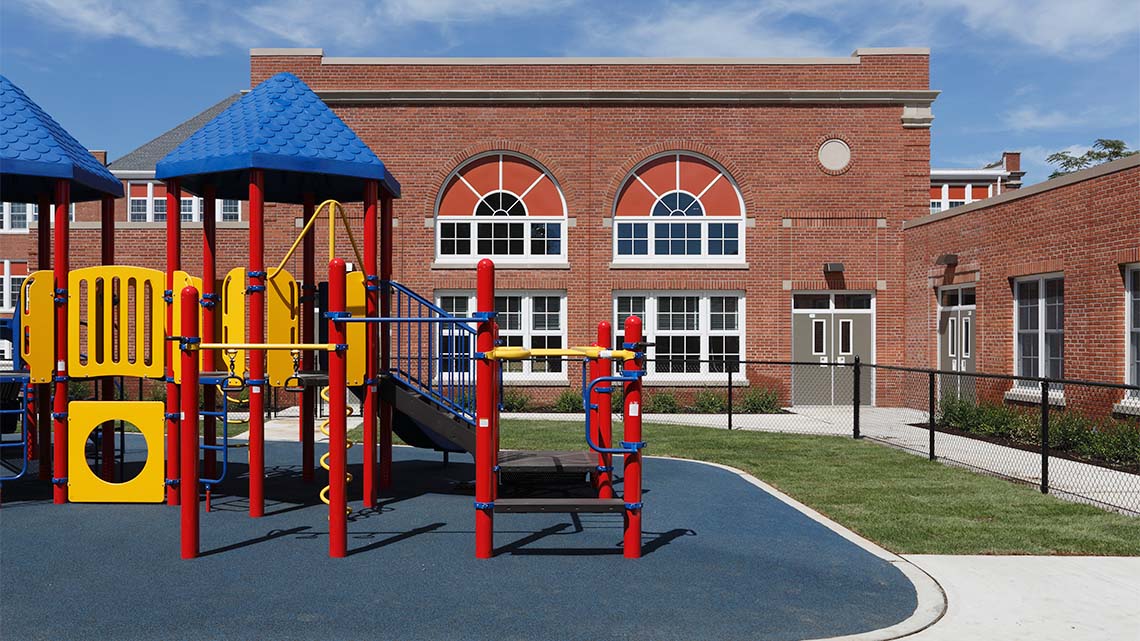
- A school and playground are used for children to learn and play.
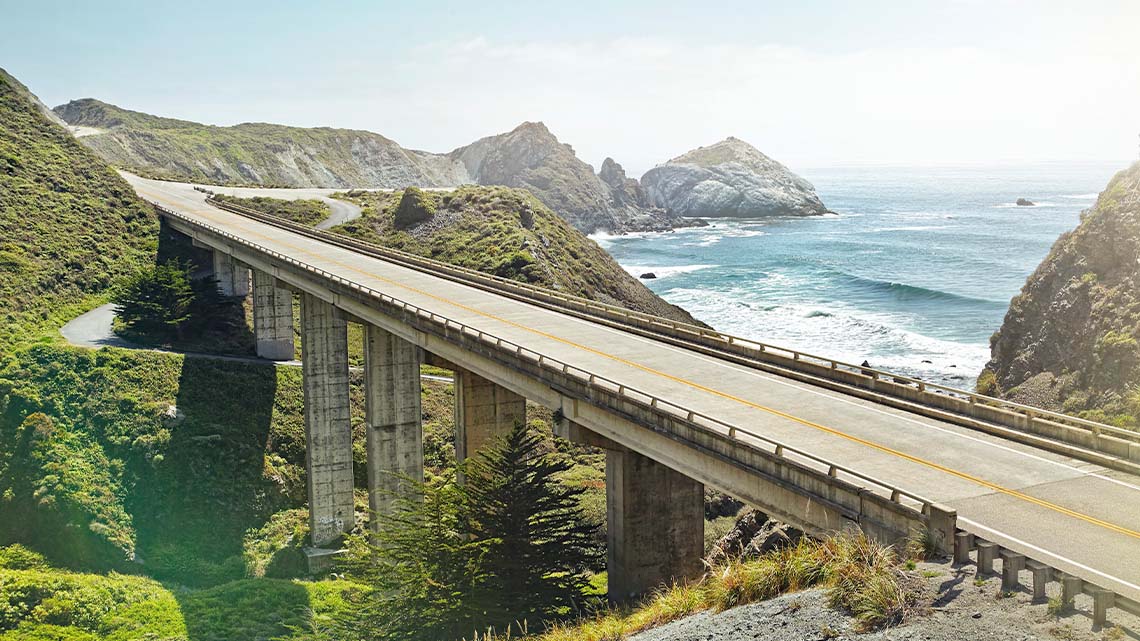
- A bridge is used to safely move cars and people over something.
All structures made by humans or made in nature have a form and a function.
Press the following tabs to access descriptions of the form and the function of structures.
The form of a structure is the characteristics that it has. This includes shape, size, and the material that it is made out of.
- Shape is what the structure mostly looks like.
- Size is the height, weight, and width of a structure.
- Materials are what is used to make a structure. These can be natural (wood, sand, stone) or artificial (plastic, glass).
The function of a structure is the purpose that a structure serves, or what it helps to do.
For example, the function of a pencil is that it allows people to write on materials such as paper. A chair allows people to sit comfortably and at the right height to work.
Form follows function
Consider how the form of a structure is decided by the function that it will serve.
Explore the following structures and determine the function and form of the structure, as well as making connections between the form and function.
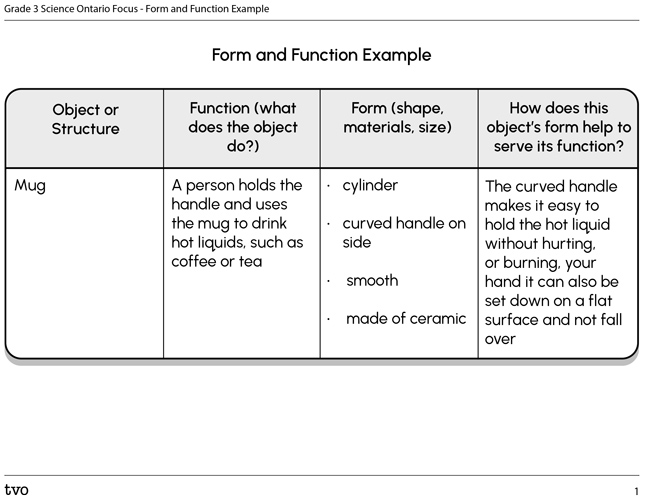
First, explore the following image of a coffee mug.
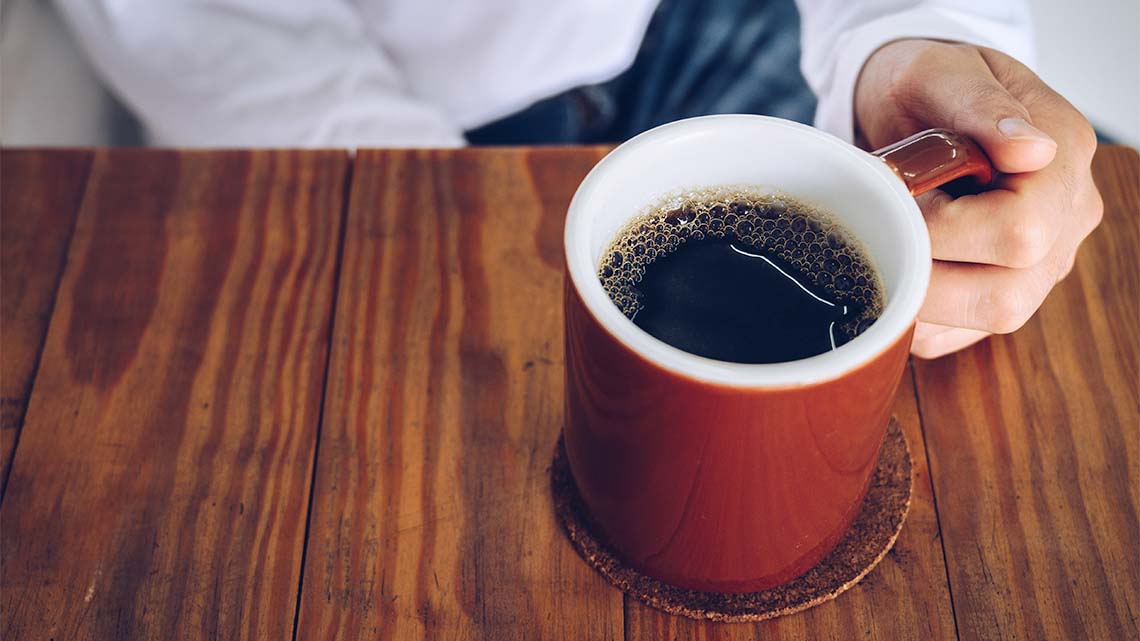

