Minds On
Lake profiles
Explore the following information about each of the Great Lakes and answer the following questions:
- Who do the Great Lakes benefit?
- Why might it be important to protect the Great Lakes?
Record using a method of your choice.
Press the following tabs to access profiles of the Great Lakes.
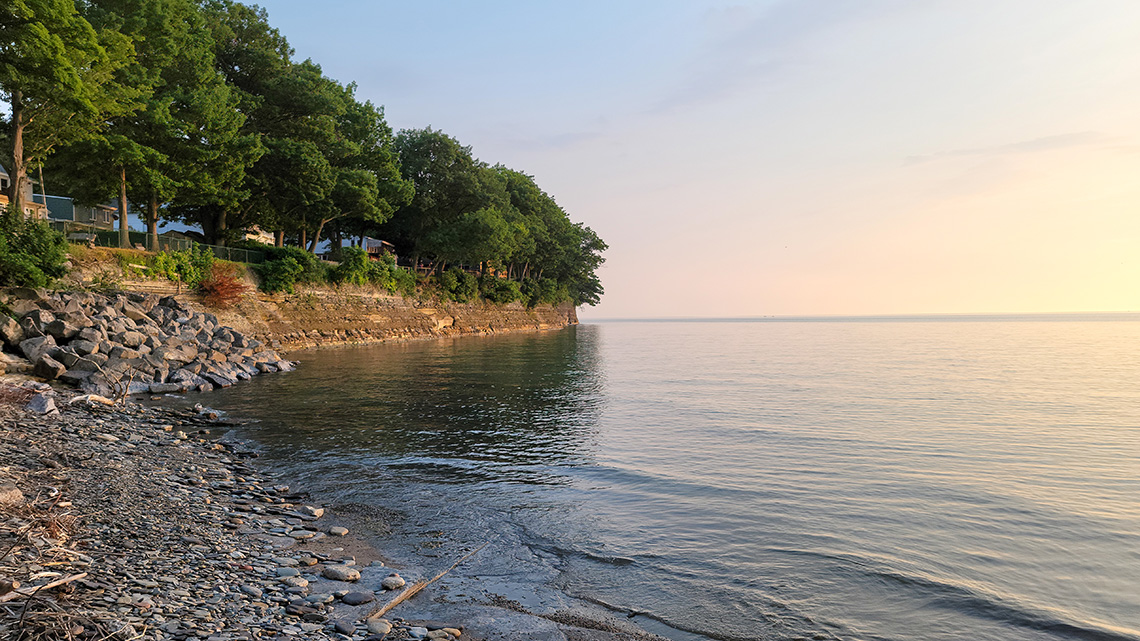

Lake Erie is the shallowest and the warmest of all the five lakes. This lake and the surrounding areas are rich in natural resources which has led to the addition of manufacturing industries in both Canada and America. Commercial fisheries are also connected to the lake because Lake Erie’s fish population is estimated to be 50% of all fish in all the Great Lakes. In the 1970’s an agreement was made between Canada the US to combat the major pollution issues that Lake Erie has. Lake Erie's condition has improved however there are still concerns such as pollution and algae blooms.
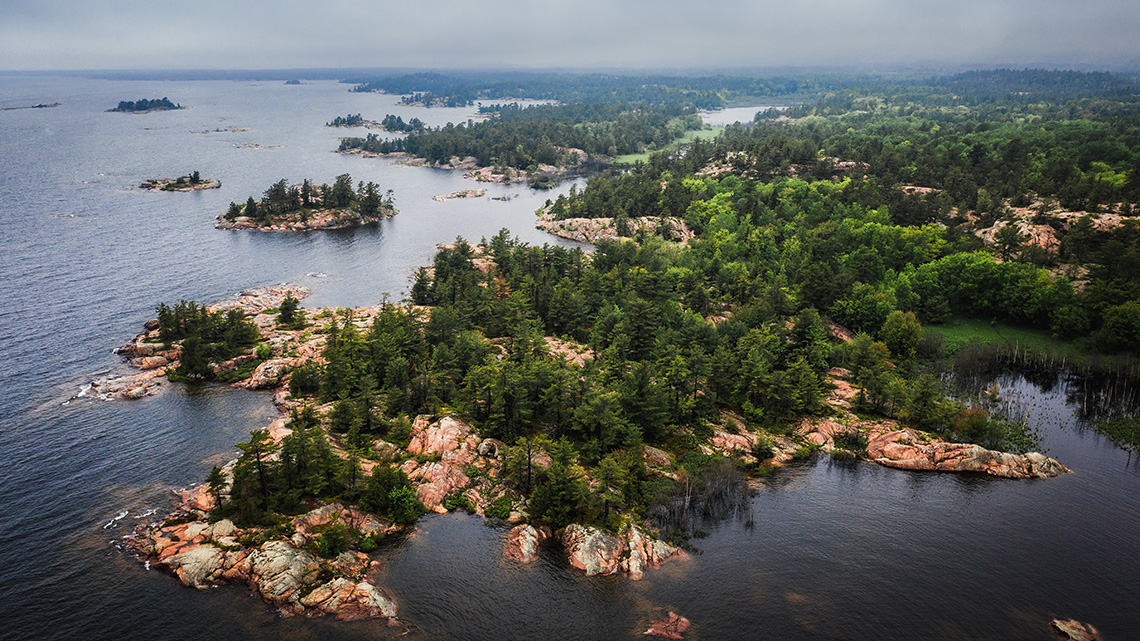

