Minds On
Evolving technology
Technology evolves and changes over time. Let’s consider two early technologies as an example.
The first telephone, invented in the 1800s has very few similarities to the smartphones of present day. Likewise, the first camera, also invented in the 1800’s, was very different than cameras we use today.

An image of an old telephone from the 1800s with an arrow pointing to the right to an image of a smart phone from today. Underneath there is an image of an old camera from the 1800s with an arrow pointing to the right with an image of a current camera from today.
Select one of these technologies to focus on for this exercise. Taking what you know, what are some similarities and differences between the two images of your chosen technology?
Jot these similarities and differences in a Venn diagram or in a method of your choice.
Complete the Similarities and Differences of Evolving Technology in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
Press the Activity button to access Similarities and Differences of Evolving Technology.
Activity (Open PDF in a new tab)The examples of technology explored here show us how technology continues to change over time as scientists come up with new and innovative ideas for improving each design and to improve our daily lives. However, as technology rapidly evolves and changes, what happens to the technology that we no longer need or want?
Brainstorm
Brainstorm
Consider the following questions. Record your thoughts in a notebook or using another method of your choice. If possible, share your thinking with a partner.
- How do you think technology is disposed of when a new and improved version of that technology is acquired?
- Do you think there are any consequences to the disposal of technology? Consider the impact on our environment?
Action
Ontario connection
This learning activity highlights people, places, or innovations that relate directly to the province of Ontario. Enjoy the exploration!

Changing technology
Explore the following images.
The evolution of the smart phones, cameras, and other electronics alike are great examples of scientific innovations. It is also an example of how quickly new technologies can replace old ones.
As different types of technology continue to evolve to meet the needs of people, new models replace older models.
So, where do old models go?
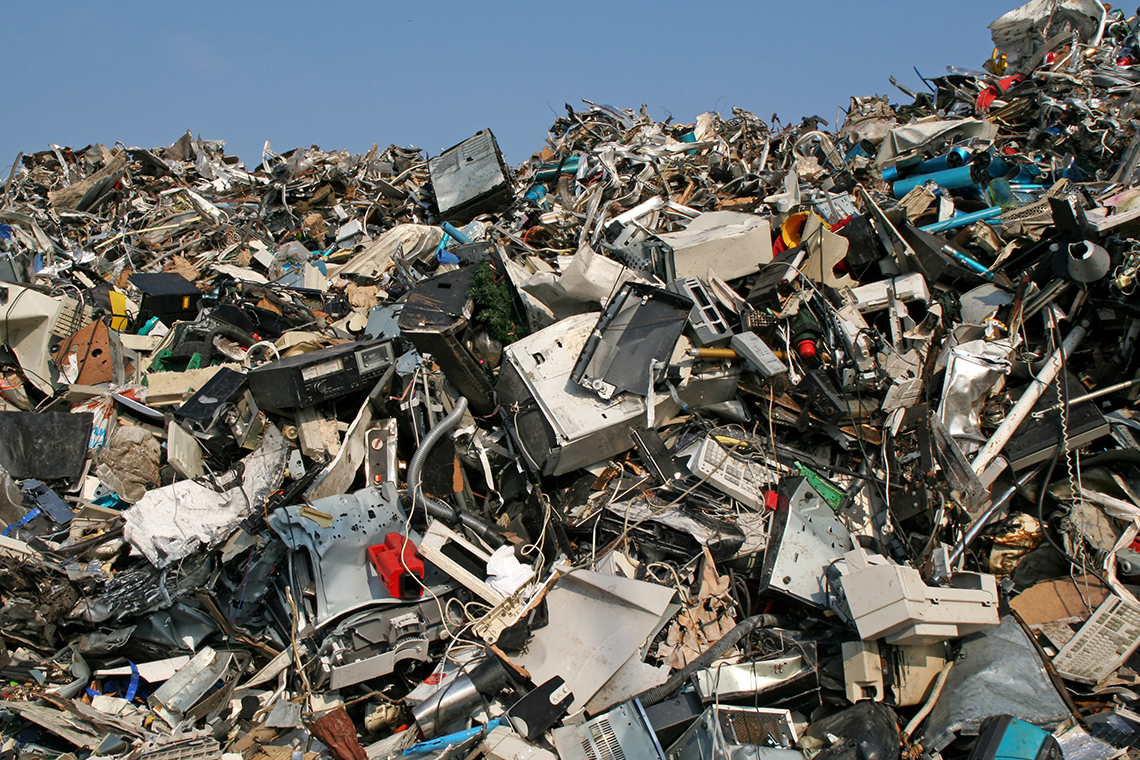

Oftentimes, older models are discarded and contribute to electronic waste also known as e-waste.
In 2014, Canadians generated 724 million kilograms of e-waste. That is about 20.4 kilograms of e-waste per person! Worldwide, humans generate up to 50 billion kilograms of e-waste.
Until recently in Canada, much of this type of waste was shipped to other countries for disposal. However, this is changing. Now it is up to Ontario to deal with this type of e-waste.
Ontario’s e-waste
Reading Time
Let’s read!
Let’s explore the following summary and printable document, Reducing Electronic Waste in Ontario.

