Minds On
Condition and action
Consider the following actions that might occur if it is raining outside.

You may use the following fillable and printable Condition and Action document to record your answers. You may also use your notebook or a voice recorder.
| Condition | Action if true | Action if not true |
|---|---|---|
| It is raining. | Don’t water plants. | |
| It is raining. | Don’t bring umbrella. | |
| It is raining. | Turn windshield wipers on. |
Press the ‘Activity’ button to access Condition and Action.
Action
Pseudocode and Flow Chart
Part 1
In the Minds On, we explored the condition “it is raining,” then indicated the action that might occur if this condition were true, and another action if this condition were not true (false).

With coding, computers use conditional statements to help make decisions. When computers use conditional statements that include an option if a condition is true as well as an option if the condition is not true, they take on the following form:
if <condition is true> then
<do this>
else
<do this>
The condition is checked by the computer. If it is true, the computer will do a certain action, but if it is false, the computer will do another action. Else, in this case, means “otherwise.”
Let’s consider how we can use coding to write a conditional statement for a computer application.
The following is a pseudocode we might come across for a computer number guessing game:
if userGuess == secretNumber then
output: “You guessed it!”
else output: “Sorry–Incorrect”
End if
Pseudocode is an informal way of describing a computer program or algorithm that is an intermediary between everyday language and programming code.
In coding, many programming languages require two equal signs when checking to see if something is equal to something else. This is called a comparison operator because we are comparing two values.
Let’s plug in some numbers to check our understanding of conditional statements. Let’s assume the secretNumber is 5. You can find the user’s guesses in the following table. Determine the output for each example.
| userGuess value | secretNumber value | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 5 | ? |
| 1 | 5 | ? |
| 5 | 5 | ? |
If secretNumber is 5 for each of the following examples, what do you think would be the output? Select the correct answer.
We could make this guessing game even better by changing the code so that it checks a condition using more than one comparison operator.
if userGuess > secretNumber then
output: “Too high!”
elseif userGuess < secretNumber then
output: “Too low!”
else output: “That’s correct!”
end if
Remember – else means otherwise! So, if both of the first two conditions are false, we will end up with the else code, which will output “That’s correct!.”
For a more detailed explanation on the meaning of the code, click on the ‘Explain’ button.
If the first condition is true, then the computer will do the first action, which is to output “Too high!” and will skip the rest of the code in the conditional statement.
If the first condition is not true, then the computer will skip the code (action) on the next line and check the second condition.
If the second condition is true, the computer will do the second action, which is to output “Too low!” and will skip the rest of the code in the conditional statement.
If the second condition is false, the computer will skip the code (action) on the next line and move to the else portion. This is the action that will happen if all conditions are false! If the userGuess is not bigger or smaller than the secretNumber, then it must be equal to the secretNumber value!
Consider the user’s guesses in the previous table.
If secretNumber is 5 for each of the following examples, what do you think would be the output? Select the correct answer.
Part 2
Sometimes, instead of pseudocode, programmers might use flow charts to help with planning out their computer applications.
Let’s consider our secretNumber 5 guessing example and how it might look in a flow chart.
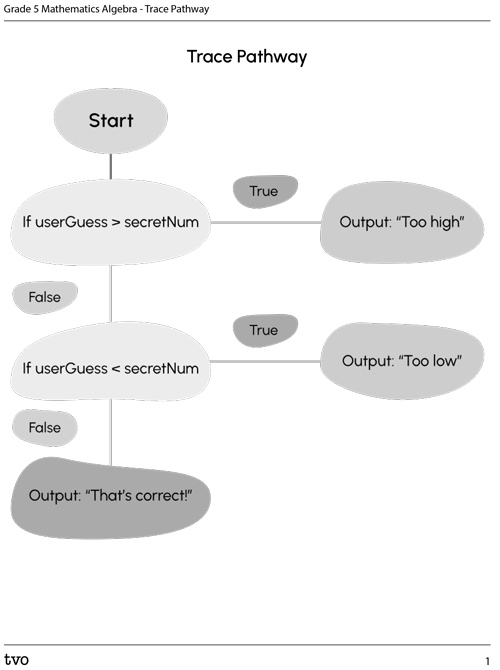