Lake Huron has the longest shoreline out of all the Great Lakes. It is the only Great Lake that doesn’t have a major city next to it which means that the area around Lake Huron is forested and has lots of natural resources. Lake Huron is home to over a thousand shipwrecks. A type of fish, the lake trout, was mostly eliminated from Lake Huron because of overfishing. There have been attempts to add lake trout back into the lake.
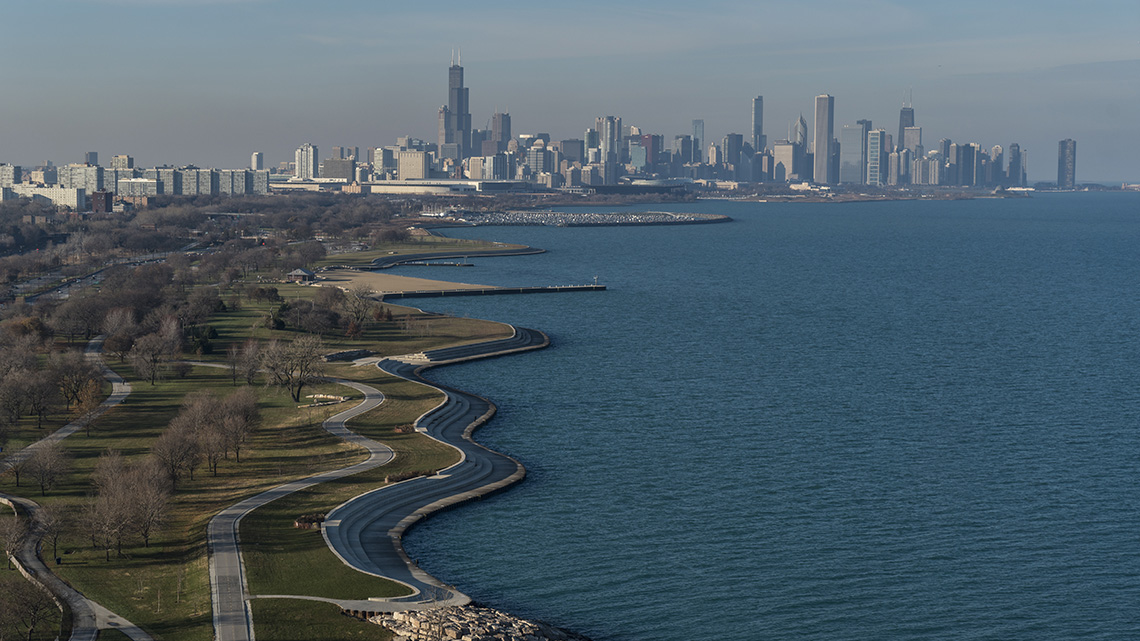