Press ‘Example’ to access an example of determining the form and function of a mug.
Now it’s your turn! Explore the following carousel of structures and complete the organizer below. There is a blank space at the bottom to add your own idea if you’d like!
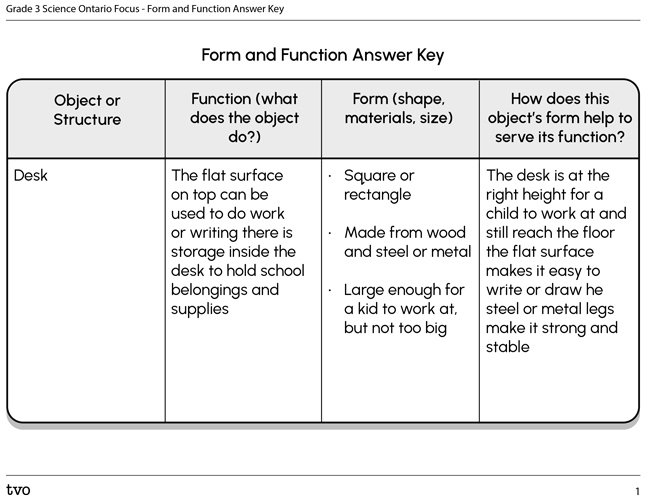
Press ‘Answers’ to access the answer key.
How might changing the form of an object or structure change its function?
Record your answer using a method of your choice.
Press ‘Hint’ to access some help.
Think back to the example of the mug. What if that mug was made out of paper instead of ceramic? How would that change in form affect its function?
Playgrounds
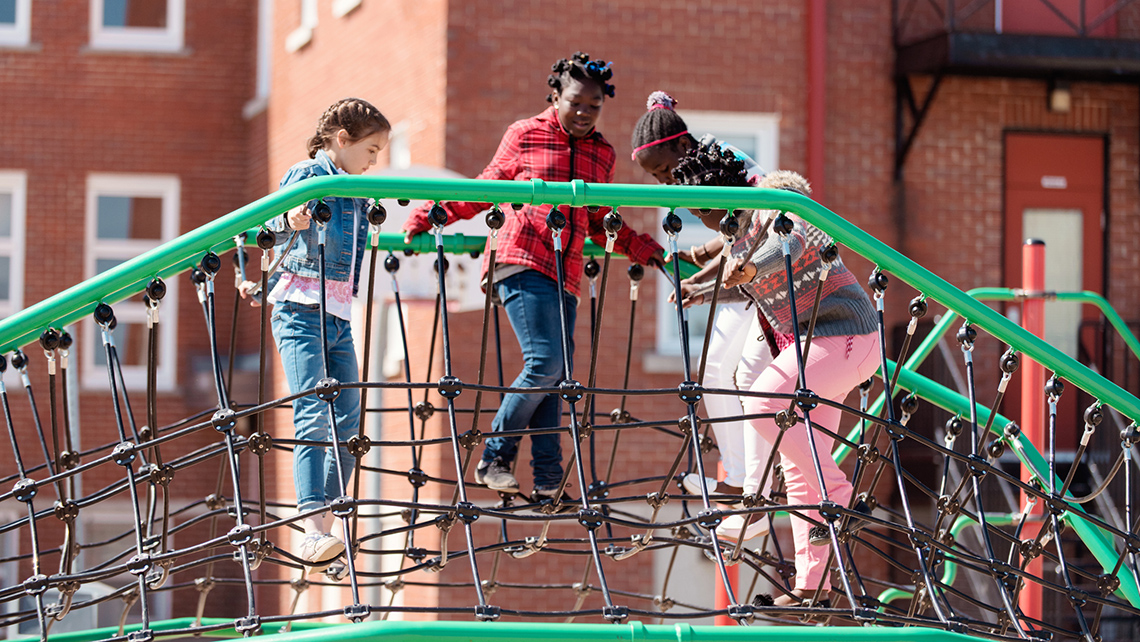