The word “Start” is in an oval with an arrow pointing downward to a diamond. The text inside the diamond is “if userGuess is greater than secretNum.” An arrow with “True” above it points from the diamond to a parallelogram on the right with the following text: Output: “Too high.” An arrow with “False” beside it points from the diamond to another diamond below it with the following text: “if the userGuess is less than secretNum”. An arrow with “True” above it points from the diamond to a parallelogram on the right with the following text: Output: “Too low.” An arrow with “False” beside it points from the diamond to a parallelogram with the following text: Output: “That’s Correct!”
Trace the pathway that the computer would follow if the secretNumber is 5, and the user types in the following answers. As an example, the first one is done for you.
A) 3
B) 9
C) 5
If user guesses secret number is 3, then the output would be “too low” and would be represented in a flow chart as follows:
A flowchart traces the path for the output when the input is the number “3.” The path begins at “Start” in an oval and is traced down to the second diamond. The user has guessed a number less than the secret number. The output result is represented within a parallelogram connected to the right of the diamond by an arrow labeled “True” and yields the result “Output: Too low.”
You can use the following printable document Trace Pathway to record your answers. You may also use your notebook or a voice recorder to describe the pathways.
Let’s consider another flow chart for a computer application.
The word “Start” is in an oval with an arrow pointing downward to a diamond. The text inside the diamond is “if the unitPriceA is greater than the unitPriceB.” An arrow with “True” above it points from the diamond to a parallelogram on the right with the following text: Output: “unitRateB is a better deal.” An arrow with “False” beside it points from the diamond to another diamond below it with the following text: “if the userPriceA is less than unitPriceB”. An arrow with “True” above it points from the diamond to a parallelogram on the right with the following text: Output: “unitRateA is a better deal.” An arrow with “False” beside it points from the diamond to a parallelogram with the following text: Output: “The unitPrices are the same.”
What do you think is happening in this application?
If you said that this program tells you whether one unitPrice is a better deal than another, you are correct! The program will also indicate if the unitPrices are the same.
What would be the output when unitPriceA and unitPriceB have the following values?
| unitPriceA value | unitPriceB value | Output |
|---|---|---|
| $5 | $4 | ? |
| $7.50 | $7.75 | ? |
| $3.50 | $3.50 | ? |
What would be the output when unitPriceA and unitPriceB have the following values? Select the correct answer.
Consolidation
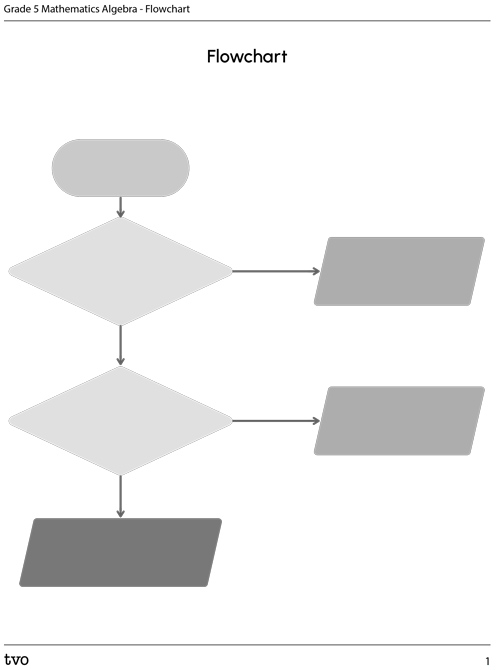
Create your own flowchart
Create your own flowchart for the conditional statements needed for one of the following situations. Use the same format as in the Action section.
Select one:

Magic 8 ball application that will say:
- “Yes” if the randomNumber = 0,
- “Maybe” if the randomNumber = 1 or
- “No” if the randomNumber = 2

An angle identifier program that will accept angles less than 180 degrees and will say:
- “acute” if the angle is less than 90 degrees,
- “obtuse” if the angle is greater than 90 degrees or
- “right” if the angle is 90 degrees

An application that will indicate if the temperature is:
- “above freezing” if the temperature is greater than 0 degrees Celsius
- “below freezing” if the temperature is less than 0 degrees Celsius
- “at freezing” if the temperature is equal to 0 degrees Celsius
You can use the following fillable and printable Flowchart document to record your answers. You may also use your notebook or a voice recorder.
Reflection
As you read through these descriptions, which sentence best describes how you are feeling about your understanding of this learning activity? Press the button that is beside this sentence.
I feel...
Now, record your ideas using a voice recorder, speech-to-text, or writing tool.
Connect with a TVO Mathify tutor
Think of TVO Mathify as your own personalized math coach, here to support your learning at home. Press ‘TVO Mathify’ to connect with an Ontario Certified Teacher math tutor of your choice. You will need a TVO Mathify login to access this resource.
TVO Mathify (Opens in a new tab)