Lake Michigan is the only Great Lake that isn’t in Canada-the whole lake is in the United States. 12 million people live along the shores of Lake Michigan. There is also lots of agricultural and industrial production. The lake is also used as a way to transport bulk goods. Because there are industrial operations like steel mills and oil refineries, Lake Michigan continues to be polluted. There have also been major oil spills.
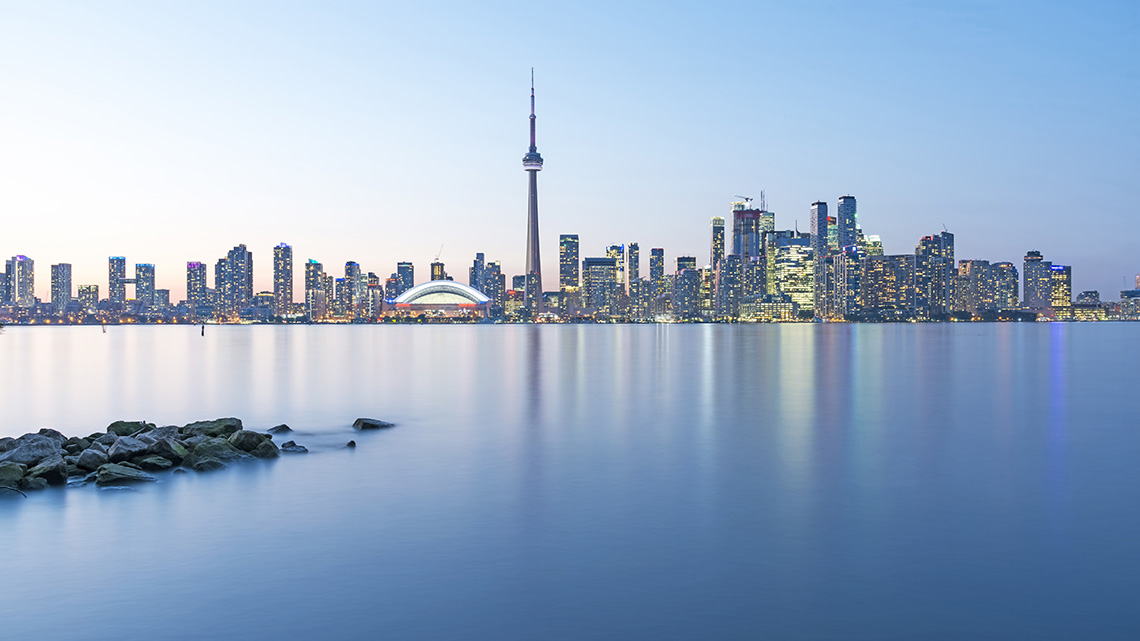

Out of all the Great Lakes, Lake Ontario is the smallest. However, it is an area that is high in biodiversity. A quarter of Canada’s populate live on or near Lake Ontario. Increased pollution and runoff and caused algal blooms in the lake as well as other issues. There are many wetlands that are a part of Lake Ontario. These wetlands are important for a variety of birds, fish, plants, and more.

Lake Superior is the world’s largest freshwater lake, and it has more water than all the other four lakes put together. The lake is more remote and there is less population than the other lakes although many tourists come each year. Fish in Lake Superior have been affected by overfishing as well as the introduction of species of fish that are not native to that area. Climate change has affected Lake Superior and there has been a steady increase in the lake’s temperature.
Action
Ontario connection
This learning activity highlights people, places, or innovations that relate directly to the province of Ontario. Enjoy the exploration!