Just like the examples that you already explored, a playground also has a specific form and function. A playground’s function is to provide a space for children to play and engage in physical and social activities with other kids. Playgrounds can be made of the following materials:
|
metal |
wood |
plastic |
|
rope |
sand |
wood chips |
When engineers design and build playgrounds, they have to ensure the playground is safe for everyone to use.
Strength, durability, and flexibility
There are a lot of different materials that can be used when building something. Engineers consider the strength, durability, and flexibility of materials to ensure the structure is strong and safe.
Press the following tabs to access definitions of strength, durability, and flexibility.
The strength of materials is important because engineers need to consider what materials will be able to hold a specific load. Engineers are always finding ways to make materials stronger which allows them to design strong and stable structures.
Steel is a strong material that is used in playgrounds because it can resist compression (pushing forces) and tension (pulling forces) that act on it. Other examples of strong materials are concrete, bricks, and metal.
It is important when a structure is built that it lasts for a long time and remains safe. An engineer chooses materials that are both strong and durable.
Some structures require materials to be flexible. Flexible materials often bend easily and can resist different forces. A plastic container is flexible because you can bend it without breaking it. Other examples of flexible materials are rope used for bridges or chains used for swings.
Check your understanding!
For each term select the corresponding definition.
Engineers have to consider strength, durability, and flexibility of materials when designing a playground and ensure they are built safely
Consider what you need to do when building a playground and answer the following questions:
- What would be the best playground surface?
- What type of space would you build a playground in?
- What is important to consider when designing where everything will be in a playground?
- What kind of signs should there be at a playground?
Press ‘Answers’ to access some possible answers.
|
1. |
Woodchips, sand, mulch, or rubber are commonly used because they won’t hurt as much if someone falls. |
|---|---|
|
2. |
A playground should be built far away from anything dangerous, in a location with shade that many children can access. |
|
3. |
A playground should be accessible to all children, regardless of abilities or age. |
|
4. |
Playground rules and safety signs. |
Engineering design process
In this section of the learning activity, you are going to be designing, and if possible, building a model, of a playground! Let’s review the engineering design process first.