Press the Activity button to access Reducing Electronic Waste in Ontario.
Activity (Open PDF in a new tab)As you read in the article Reducing Electronic Waste in Ontario, The Minister of the Environment, Conversation and Parks raises a very important concern. How are our landfills being impacted by this technological waste?
The impact of e-waste on our environment
The Geneva Environment Network studied the effects of e-waste on the environment. It was found that several of the materials used in electronic devices are very harmful to the planet and improper disposal has led to negative impacts to biodiversity.
Many electronic devices are not biodegradable. As a result, e-waste often sits in landfills for years at a time, seeping into the ground and contaminating the soil beneath it.
Press Key Terms to reveal the definitions for biodiversity and biodegradable.
Biodiversity: A variety of living things in a given place.
Biodegradable: Materials that can be broken down naturally and return to nature without harming the environment.
Plant species that grow in this soil come in direct contact with heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and cadmium, which not only damage the plant itself but also harms the animals and wildlife who depend on these plants for their survival.

This image shows how contaminated soil from e-waste effects the environment. The food chain starts with contaminated soil with heavy metals from e-waste disposal, then plants, which live on the soil and absorb the contaminants from the soil. Mice would consume grains, fruits, and crops which grow in the contaminated soil, and the owls consume the mice, who feed on grains, fruits, and crops that grow in the contaminated soil.
Why is this a problem?
Soil, which is essential for its role in providing nutrients to a number of organisms now become harmful when these nutrients are replaced with heavy metals.
By entering and making its way up the food chain, this exposure to these contaminants have led to biodiversity loss and disruption to plants and animals within the contaminated environment.
Press Key Terms to reveal the definitions for organisms and food chain.
Organisms: Living things that can be seen in nature such as plants, animals, fungi, and algae.
Food chain: The order in which living things or organisms depend on each other for food.
Similarly, the metals and contaminants found in the e-waste can also seep into the groundwater and local water sources. These high levels of toxic material not only reduce water quality but can destroy aquatic, bird and mammal life as these heavy metals are absorbed, consumed, and ingested.

This image demonstrates how contaminated water, and heavy metals impact smaller organisms which impacts fish. The food chain starts with heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and cadmium that are at the bottom of the water which impacts phytoplankton. This would then impact zooplankton which effects the fish.
Why is this a problem?
The negative effects of contaminated water multiply as these heavy metals spread throughout the food chain and directly threaten the organisms who depend on one another for survival. This contaminated water, a by-product of the disposal of e-waste in our landfills, has led to a disruption in the balance of ecosystems in our environment.
Use your learning about the impacts of electronic waste in landfills to answer these true/false questions. For each answer that is false, give examples to show why it is false in a method of your choice.
Learning check!
Select the correct answer, then press ‘Check answer’ to see how you did.
Solutions
The issues involving electronic waste disposal are serious but as we have learned, the province of Ontario has been working on solutions to help protect the environment and the biodiversity in these areas.
In this section, we are going to explore how some municipalities around the province are working on their own solutions to keep electronic waste out of landfills.
Press the following tabs to access the different municipalities.

Recycle My Electronics is an organization working in provinces across Canada. They have partnered with businesses and with cities and towns across Ontario. They help provide local solutions to manage electronic waste disposal. They also help to make sure that materials are collected and recycled safely and in a way that helps to protect the environment.

In the city of Thunder Bay’s waste management section of their website, it outlines how dangerous it is to the environment to dispose of electronic waste in the city’s landfills. The website shares that electronic waste needs to be disposed of in a safe way.
The city has a Household Hazardous Waste Depot which is at the Waste and Recycling Facility. There is a list of many electronics that are accepted here.
There is also an organization that collects and ships electronic waste to different industries from this facility. They take the electronics apart and are able to reuse up to 90% of the parts.

The City of Toronto collects electronics on garbage days for free. By doing this, they can make sure that electronics are disposed of properly and safely. There are seven drop off depots throughout the city where people can drop off their electronics. For this service there is a fee. The depots do host a number of Community Environment Days held each year which allow drop offs and pickups for free.

The Township of South Stormont has partnered with the City of Cornwall to safely dispose of electronic waste at the local landfills. People living in both South Stormont and Cornwall can get two free passes per year to dispose of their electronic waste.
Using an app called the Recycle Coach app, people can learn how to safely dispose of all types of waste, including electronic waste.
Reflection questions:
- What is the goal of these programs?
- Do you think these areas of Ontario are effectively helping to protect the environment and the biodiversity of the areas around the landfills? Why or why not?
Investigate
Investigate your community!

Does your community have an electronic waste program? If so, which program do you think is the most like your community’s program? Why?
Consolidation
Putting it all together

Consider what you have learned about electronic waste and the impacts of their disposal in landfills. We also learned about solutions various municipalities, including your own, are taking to ensure that electronic waste does not end up in our landfills.
To communicate your learning about these topics, select one of the two options provided.
Press the following tabs to access your options.
You have started your own safe disposal program for electronic waste.
Create an advertisement to promote your safe disposal program. Be sure to include a name for your program, the problem that your program is trying to solve and why, the way this program works, and how safe and proper disposal methods are important in protecting the environment and the organisms within it.
You have been hired to advertise for a local disposal program in your community.
Using the information you learned about a program available in your area, create an advertisement that highlights the importance of proper and safe electronic waste disposal. Be sure to include the program’s name, the problem that your program is trying to solve and why, the way this program works, and how safe and proper disposal methods are important in protecting the environment and the organisms within it.
For either option chosen, use this checklist to include the following information in your advertisement:
Did I include the following information?
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel…
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.