The Great Lakes are a valuable natural resource that provides drinking water, food, homes for animals and more. They are a large portion of Ontario’s ecosystems and therefore they must be protected.
Press ‘Ecosystem’ to access the definition of an ecosystem.
Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a specific area on earth where various plants, animals and other creatures live. All parts of the ecosystem, including the weather and overall landscape, work together to create a system of life.
Did You Know?
Did you know?
- The Great Lakes contain nearly 20% of the Earth’s fresh water
- There are over 3500 plant and animal species found in the region of the Great Lakes
- 8.5 million Canadians rely on drinking water from the Great Lakes
Great Lakes concerns
There are many areas of concern when it comes to the Great Lakes.
Explore the following flashcards to learn more about these concerns.
Pause and Reflect
Pause and reflect
Which of these areas of concerns are caused by human actions?
Do you think that these areas of concerns affect all of the Great Lakes? Why or why not?
What might scientists do to address these issues?
Great Lakes Observing System (GLOS)
The Great Lakes Observing System or GLOS is a joint project between Canada and the US. Its aim is to use technology to observe conditions and environmental concerns on all five of the Great Lakes, such as:
- water temp
- wave height
- emerging containments
- harmful algal looms
Scientists use this data and their own observations to come to conclusions and identify what needs to change. The data is also shared with the public through notifications both on mobile and desktop.
How do you think having real-time technology help scientists and the community understand the changing concerns of the Great Lakes?
Share your thoughts with a partner, if possible.
Did You Know?
Did you know?
GLOS has developed a cloud-based platform called Seagull. It allows anyone access to things like lake conditions, buoy locations, sea levels, water temperature and more. This aids everyone from swimmers to fisherman to those studying climate change. People can get real-time data when they need it the most.
The main technologies of GLOS
GLOS uses many different types of technologies to collect data from the Great Lakes. Explore the following technologies and think about how they would aid scientists in improving the Great Lakes.
Buoys
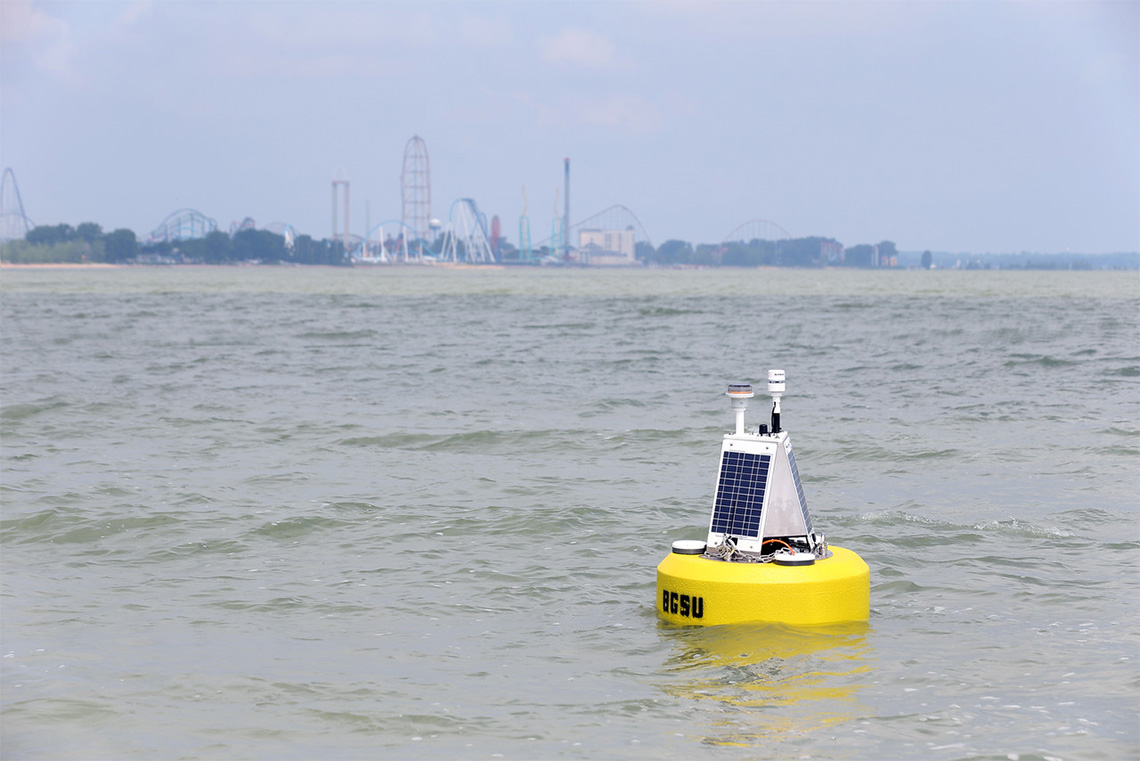