In Science we ask questions to help us figure out what the problem is.

Brainstorming is when you think about ideas like how to solve a problem.

When you plan something, you think about the steps you have to follow and the materials you will need.

It’s time to build. Gather your materials and your plan and start building!

Testing lets you try out your design to see if it works.

Improving is about making your design even better.

Sharing what you have learned lets other people know about your topic too!
Designing a playground
Explore the following Giver video entitled “Ontario Playground” to learn more about playground designs.
Now create a drawing or detailed description of your playground design using a method of your choice. Use the following checklist to help you create your playground design.
Playground Design Checklist
Your design should include the following:

Creating a playground design
If possible, create a 3D model of your playground. You can use a computer program/website, or build it using safe materials.
Consolidation
Sharing a playground design

A community is seeking input about a new playground being built!
They have asked you to share your playground design with them and highlight all of the important things that they should consider. If you also made a model, you should share that too.
Create your presentation using a method of your choice. It can be a detailed description, a video or audio clip, a brochure, an advertisement, or any other method of your choice.
Use the two following checklists to help guide you create you design and presentation
Playground Design Checklist
Create your design by answering the following questions:
Sharing My Playground Checklist
Your design should include answers to the following questions:
Reflection
How do you feel about what you have learned in this activity? Which of the next four sentences best matches how you are feeling about your learning? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas about your feelings using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.