There are 57 buoys across all of the Great Lakes. GLOS maintains these buoys with partners including tech companies and universities. Buoys are used in the Great Lakes because they are very versatile. Buoys are put into the Lakes in the spring and then removed in the fall because of weather conditions around the Great Lakes area.
Buoys can either be anchored to the floor of the lake or can be free-floating in order to drift with the lake currents.
Buoys provide data such as:
- wind speed
- wave height
- water temperature
- pH level
- turbidity (how clear or hazy the water is)
Check out this video entitled “Smart Buoys” to learn more about buoys.
How do buoys ensure that the Great Lakes continue to provide safe drinking water?
Press ‘Answer’ to access how buoys help ensure the Great Lakes provide safe drinking water.
Buoys provide continuous and real-time data to ensure that the conditions of the water remain the same and don’t cause things like algal blooms.
Why would having advance knowledge of water conditions be helpful?
Press ‘Answer’ to access why having advance knowledge would be helpful.
Having advance knowledge of water conditions would be helpful because scientists can create models that predict the creation and movement of algal blooms and hypoxic water. They then can give advance notice to drinking water plants that may be affected by the water.
Uncrewed systems
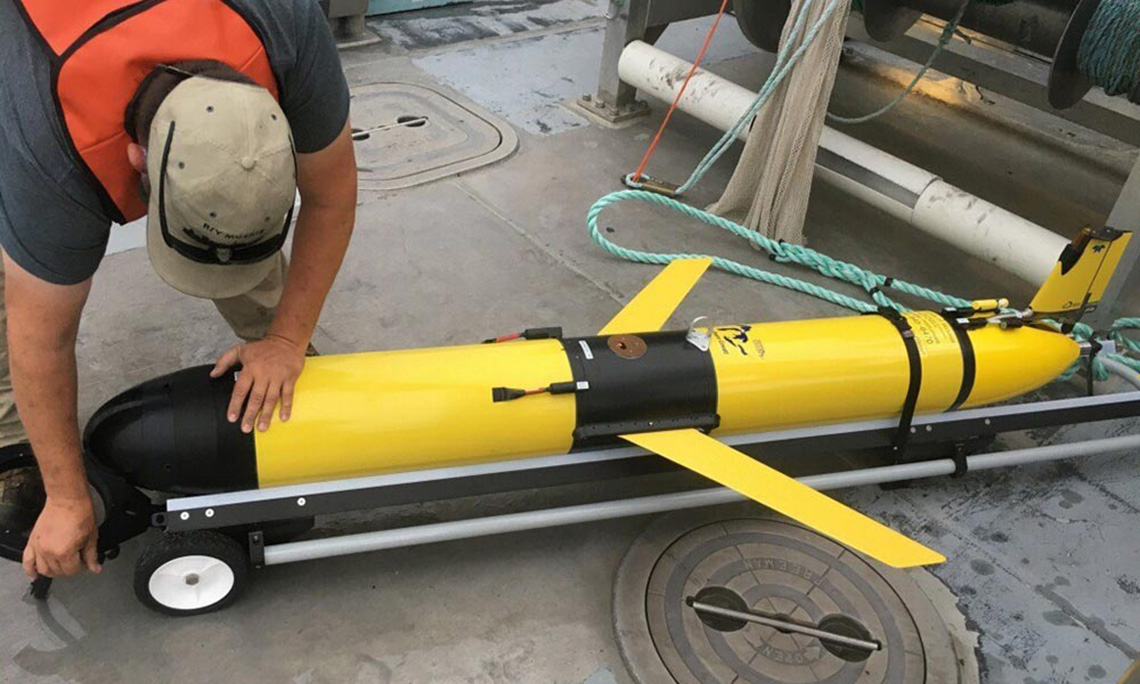

An uncrewed system is a system that can monitor lakes without the need for a crew of people. Uncrewed systems are important because often they can go where people cannot. It also costs less than a mission involving a crew of people.
An example of an uncrewed system is the underwater gilder. The glider can take measurements underwater in remote areas or even in dangerous conditions. Scientists program the glider with a specific task or “mission” which tells them how often to send data and where they should go. Gliders can travel for months and sometimes up to 1000 kilometers!
Explore this video called “Glider Program at Fisheries and Oceans Canada” to learn more about gliders.
What are some of the measurements that the gilder takes?
Press ‘Sample Answer’ to access some of the measurements the glider takes.
Measurements include:
- salinity
- water temperature
- chlorophyll levels
How can gliders help assess climate change issues?
Press ‘Answer’ to access how gliders can help assess climate change issues.
Gliders can share data the shows how much of the body of water is warming. This can give scientists a better understanding of the climate change issues for that body of water.
High-frequency radar

High-frequency radar is a remote sensing system that is based on the shore. It measures water currents by using a low-power electromagnetic pulse. This pulse is sent over the water, and it interacts with the waves on the lake and then gets sent back to the antenna. The high-frequency radar can measure a very large area of the lake, therefore giving much more data.
Using high-frequency radar allows scientists to determine the speed and direction of lake currents.
This radar is used to:
- monitor hazardous spills or algal blooms and determine which way they are moving
- track boats and ships when they are in dangerous conditions
- find people during search and rescue operations
Check out the following video entitled, “High Frequency Radar: Supporting Critical Coastal Operations with Real-time Surface Current Data” to learn more about a high-frequency radar.
Why does high-frequency radar work better than satellites when gathering coastal data?
Press ‘Answer’ to access why high-frequency radar works better than satellites.
Satellites don’t measure currents near the coastline. They also don’t provide near-real-time 24/7 data.
How does high-frequency radar help when there is an oil spill (like the one in the video)?
Press ‘Answer’ to access how high-frequency radar can help when there is an oil spill.
High-frequency radar can be used to determine the movement of the oil spill so the right amount of equipment and personnel can be brought in to fight the spill.
Review your learning!
For each term, select the corresponding description.
Technology and the Great Lakes

How can scientists use the data gathered through buoys, gliders, and high-frequency radar to help protect the Great Lakes?
Complete the Technology Chart in your notebook or using the following fillable and printable document. If you would like, you can use speech-to-text or audio recording tools to record your thoughts.
| Technology | How the Data Helps Protect the Great Lakes |
|---|---|
| Buoys | |
| Gliders | |
| High-frequency radar |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Technology Chart.
Consolidation
The Great Lakes research project

As you have been exploring the impact of different innovations and new technologies on the Great Lakes water system, you have been engaging in different aspects of the Scientific Research Process.
In this final task, you will apply the information you have gathered throughout this process to make a written, oral, or audio presentation about one of the Great Lakes. Your presentation must address:
- how technology can improve the conditions of the Great Lakes
- the impact of technology on the preservation of one of the Great Lakes
Record your presentation in a method of your choice
Before you begin, check out the following video to learn more about the steps of the Scientific Research Process to help frame your response. As you explore the video, consider which steps could apply to the work you’ve done so far. For example, the “Record” stage was involved in recording new findings using the Technology Chart in the Action section.
Your presentation must include:
- who uses the Great Lakes (people, animals, industry, etc)
- areas of concern specific to that lake
- how technology can help improve the conditions of the lake
You may choose to go back to the Action section for your research or you can go search for an appropriate source.
Student Tips
Student tips
When researching your Great Lake, it is important that you begin your search using websites, videos, audio recordings, or print resources from sources that would have reliable first-hand knowledge of the topic you’re reaching.
Websites ending with .com, .org, and .net can be created and used by any person. Be careful when using these websites and ask yourself if these websites are credible or have bias. Those ending in .org are usually used by non-profit organizations, which may have an agenda of persuasion rather than education.
Websites ending in .edu are reserved for colleges and universities. Canadian websites have a .ca ending. It is important to consider using credible Canadian websites for research when possible!
Reflection
As you read the following descriptions, select the one that best describes your current understanding of the learning in this activity. Press the corresponding button once you have made your choice.
I feel…
Now, expand on your ideas by recording your thoughts using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.
When you review your notes on this learning activity later, reflect on whether you would select a different description based on your further review of the material in this learning activity.